The Design of Learning Environments Presented by Patty Copeland
advertisement

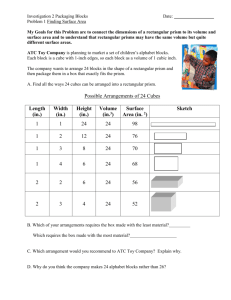
The Design of Learning Environments Presented by Patty Copeland Changes in Educational Goals Math Through the Decades Teaching Math in 1950: A logger sells a truckload of lumber for $100. His cost of production is 4/5 of the price. What is his profit? Math Through the Decades Teaching Math in 1960: A logger sells a truckload of lumber for $100. His cost of production is 4/5 of the price, or $80. What is his profit? Math Through the Decades Teaching Math in 1970: A logger exchanges a set, "L", of lumber for a set, "M", of money. The cardinality of set "M" is 100. Each element is worth one dollar. Make 100 dots representing the elements of the set "M." The set "C", the cost of production contains 20 fewer points than set "M." Represent the set "C" as a subset of set "M" and answer the following question: What is the cardinality of the set "P" of profits? Math Through the Decades Teaching Math in 1980: A logger sells a truckload of lumber for $100. His cost of production is $80 and his profit is $20. Your assignment: Underline the number 20. Math Through the Decades Teaching Math in 1990: By cutting down beautiful forest trees, the Logger makes $20. What do you think of this way of making a living? Topic for class participation after answering the question: How did the forest birds and squirrels feel as the logger cut down the trees? There are no wrong answers. Math Through the Decades Teaching Math in 2000: A logger sells a truckload of lumber for $100. His cost of production is $120. How does an Enron Accountant determine that his profit margin is $275? Math Through the Decades Teaching Math in 2010: El hachero vende un camion carga por $100. La cuesta de production es . . . . Changes in Educational Goals 1800s Instruction in writing focused on the mechanics---oral messages to written messages. Writing instruction aimed at giving children the capacity to closely imitate very simple text forms. Changes in Educational Goals 1930s Primary students were expected to express themselves in writing. Analysis and interpretation of what is read became an expectation of all school children. Literacy: Then and Now Colonist were literate enough if they could sign their name, or even an “X”… Immigrants arrived in large numbers and schools gave them “recitation literacy” Literacy: Then and Now WWI—Army redefined reading....“extraction literacy”…who, what, when, where, or how. Now—full or “higher literacy”…inferences, questions, or ideas Literacy: Then and Now “The idea of a classroom where young women, poor and minority students, and learning disabled students all read (not recite) and write about (not copy) Shakespeare or Steinbeck is a radical and hopeful departure from the longrunning conception of literacy as serviceable skills for the many and generative, reflective reading and writing for the few” (Wolf, 1988). Eighth Grade Test - 1895 Name and define the fundamental Rules of Arithmetic. A wagon box is 2 feet deep, 10 feet long, and 3 feet wide. How many bushels of wheat will it hold? If a load of wheat weighs 3942 lbs., what is it worth at 50 cents/bushel, deducting 1050 lbs. for tare? Eighth Grade Test - 1895 What is the cost of 40 boards 12 inches wide and 16 feet long at $20 per meter? Find bank discount on $300 for 90 days (no grace) at 10 percent. What is the cost of a square farm at $15 per acre, the distance which is 640 rods? Write a Bank Check, a Promissory Note, and a Receipt. Eighth Grade Test - 1895 District No. 33 has a valuation of $35,000. What is the necessary levy to carry on a school seven months at $50 per month, and have $104 for incidentals? Find cost of 6720 lbs. of coal at $6.00 per ton. Find the interest of $512.60 for 8 months and 18 days at 7 percent. Mass Production Vs. Providing Mass Education in Factories Structure efficient “Scientific” organization of classrooms factories Children Raw materials Teachers Technical workers Assembly line process Assembly line process to to graduation end product Administrators & Efficiency experts/superiors researchers. Measurement of product Standardized Test cost and progress Central District Management Authorities Society today… Envisions graduates of school systems who: Identify and solve problems Make contributions to society through their lifetime Display the qualities of “adaptive expertise” Why Are We Doing This? Curriculum/Instruction/Assessment Curriculum: What (TEKS/TAKS, district, campus, teacher) Quality Student Performance Instruction: How (lesson attributes, designs, strategies) Assessment: To what extent (TEKS/TAKS, district, teacher) Assessing Student Progress Addressing the Varied Needs and Characteristics of All Learners Alignment of Learning Objectives Thinking at High Cognitive Levels and Making Connections Perspectives on Learning Environments Community Learner Centered Knowledge Centered Assessment Centered Learner-Centered Environments Knowledge, skills, attitudes, and beliefs that learners bring Culturally responsive, appropriate, compatible, and relevant Diagnostic teaching Learner-Centered Environments Students use their current knowledge to construct new knowledge. What they know and believe at the moment affects how they interpret new information. Sometimes learners’ current knowledge supports new learning, sometimes it hampers learning. Learner-Centered Environments Previous Knowledge & Experiences Academic Tasks Building Background Listen to the passage Write a description or draw a picture of the main character Compare your vision of the character to the visions of others Martin… Building Background What is meant by activating prior knowledge? What is meant by building background? Do they differ instructionally? Building Background Activate Prior Knowledge: Discuss Brainstorm KWL Think-Pair-Share Show and Tell Building (Knowledge) Background Realia Demonstrate Model Pictures Frayer Model Definition Picture (in your own words) (that will be relevant to you) Word Example (from your life experiences) Non-example (from your life experiences) Function that is not constant and is not a line. ax2 + bx + c = 0 y = x2 Quadratic Function Building Background The inverse of the positive side of the quadratic parent function. Square Root Function Word Wall A A A A R R R R E E E E A A A A Sim i lar Building Background Knowledge-Centered Environments The ability to think and solve problems requires well-organized knowledge that is accessible in appropriate contexts. Overlaps with Learner-centered Begins with concern for students’ initial preconceptions about the subject matter. Concerns about what is developmentally appropriate at various ages. Knowledge-Centered Environments Highlights the importance of thinking about designs for curricula Learning with understanding vs. promoting the acquisition of disconnected sets of facts and skills? Assessment-Centered Environments Assessment-Centered Environments Formative Assessments Feedback Theoretical Frameworks Formats for Assessing Understanding Assessment Lower level reproduction, procedures, concepts, definitions Assessment Middle level connections and integration for problem solving Assessment Higher level mathematization, mathematical thinking, generalization, insight Consider the following: A rectangular prism is 2cm x 4cm by 6cm. One dimension is enlarged by a scale factor of 3. What is the volume of the enlarged figure? A rectangular prism is 2.7cm x 0.45cm by 609.01cm. One dimension is enlarged by a scale factor of 3.5. What is the volume of the enlarged figure? When a figure is dilated by a scale factor k to form a similar figure, the ratio of the areas of the two figures is ___ : ___ . A certain rectangular prism can be painted with n liters of paint. The factory enlarged it by a scale factor of 3 to make a similar prism. How much paint do they need to paint the larger box? Assessment Items - Where? Assessment Items - Where? A rectangular prism is 2cm x 4cm by 6cm. One dimension is enlarged by a scale factor of 3. What is the volume of the enlarged figure? A rectangular prism is 2.7cm x 0.45cm by 609.01cm. One dimension is enlarged by a scale factor of 3.5. What is the volume of the enlarged figure? When a figure is dilated by a scale factor k to form a similar figure, the ratio of the areas of the two figures is ___ : ___ A certain rectangular prism can be painted with n liters of paint. The factory enlarged it by a scale factor of 3 to make a similar prism. How much paint do they need to paint the larger box? Content-process space of Science Assessments Science Content Knowledge Rich Science Process Skills Open Constrained Lean Organized Cognitive Activity Structure of Knowledge Fragmental Meaningful Problem Surface Features and Underlying Representation shallow principles and understanding relevant concepts Strategy Use Undirected trial-and- Efficient, error problem solving informative, and goal oriented Self-Monitoring Minimal and sporadic Ongoing and flexible Explanation Single statement of fact of description of superficial factors Principled and coherent Community-Centered Environments Classroom and School Communities Value learning High standards These norms increase opportunities to: Interact Receive feedback learn Community-Centered Environments Connections to the Broader Community Homes Community centers, After-school programs businesses Comparison of time spent in school, home and community, and sleep. 33% 53% 14% Home and Community School Sleep Television Watching Different Kinds of Programs Educational Purely entertaining Effects on Beliefs and Attitudes Personal perception Perceptions of others The Importance of Alignment What is taught. How it is taught. How it is assessed. Without this alignment, it is difficult to know what is learned!! Conclusion Student-centered Knowledge-centered Assessment-centered Community-centered There needs to be alignment among the four perspectives of learning environments. They all have the potential to overlap and mutually influence each other. Thank you! pcopeland@esc11.net