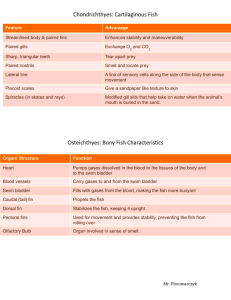
Adaptations in Fish
advertisement

Adaptations in Fish Body Part Mouth Eyes Fins Body shape Scales Coloration Fantastic Fish Adaptation at the end of the snout, symmetrical angled downward/longer upper jaw angled upward/longer lower jaw strong jaws - teeth sucker-shaped barbels duckbill jaws no teeth very large mouth both on the same side of the head small large Large, forked caudal fin spines on fins large pelvic fins small pelvic fins round flat bottomed long, eel-like torpedo shaped flat from side to side flat from top to bottom hump backed large small no markings stripes mottled countershading – dark on top, light on bottom stripe through eye false eye spot Purpose open water feeder feeds on prey below it, bottom feeder feeds on prey above it, surface feeder preys on other fish eats small plants and animals feeds off bottom, senses food in murky water grasps its prey eats plankton surrounds prey lies flat on the bottom of the ocean shallow water fish usually deep water fish strong, fast swimmer protection, more difficult to swallow, can be poisonous bottom dweller open water swimmer difficult to swallow, slow swimmer feeds on the bottom hides in rocks and weeds high speed swimmer almost invisible from the front and rear, feeds above and below hides on the bottom stable in fast moving water uses its scales for protection fast swimmer swims in the open water hides in seaweeds and grasses hides in rocks or on the bottom less visible to predators above and below helps to camouflage fish by hiding the eye predator will attack tail giving fish a greater chance to escape Susan Seagraves