Unit II, 2010-2011
advertisement
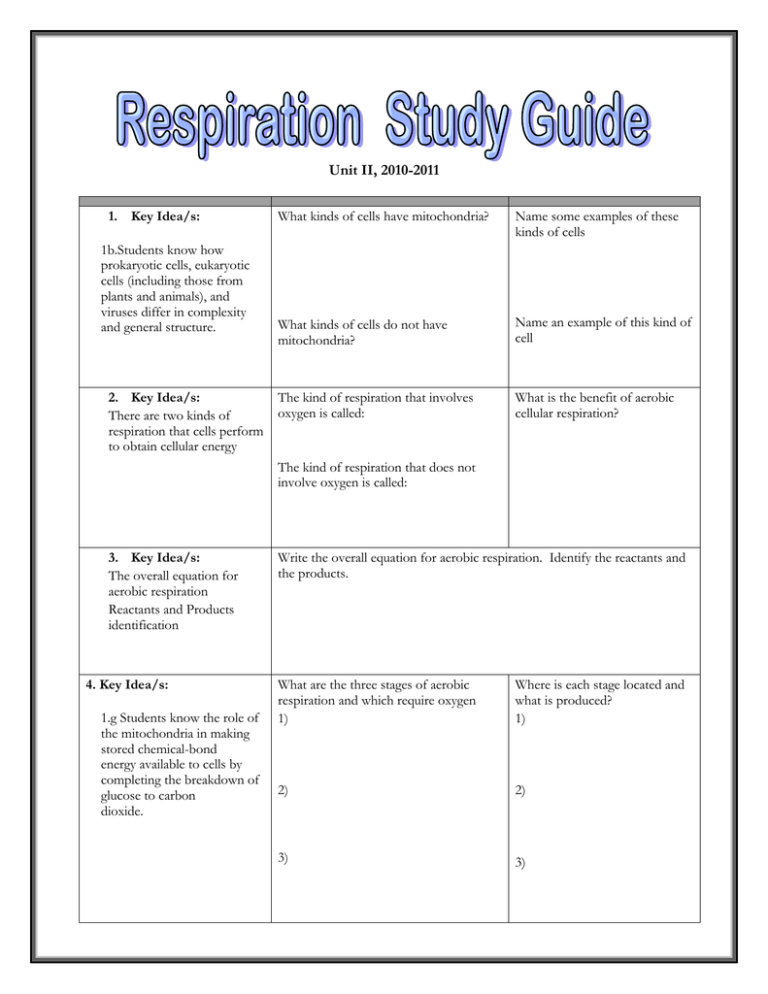
Unit II, 2010-2011 1. Key Idea/s: 1b.Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), and viruses differ in complexity and general structure. 2. Key Idea/s: There are two kinds of respiration that cells perform to obtain cellular energy What kinds of cells have mitochondria? Name some examples of these kinds of cells What kinds of cells do not have mitochondria? Name an example of this kind of cell The kind of respiration that involves oxygen is called: What is the benefit of aerobic cellular respiration? The kind of respiration that does not involve oxygen is called: 3. Key Idea/s: The overall equation for aerobic respiration Reactants and Products identification 4. Key Idea/s: 1.g Students know the role of the mitochondria in making stored chemical-bond energy available to cells by completing the breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide. Write the overall equation for aerobic respiration. Identify the reactants and the products. What are the three stages of aerobic respiration and which require oxygen 1) Where is each stage located and what is produced? 1) 2) 2) 3) 3) 5. Key Idea/s: Energy is stored until it is used 6. Key Idea/s: The mitochondrion is a complex double membraned organelle 7. Key Idea/s: Interpret graphic data What are three energy storage molecules Which energy storage molecule is the most useful. Draw and label a mitochondrion What is the effect of adding more and more sugar [glucose] into the rate of cell respiration? The amount of ATP produced is directly proportional to the ____________________. 8. Key Idea/s: Which molecule is represented by “A”? Which other products are represented by “B”? How can we tell that the process happening is NOT photosynthesis? MElizabeth/HS_2_Rio_Respiration_review/2010


