Catastrophic Event 2. Evolution Study Guide (Semester)
advertisement

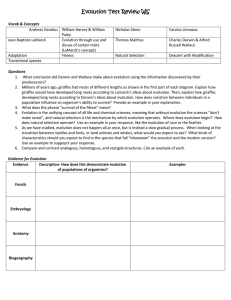
2. Evolution Study Guide (Semester) 1. What would a large meteor impact that could cause a mass extinction be called? Catastrophic Event 2. On what major changes is the geologic timeline structured? Biodiversity Changes 3. What is it called when a majority of life forms die out due to an event in Earth's history? Mass Extinction 4. At the end of the Paleozoic Era 90% of all life on Earth died out. What is this called? Mass Extinction 5. If the climate on earth changed suddenly it could cause many species to become extinct. What would this be called? Catastrophic Event 6. What are the eras depicted in the geological time scale are characterized by? By the type of life that dominated the Earth at the time 7. What were the first organisms to appear on Earth? Bacteria (single celled prokaryotes) 8. Dinosaurs, humans and bacteria evolved at different times in Earth's history. What order this occur in? Bacteria – Precambrian Era Dinosaurs – Mesozoic Era Humans – Cenozoic Era 9. When did the first cells appear? 3.5 billion years ago – Precambrian Era 10. What do most scientists believe that the cause of the dinosaur mass extinction was? A large meteorite impact 11. Use this illustration to answer the following question. 11. How are a human's arm, a cat's front leg, a dolphin's front flipper, and a bat's wing evidence of evolution? These are homologous structures having similar kinds of bones indicating that they came from a common ancestor. 12. Fossils of whale ancestors show that present-day whales are distant cousins to a land-dwelling mammal called Mesonychid. What do these fossils provide evidence of? The fossils provide evidence that organisms have evolved over time. 13. What can the fossil record supply evidence about? The fossil record provides evidence about the sequence of life and changes in biodiversity, the order that evolutionary changes have occurred, and how environmental conditions may have changed through time. 14. Use the illustration to answer the following question. 14. Compare the structure of the vertebrate hearts; which is the most closely related to birds and mammals? The vertebrate heart that is most closely related to birds and mammals is the reptile because it has the beginnings of a divided chamber. 15. The opposable thumb allows humans to grasp objects firmly. What is this feature called since it has helped humans to survive over time? An adaptation is what the advantageous feature is called. 16. What are structures and behaviors for finding food, protection, and for moving from place to place in an organism’s environment called? These are called adaptations. 17. Although dinosaurs lived for over 150 million years, they may have become extinct because a catastrophic event changed the environment more rapidly than the dinosaurs could do what? Adapt 18. What is a group of individuals which live together in the same area at the same time is called? A population consists of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time. 19. Describe an example of a population? Population: a group of individuals of the same species living in the same area; for example all of the red oaks in a particular forest are a population, because they are all the same species and live in the same area. 20. Individuals of the same species are similar but they still have some differences. What is this called? Genetic variation, also just called variation. 21. What will populations with traits well suited to the environment do? Survive and reproduce more successfully than other populations 22. What allows natural selection to occur? Genetic variation. Natural selection occurs because there is genetic variation in a species and some individuals have traits which are more advantageous than others. 23. If a population does not adapt when the environment changes what will happen? Die out. When the environment changes a population must adapt or else the population will die out. 24. What is a key component of the process of natural selection because without it an adaptation would not be passed down from generation to generation? Successful reproduction 25. What environmental challenges could lead to natural selection? Climate change, a new predator, asteroid impact 26. The Stick Insects look like sticks on plants so that they can blend into their environment. Why is this an adaptation? (source: http://home.vicnet.net.au/~grange/Birds.html) The adaptation makes it more difficult for predators to find them. It is an adaptation because the stick insects that survive can reproduce. 27. The arctic hare lives in an area which has snow in the winter. For part of the year they are white and part of the year they are brown. Which season(s) would they be white? Which season(s) would they be brown? (source: http://www.vistainternetproducts.com/arcticha.htm) The hares would be white in the winter and brown in summer. In the spring and fall the hares would have an intermediate color while changing seasons from or to a season with snow. 28. Why do Giraffes have long necks to reach food high in trees? Giraffes have long necks to reach food high in trees because some of their ancestors had long necks and they survived to reproduced while those giraffes that had shorter necks did not survive and so did not reproduce. 29. Individuals in a population that have traits or abilities that give them a competitive advantage over other population members are more likely to survive and reproduce. What is this called? Natural Selection. 30. What process does natural selection explain? Natural selection is the process that explains how evolution happens, why some species become extinct, and how speciation occurs. 31. What is the process that explains how evolution happens called? Natural selection and genetic inheritance 2. Evolution Review Guide (Semester) Correlation with District Standards 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: GJUHSD 2a-1 GJUHSD 2a-1 GJUHSD 2a-1 GJUHSD 2a-1 GJUHSD 2a-1 GJUHSD 2a-2 GJUHSD 2a-2 GJUHSD 2a-2 GJUHSD 2a-2 GJUHSD 2a-3 GJUHSD 2a-3 GJUHSD 2a-3 GJUSHD 2a-3 GJUHSD 2b-1 GJUHSD 2b-1 GJUHSD 2b-1 GJUHSD 2b-1 GJUHSD 2b-1 GJUHSD 2b-2 GJUHSD 2b-2 GJUHSD 2b-2 GJUHSD 2b-2 GJUHSD 2b-2 GJUHSD 2b-2 GJUHSD 2b-3 GJUHSD 2b-3 GJUHSD 2b-3 GJUHSD 2b-4 GJUHSD 2b-4 GJUHSD 2b-4