Chapter 15 (part 3) Carbon Fixation (dark reactions)
advertisement

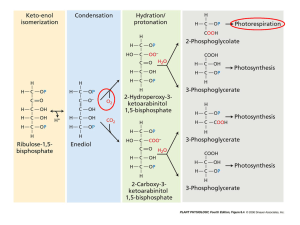
Chapter 15 (part 3) Carbon Fixation (dark reactions) Carbon Dioxide Fixation • A unique ability of plants, algae, etc. • Melvin Calvin at Berkeley in 1945 showed that Chlorella could take up 14CO and produce 3-phosphoglycerate 2 • What was actually happening was that CO2 was combining with a 5-C sugar to form a 6-C intermediate • This breaks down to two 3-P glycerates Reductive Pentose Phosphate Cycle 6CO2+9ATP+5H20 9ADP+8Pi+6NADP++(DHAP or G3P) Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubbisco) • Probably the world's most abundant protein • In leaves greater than 50% of the soluble protein is rubisco (stromal conc. 4 mM) • Rate Limiting step in RPP cycle • Rubisco is a slow enzyme (turnover number is 3 rxn per second) • Composed of 8 large subunits (LSU) (56,000 dal) and 8 small subunits (SSU) (14,000 dal). Active sites assocaited with LSU. • LSU encoded by chloroplast genome. SSU encoded by nuclear genome. Activation of Rubisco • Rubisco cycles between active and inactive form. • Active form requires a bound Mg2+ ion, light and high pH. • A none substrate CO2 molecule participates in Mg2+ binding to active site. • CO2 molecule binds reversibly to lysine residue forming carbamate adduct • Activation facilitated by the enzyme rubisco activase. • In the dark, carbamate adduct disassociates from active site. R 1,5-BP then binds tightly to active site and inhibits enzyme Mg2+ plays role in binding and activating R 1,6-BP to accept CO2 Rubisco Rxn Mechanisms carboxylase oxygenase Reductive Pentose Phosphate Cycle Reduction Stage •Conversion of 3phosphoglycerate to glucose is very similar to gluconeogenesis, but glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase uses NADPH not NADH. •Steps require consumption of ATP and NADPH. •3-phosphoglycerate could also be exported to cytsol and be used in normal gluconeogenesis. •Hexoses can then be used for energy or starch synthesis cytosol F 1,6-bisphophatase aldolase Glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase Phosphoglycerate kinase Reductive Pentose Phosphate Cycle Regeneration Step • Need to regenerate ribulose 1,5phosphate for subsequent rubisco reactions • One of the two 3-phosphoglyserates goes towards regeneration. • Need to generate 5 carbon sugar from 3 carbon and 6 carbon sugars. • Most expensive part of RPP cycle. Transketolases and Aldolases are used to make 5 carbon sugars Formation of 5 Carbon Sugars F-6-P + 2 G3P + DHAP + 3 ATP 3 R-1,5-BP + 3 ADP Regulation of RPP Cycle • Rubisco activity is regulated by pH Mg2+ • Other enzymes regulated by redox state of chloroplast • All factors are influenced by light Thioredoxin • 12 kD protein • Contains Cysteine residue that can cycle between reduced –SH and oxidized – S-S-. • Reduced thioredoxin can activate enzymes by reducing disulfides in regulatory domains. • thioreodxin ties light rxns to RPP cycle regulation • In light Thioredoxin is reduced. • Reduced thioredoxin activates RPP cycle enzymes. • “dark Rxns” don’t really function well in the dark. Oxygenase Activity of Rubisco • CO2 and O2 compete for binding at active site. • Under normal conditions the rate of carboxylation is 3 to 4 times the rate of oxygenation. • Both require activation by carbamate adduct (therefore no oxygenation w/o CO2) • Oxygenase activity produces 3-phosphoglycerate (normal C3 product) and 2-phosphoglycolate (C2 product) Photorespiration (recycling of 2-phosphoglycolate) • 4 of five carbons from R 1,5-BP salvaged. • Loose one carbon as CO2 • Because O2 consumed and CO2 released the process is called photorespiration • Wasteful process, loose carbon as CO2 w/o producing ATP or NADH • Biochemist have been trying to engineer better rubisco (no luck) Mechanisms to Avoid Photorespiration • C4 Photosynthesis – Spatial separation of carbon fixation and carbon utilization • CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) Photosynthesis – temporal separation of carbon fixation and carbon utilization C4 Photosynthesis • C4 cycle is way to pump CO2 into bundle sheath cells making concentration 20 fold higher than in mesophyll cells. • Important in plants from hot climates. • Under elevated temperature rubisco favors oxygenase function causing plants to undergoe photorespiration. • By fixing CO2 in Ms Cells with PEP carboxylase and transferring it to the Bs Cells as a 4 carbon sugar can concentrate CO2 and prevent photorepsiration. CAM Photosynthesis • Found in succulent plants (Crassulacea). • Drought tolerant plants. • Gas exchange occurs by opening pores called stoma • What to import CO2 without loosing water through stoma. • CAM plants open stoma at night to fix CO2, • They then store it until daytime when it is release it to rubisco stoma