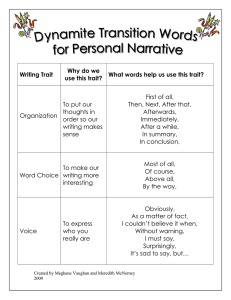
Biology Chapter 14 and 15 Evolution Pg. 390-413, 416-447 Name Term
advertisement

Biology Chapter 14 and 15 Evolution Pg. 390-413, 416-447 Term 1. Fossil Name Definition Guided 3rd Look at table 14.1 on pg. 393. List the types of fossils. ________________ fossils ________and________ ________________ _______________ or Permineralized fossils ________________ 2. Biogenesis 3. Spontaneous Generation 4. Analogous Structure 5. Artificial Selection 6. Camouflage ______________- preserved On pg. 402, which scientist helped prove that biogenesis did occur? On pg. 401, which scientist used decaying meat to try and disprove spontaneous generation? In fig. 15.7 on pg. 426, what two things are considered an example of analogous structures? Give an example of an animal that humans artificially breed today (not in book). Look at fig. 15.11 on pg. 428. What organism uses camouflage as a protective adaptation? 7. Embryo Look at fig. 15.8 on pg. 262. How can embryology be used to support evolution? 8. Homologous structure Look at fig. 15.6 on pg. 425. What five things are compared to being homologous structures? ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ Biology Chapter 14 and 15 Evolution Pg. 390-413, 416-447 9. Endosymbiont Theory 10. Fitness Look at Figure 14.17 on pg. 407 List the evidence used by Lynn Margulis. How is fitness an evolutionary adaptation (pg 428) 11. Mimicry Look at fig. 15.12 on pg. 429. What organism uses mimicry as a protective adaptation? 12. Natural Selection Read fig. 15.3 on pg. 421. How did natural selection change the population of sunflowers over time? 13. Vestigial Structure Look on pg. 425. List the three examples of a vestigial structure of the animals listed in on the page. 14. HardyWeinberg Principle List the five conditions that are needed for populations in genetic equilibrium (pg 432) 15. Coevolution On pg. 439 give an example of coevolution and what kind of evolutionary relationships are possible Biology Chapter 14 and 15 Evolution Pg. 390-413, 416-447 16. Convergent evolution Look at table 15.4 on pg. 440 and the paragraph below it. Explain how the mara and rabbit evolved convergently. 17. Directional selection On pg. 435, which type of trait variation does directional selection favor? Normal Trait Extreme variation of one trait Both extremes of a trait Draw the graph that shows directional selection (pg 434) 18. Disruptive selection On pg. 436, which type of trait variation does directional selection favor? Normal Trait Extreme variation of one trait Both extremes of a trait Draw the graph that shows disruptive selection (pg 434) 19. Divergent evolution aka adaptive radiation Y How does the picture above show divergent evolution? Biology Chapter 14 and 15 Evolution Pg. 390-413, 416-447 20. Gene pool The percentage of any specific allele in the gene pool is called (pg. 432)? 21. Genetic drift Look on pg. 433. Does genetic drift affect small populations or large populations more? What are two extreme examples of genetic drift 22. Geographic isolation Look on pg. 438. Give an example of a geographic barrier that may lead to geographic isolation. 23. Gradualism Which one shows gradualism?(circle) 24. Punctuated equilibrium Which one shows punctuated equilibrium?(circle) 25. Reproductive isolation There are two types of reproductive isolation listed on pg. 437. What are the two types? _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 26. Speciation What are the two types of speciation (both listed as vocab words) listed on pg. 438. __________________________ __________________________ Biology Chapter 14 and 15 Evolution Pg. 390-413, 416-447 27. Allopatric speciation List examples of allopatric speciation (on pg438) 28. Sympatric speciation Explain how reproductive isolation and polyploidy are examples of sympatric speciation 29. Stabilizing selection On pg. 434,, which type of trait variation does stabilizing selection favor? Normal Trait Extreme variation of one trait Both extremes of a trait Draw the graph that shows stabilizing selection (pg 434) 30. Genetic drift Look on pg. 433. Does genetic drift affect small populations or large populations more? What are two extreme examples of genetic drift 31. Founder Effect 32. Bottleneck Summarize the example of founder effect (pg 433) Summarize the example of Bottleneck (pg 433)