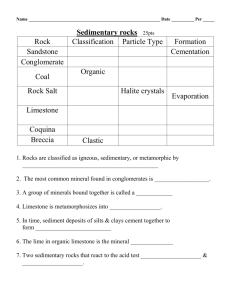
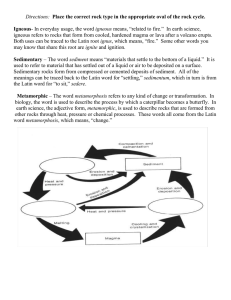
HISTORICAL GEOLOGY LECTURE TEST # 1 – 2009
advertisement

HISTORICAL GEOLOGY LECTURE TEST # 1 – 2009 1. An unconformity between granite and a sandstone would be a A.paraconformity B.nonconformity C.disconformity D.angular unconformity 2. The fundamental unit of worldwide time-stratigraphic classification is the A.eonothem B.stage C.series D.erathem E.system 3. Sedimentary ? include the size, shape and arrangement of grains. A.texture B.structure C.sedimentary texture and structure include the size, shape and arrangement of grains 4. A ? is the "time unit" equivalent of a system. A.age B.epoch C.era D.eon E.period 5. Most rock-forming minerals are A.oxides B.sulfides C.silicates D.native elements E.sulfates 6. ? are sand-size concentrically-ringed carbonate particles. A.intraclasts B.pellets C.oolites D.micrite E.sparite 7. Which of the following are "organic-walled microfossils"? A.acritarchs B.dinoflagellates C.spores D.pollen E.all of these are "organic-walled microfossils" 8. Well logs and seismic techniques are often used for stratigraphic A.diagenesis B.facies C.correlation D.biostratigraphy E.chronostratigraphy 9. Isotopes of a particular element would have a different number of A.protons B.neutrons C.isotopes of a particular element may have different numbers of protons or neutrons 10. The most abundant mineral group in the Earth's crust is A.quartz B.amphibole C.pyroxene D.carbonates E.feldspar 11. ? sedimentary structures are usually due to groundwater interaction with buried sediments or rocks. A.primary B.secondary C.both primary and secondary structures are usually due to groundwater interaction with buried sediments or rocks 12. ? is a body of sedimentary rocks with distinctive characteristics. A.facies B.primary sedimentary structures C.secondary sedimentary structures D.sedimentary textures E.diagenesis 13. A good index fossil should occur during a ? biostratigraphic interval of time. A.short B.long 14. Ka represents ? of years in the radioisotopic time scale. A.thousands B.millions C.billions 15. ? magmas are characteristic of the oceanic crust. A.mafic B.felsic C.both mafic and felsic magmas are characteristic of the oceanic crust 16. The atomic nucleus has a ? charge. A.positive B.negative C.neutral 17. Lithology is A.fossil content B.a biostratigraphic unit C.rock type D.geochemical criteria E.a transgressive sequence 18. The Cambrian and Cretaceous are A.stages B.series C.erathems D.systems E.eonothems 19. Soil duricrusts typically form in areas of ? rainfall. A.high B.low 20. ? is magma blown onto the Earth's surface. A.migmatite B.schist C.tephra D.hornfels E.carbonate 21. ? facies are constructed by organisms. A.lacustrine B.fluvial C.deltaic D.reef E.terrigenous shelf 22. ? are desert lakes. A.alluvial fans B.paleosols C.playas D.crevasse splays E.steppes 23. ? are "dry washes". A.alluvial fans B.barchan dunes C.monsoons D.wadis E.playas 24. Ions are A.charged atoms B.atoms with no mass C.ions are charged atoms with no mass 25. ? rocks are the most important rocks for interpreting Earth history. A.igneous B.sedimentary C.metamorphic 26. Climate type A.does not affect soil formation B.greatly affects soil formation 27. A meandering river facies typically ?-upward in grain size. A.fines B.coarsens 28. ? cannot be recognized at outcrops. A.paraconformities B.nonconformities C.disconformities D.angular unconformities 29. ? dating often is used to date zircon grains in igneous and metamorphic rocks. A.carbon-14 B.uranium-lead C.potassium-argon 30. ? is the degree of curvature of the corners of sedimentary particles. A.roundness B.sphericity C.this defines both roundness and sphericity 31. Most deserts are due to A.the presence of "rain shadow" topography B.the presence of adjoining cold ocean currents with dry air above them C.global circulation patterns 32. The Earth's magnetic field is due to motions in the Earth's A.crust B.mantle C.core 33. Epicontinental shelves A.are very common now B.were more common during periods of sea level rise in the geologic past 34. The basic mapping unit in geology is the A.bed B.member C.group D.formation E.supergroup 35. ? are mineral segregations that replace or force aside the surrounding sediment. A.concretions B.nodules C.geodes D.these are all mineral segregations that replace or force aside the surrounding sediment 36. The Comanchean and Gulfian are ? of the Cretaceous. A.stages B.series C.erathems D.systems E.eonothems 37. Cyclothems, and upward-coarsening grain size, is diagnostic of ? facies. A.beach B.fluvial C.deltaic D.paleosol E.glacial 38. The Law of ? is especially utilized to determine if the strata have been deformed. A.superposition B.inclusions C.original horizonality D.cross-cutting relationships 39. Alluvial fans are especially common in ? environments. A.desert B.delta C.lacustrine D.fluvial E.eolian 40. Sedimentary cement is often in the form of A.calcite B.quartz C.both calcite and quartz often form sedimentary cement 41. A "key bed" A.has economic significance B.is used in mapping C.key beds may be useful for mapping or may be of economic significance 42. Lagoonal facies would typically be characterized by the presence of A.sand B.mud C.lagoonal facies typically have a mixture of sand and mud 43. Stoping is characteristic of ? processes. A.sedimentary B.metamorphic C.igneous 44. ? are broad, shallow seas that form over continental areas. A.continental shelves B.epeiric platforms C.terrigenous shelves D.carbonate shelves E.reefs 45. ? is the ability of fluids to flow through sediment or sedimentary rocks. A.porosity B.permeability C.this defines both porosity and permeability 46. Biostratigraphic distributions are controlled by A.evolution B.paleoecology C.biostratigraphic distributions are controlled by both paleoecology and evolution 47. Which of the following is a clastic rock? A.limestone B.dolomite C.gypsum D.sandstone E.all of these are clastic rocks 48. ? are subdivided into ?. A.groups, formations B.formations, groups 49. Plutonic igneous rocks are characterized by ? crystals. A.small B.large C.the crystals may be large or small, depending upon whether the plutonic rock is intrusive or extrusive 50. Lacustrine environments include A.rivers B.deltas C.lakes D.wadis E.lacustrine environments include all of the above 51. Pellets and intraclasts are found in A.sandstones B.conglomerates C.evaporites D.limestones E.pellets and intraclasts are found in all of these rocks 52. Provenance is A.the source of sediments B.sedimentary process, including transport and deposition C.provenance includes all of the above 53. Conformities represent A.continuous depositional histories B.breaks in deposition 54. "Mammal Ages" are special types of A.taxon range zones B.concurrent range zones C.assemblage zones D.mammal ages consist of all of the above 55. Limestones and dolomites ? be precipitated in lakes. A.can B.cannot 56. A ? is a mountain-building event. A.diagenesis B.migmatite C.orogeny D.lithification E.facies 57. Gypsum and halite is precipitated A.only in marine environments B.in both marine and nonmarine environments 58. ? are large fossils (macrofossils) that have proven very useful for Permian and Mesozoic correlation. A.Foramininferans B.Radiolarians C.Acritarchs D.Condonts E.Ammonites 59. Extinction and emigration controls the ? appearances of fossil types. A.first B.last C.extinction and emigration control both first and last appearances 60. ? load includes the sedimentary particles carried by a current. A.physical B.chemical C.this includes both physical and chemical load 61. The Phanerozoic and Proterozoic are A.stages B.series C.erathems D.systems E.eonothems 62. Sediment sorting is typically ? in meandering rivers versus braided rivers. A.better B.worse 63. A steppe is a A.biostratigraphic unit B.lacustrine facies C.fluvial facies D.paleosol E.semiarid area 64. Primary sedimentary structures are formed ? the sediment is deposited. A.when B.after 65. In limestones the matrix is termed A.cement B.pellets C.oolites D.micrite E.sparite 66. Hornfels and phyllites are ? rocks. A.igneous B.sedimentary C.metamorphic 67. ? dating is not useful for dating materials much over 50 thousand years old. A.carbon-14 B.uranium-lead C.potassium-argon 68. Stratification is most characteristic of ? rocks. A.igneous B.metamorphic C.sedimentary 69. Polarity reversals are preserved in ? rocks. A.igneous B.sedimentary C.polarity reversals may be preserved in either igneous or sedimentary rocks 70. Alpine glaciers are ? than continental glaciers. A.smaller B.larger C.the terms "alpine" and "continental" refer to the same types of glaciers 71. In ?, the tetrahedra may be isolated or form single chains, double chains, sheets, or frameworks. A.oxides B.sulfides C.silicates D.native elements E.sulfates 72. ? rocks are made from magma. A.sedimentary B.metamorphic C.igneous 73. ? are subdivisions of ?. A.series, systems B.systems, series 74. The most common element in the Earth's crust is A.iron B.silicon C.aluminum D.calcium E.oxygen 75. Barrier islands and beaches are built primarily by ? action. A.wave B.tidal C.wave and tidal action are both important for building beaches and barrier islands 76. Magnetite and hematite are ? minerals. A.oxide B.sulfide C.carbonate D.silicate E.sulfate 77. ? are represented by overlapping ranges of taxa. A.taxon range zones B.concurrent range zones C.assemblage zones 78. ? dating measures the number of electrons caught in defects in the crystal structure of minerals. A.fission track B.paleomagnetic C.potassium-argon D.uranium-lead E.thermoluminescence 79. Tuffs are ? rocks. A.sedimentary B.contact metamorphic C.regional metamorphic D.intrusive igneous E.extrusive igneous 80. A ? is a relative drop in sea level. A.transgression B.regression 81. Humus is an important component of A.limestones B.dolomites C.sandstones D.evaporites E.soil 82. Massive beds in sedimentary rocks are typically formed when sedimentary conditions are A.constant B.continuously changing 83. The term "terrigenous" means that the sediments were derived from A.land B.the marine environment C.terrigenous sediments could come from land or the marine environment 84. In a clastic shelf environment, the facies typically ?-upward during regressive sequences. A.fine B.coarsen C.it depends upon the type of clastic shelf 85. ? are due to deformation of the underlying beds. A.paraconformities B.nonconformities C.disconformities D.angular unconformities 86. ? dating techniques yield dates in years before present. A.relative B.absolute C.both of these dating techniques yield dates in years before present 87. Sand dunes form ? facies. A.turbidite B.pelagic C.lacustrine D.fluvial E.eolian 88. Oozes are composed mostly of A.quartz B.feldspar C.sand-size rock fragments D.plankton shells E.evaporites 89. ? defines rock units on the basis of their physical features. A.chronostratigraphy B.biostratigraphy C.lithostratigraphy D.all of these define rock units on the basis of their physical features 90. Lake characteristics ? influenced by climate. A.are B.are not 91. A dike cutting across sedimentary layers would be ? than the sedimentary layers. A.older B.younger C.you cannot determine which would be younger by this information 92. Bauxites and laterites typically form in areas of ? rainfall. A.high B.low 93. Cross-bedding is especially utilized to determine A.sedimentary textures B.postdepositional structures C.secondary structures D.graded bedding E.paleocurrent direction 94. Most mapping of formations is by A.ground reconnaissance B.aerial photography 95. ? includes the physical, chemical and biologic changes that occur after deposition and before metamorphism. A.facies B.primary sedimentary structures C.secondary sedimentary structures D.sedimentary textures E.diagenesis 96. Cyclical, repetitive sedimentary units are especially characteristic of ? facies. A.eolian B.braided river C.meandering river D.lacustrine E.alluvial fan 97. Carbonate shelves typically develop in ? climates. A.temperate B.tropical C.carbonate shelves are very common in both temperate and tropical climates 98. ? was a Scottish gentleman farmer who formulated the concept of "uniformitarianism". A.Lyell B.Darwin C.Playfair D.Hutton E.Steno 99. ? are composed of ?. A.rocks, minerals B.minerals, rocks 100. Calcite is a ? mineral. A.oxide B.sulfide C.carbonate D.silicate E.sulfate