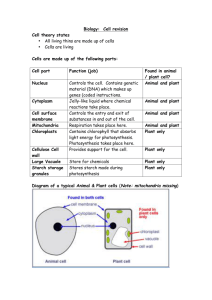
Name:___________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____
advertisement

Name:___________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____ Agenda Week of 11 Oct – 15 Oct 2010 Class website: www.marric.us/teaching Unit 2 Cell Biology Exam 11/4/10 1c. Students know how prokaryotic Unit 2 Quiz 4 October 19, 2010 cells, eukaryotic cells (including 1. Why do eukaryotic cells require mitochondria those from plants and animals), and viruses differ in complexity and general structure. 2. The source of energy for photosynthesis is the ______ 1f. Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar from carbon dioxide. Monday 10/11/10 - Enzyme graphing review - Cell City HW: Study for Quiz #3 Ch.8 SG due Tuesday Tuesday 10/12/10 - Unit 2 Quiz 3 (20 min). - Photosynthesis Notes 3. A mutation that stops a tree from getting gasses from the atmosphere would affect the process of ____________________ 4. The waxy coating on some leaves that help prevent water loss are made from the macromolecule ____________. 5. Lactase or maltase or pepsidase are examples of ________________. 6.The first stage of photosynthesis is ___________ _________________ AND the second stage of photosynthesis is _______________________. 7.Aerobic respiration begins in the _______________ and ends in the _______________________. - Cell identification coding HW: Ch 9 Study Guide due 10/20 8. Which two cell structures are involved in the packaging and secretion of proteins? Wednesday 10/13/10 –Late Start - Animal Cell Coloring HW: Ch 9 Study Guide due 10/20 9. Materials can be moved around within a cell through the ____________________________. 10. The rough appearance of some endoplasmic reticulum Thursday 10/14/10 is due to ___________________. - Plant Cell Coloring HW: Ch 9 Study Guide due 10/20 Vocabulary Friday 10/15/10 – Vacuoles Virus Review Activities – Ch 9 Work Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus HW: Ch 9 Study Guide due 10/20 Rough endoplasmic reticulum Nucleolus Parents/Guardian – Peptide Phospholipids I have reviewed my child’s activities Mitochondria Krebs cycle and homework for the week of Nucleus Organelles 10/11/10 – 10/15/10. Ribosomes Pigment I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is studying to be prepared for the EXAM on 11/1/10 and has completed all assignments this week. Any late or missed work that will be accepted in Unit 2 must be submitted by 10/22/10. Parent/Guardian Printed Name Signature Date Bell Ringers: Week of 11 Oct – 15 Oct 2010 Monday – The hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon atoms in a glucose molecule are held together by ____________________________bonds. The chemical energy in these bonds is stored for future use. Explain how these bonds are made. Tuesday - Which enzyme would function best in the following pH solutions: 1) pH 9 2) pH 6 3) pH 8 4) pH3 Explain. . Wednesday –Which defines a cell? A. microscopic organisms in water B. protein molecules in animals C. the basic unit of living things D. the smallest type of animal Explain Thursday -. Elena is taking a guided hike through a New Hampshire forest in October to enjoy the changing colors of autumn leaves. Her guide explains that the leaves change color as the green pigment chlorophyll used in photosynthesis decomposes. Another hiker asks the guide to explain photosynthesis. Which is the guide’s answer? A. Photosynthesis is the process autotrophs use to make energy. B. Photosynthesis is the process autotrophs use to make sugar. C. Photosynthesis is the process heterotrophs use to make energy. D. Photosynthesis is the process heterotrophs use to make sugar. Explain. Friday - The illustration shows a Siamese cat. In Siamese cats, an enzyme determines the color of the fur. On the cooler places of the body, the enzyme causes darker fur. On the warmer parts of the body, the enzyme does not function. Which of the following statements best explains how temperature affects this enzyme? A. Cooler temperatures denature the enzyme. B. Cooler temperatures cause more enzyme production. C. The enzyme is active in a specific temperature range. D. Heat allows the enzyme to break down white pigment. Name:________________________________ Date:________________ Period:_______ Unit 2 Quiz 4 1. Why do eukaryotic cells require mitochondria 2. The source of energy for photosynthesis is the ______ 3. A mutation that stops a tree from getting gasses from the atmosphere would affect the process of ____________________ 4. The waxy coating on some leaves that help prevent water loss are made from the macromolecule ____________. 5. Lactase or maltase or pepsidase are examples of ________________. 6.The first stage of photosynthesis is ___________ _________________ AND the second stage of photosynthesis is _______________________. 7.Aerobic respiration begins in the _______________ and ends in the _______________________. 8. Which two cell structures are involved in the packaging and secretion of proteins? 9. Materials can be moved around within a cell through the ____________________________. 10. The rough appearance of some endoplasmic reticulum is due to ___________________. 11. Membranes sacs containing light-absorbing molecules such as chlorophyll are called__________ A. grana. B. pigments. C. stomata. D. thylakoid Matching 1_____. creates energy for the cell 2_____. produces proteins 3______unwanted substances would build up in the cell without this organelle 4_____. contains the cell’s DNA A. lysosome B. Mitochondria C. Nucleus D. ribosome Matching Vacuoles Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough endoplasmic reticulum Peptide Mitochondria Virus Golgi apparatus Nucleolus Phospholipids Krebs Cycle Pigment Ribosomes Organelles Nucleus _________________________ A. a colored molecule like chlorophyll. _________________________ B. site of aerobic cellular respiration (krebs cycle and electron transport chain) _________________________ C. small structural units that perform specific functions in cells. _________________________ D. second step in the breakdown of glucose, occurs in mitochondria _________________________ E. membrane-bound organelle where DNA is stored in eukaryotic organisms. _________________________ F. organelles involved in protein synthesis using coded information from the nucleus located in the cytoplasm. _________________________ G. membrane-bound storage organelle _________________________ H. dense area within the nucleus where ribosomal RNA is produced. _________________________ I. a non-living biological active structure make of a protein coat and nucleic acid core. _________________________ J. bond between amino acids _________________________ K. molecules that make of cell membranes composed of a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. _________________________ L. membrane-bound, site of protein synthesis, modification, and packaging _________________________ M. membrane-bound, site of lipid synthesis, modification, and detoxification _________________________ N. membrane-bound organelle involved in packaging materials for cellular export. Which identifies the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? A. B. C. D. Both processes generate energy for cell use. Both processes release energy for cell use. The products of one process are used as reactants by the other process. The reactants of one process are also the reactants of the other process. Name:________________________________ Date:________________ Period:_______ Unit 2 Quiz 4 10/19/10 1. Materials can be moved around within a cell through the ____________________________. 2. The source of energy for photosynthesis is the ______ 3. A mutation that stops a tree from getting gasses from the atmosphere would affect the process of ____________________ 4. The rough appearance of some endoplasmic reticulum is due to ___________________. 5. Lactase or maltase or pepsidase are examples of ________________. 6.The first stage of photosynthesis is ___________ _________________ AND the second stage of photosynthesis is _______________________. 7.Aerobic respiration begins in the _______________ and ends in the _______________________. 8. Which two cell structures are involved in the packaging and secretion of proteins? 9. Why do eukaryotic cells require mitochondria 10. The waxy coating on some leaves that help prevent water loss are made from the macromolecule ____________. 11. Membranes sacs containing light-absorbing molecules such as chlorophyll are called__________ A. pigments. B. grana. C. stomata. D. thylakoid Matching 1_____. contains the cell’s DNA 2_____. produces proteins 3______ creates energy for the cell 4_____. unwanted substances would build up in the cell without this organelle A. lysosome B. ribosome C. Nucleus D. Mitochondria Matching Vocabulary Vacuoles Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough endoplasmic reticulum Peptide Mitochondria Virus Golgi apparatus Nucleolus Phospholipids Krebs Cycle Pigment Ribosomes Organelles Nucleus _________________________ A. site of aerobic cellular respiration (krebs cycle and electron transport chain) _________________________ B. membrane-bound, site of lipid synthesis, modification, and detoxification _________________________ C. small structural units that perform specific functions in cells. _________________________ D. second step in the breakdown of glucose, occurs in mitochondria _________________________ E. bond between amino acids _________________________ F. membrane-bound organelle involved in packaging materials for cellular export. _________________________ G. membrane-bound storage organelle _________________________ H. dense area within the nucleus where ribosomal RNA is produced. _________________________ I. a non-living biological active structure make of a protein coat and nucleic acid core. _________________________ J. membrane-bound organelle where DNA is stored in eukaryotic organisms. _________________________ K. molecules that make of cell membranes composed of a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. _________________________ L. membrane-bound, site of protein synthesis, modification, and packaging _________________________ M. a colored molecule like chlorophyll. _________________________ N. organelles involved in protein synthesis using coded information from the nucleus located in the cytoplasm. Which identifies the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? A. B. C. D. Both processes generate energy for cell use. The reactants of one process are also the reactants of the other process. The products of one process are used as reactants by the other process. Both processes release energy for cell use.