IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 Project Title
advertisement

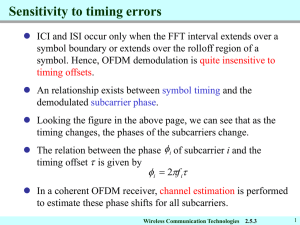
IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 Project IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group <http://ieee802.org/16> Title Synchronization Channel for IEEE 802.16m Amendment Date Submitted 2009-01-07 Source(s) Pei-Kai Liao, Yu-Hao Chang, Chih-Yuan Lin, Ciou-Ping Wu, Paul Cheng pk.liao@mediatek.com yuhao.chang@mediatek.com paul.cheng@mediatek.com MediaTek Inc. Re: IEEE 802.16m-08/053r1, “Call for Comments and Contributions on Project 802.16m Amendment Working Document”. - DL PHY control structure Abstract This contribution proposes SCH text proposal for P802.16m SDD. Purpose Propose to be discussed and adopted by TGm for the use in Project 802.16m SDD. Notice Release Patent Policy This document does not represent the agreed views of the IEEE 802.16 Working Group or any of its subgroups. It represents only the views of the participants listed in the “Source(s)” field above. It is offered as a basis for discussion. It is not binding on the contributor(s), who reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material contained herein. The contributor grants a free, irrevocable license to the IEEE to incorporate material contained in this contribution, and any modifications thereof, in the creation of an IEEE Standards publication; to copyright in the IEEE’s name any IEEE Standards publication even though it may include portions of this contribution; and at the IEEE’s sole discretion to permit others to reproduce in whole or in part the resulting IEEE Standards publication. The contributor also acknowledges and accepts that this contribution may be made public by IEEE 802.16. The contributor is familiar with the IEEE-SA Patent Policy and Procedures: <http://standards.ieee.org/guides/bylaws/sect6-7.html#6> and <http://standards.ieee.org/guides/opman/sect6.html#6.3>. Further information is located at <http://standards.ieee.org/board/pat/pat-material.html> and <http://standards.ieee.org/board/pat>. 1 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 Synchronization Channel for IEEE 802.16m Amendment Pei-Kai Liao, Yu-Hao Chang, Chih-Yuan Lin, Ciou-Ping Wu, Paul Cheng MediaTek Inc. I. Introduction This contribution is to propose text proposal to synchronization channel section for IEEE 802.16m Amendment. II. Proposed Synchronization Channel Architecture There are two synchronization channel (SCH) types in the proposed SCH architecture — Primary synchronization channel (P-SCH) and Secondary synchronization channel (S-SCH). P-SCH is responsible for superframe timing / radio frame timing / OFDM symbol boundary synchronization and signaling some system information such as channel bandwidth and sector information. Following two figures illustrates the proposed SCH architecture for 16m-only mode and legacy support mode. 802.16m Super-frame 802.16m Frame 802.16m Subrame FDD Mode D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D TDD Mode D D D D U U U D D D D U U U D D D D U U U D D D D U U U Ts = 102.857μs P-SCH Duplicate 1/2Tu=45.7145 μs S-SCH CP Tg 1/2Tu=45.7145 μs Frequency Domain Figure 1 SCH architecture for 16m-only mode 2 Idle Time 16m SCH Symbol IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 Legacy Radio Frame IEEE 802.16m Superframe IEEE 802.16m Radio Frame D FDD Mode TDD Mode D D D Frame Offset D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D U U U U Frame Offset D D D U U U D D D D U U U D D D D U U U D D D D U U U D SCH Symbol of Legacy System Idle Time SCH Symbol of IEEE 802.16m Figure 2 SCH architecture for legacy support mode III. Text Proposal ---------------------------------------------------------Start of the Text----------------------------------------------------------[Add the following into the TGm Amendment Document] 15.3.7.2.1 Synchronization Channel (SCH) The synchronization channel (SCH) is a DL physical channel which provides a reference signal for time, frequency, and frame synchronization, RSSI estimation, channel estimation, and BS identification. Two levels of synchronization hierarchy exist. These are called the primary synchronization channel (P-SCH) and secondary synchronization channel (S-SCH). The P-SCH transmits one of [10] unique identifications to support the acquisition of physical cell/sector identifications transmitted in S-SCH. The S-SCH transmits one of [520] complete physical cell/sector identifications. There are 4 OFDM symbols located every 5 ms for P-/S-SCH in a single superframe and the P-SCH and S-SCH shall share one OFDM symbol in time length as shown in Figure X-1. P-SCH and S-SCH are multiplexed by TDM inside the OFDM symbol. Each pair of P-SCH and S-SCH is located in the first DL subframe of the frame and occupies the 1st symbol position within a subframe. 3 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 Advanced Air Interface Superframe Advanced Air Interface Frame Advanced Air Interface Subrame FDD Mode D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D TDD Mode D D D D U U U D D D D U U U D D D D U U U D D D D U U U Ts P-SCH Duplicate S-SCH CP Idle Time 1/2Tb Tg Advanced Air Interface SCH 1/2Tb Figure X-1 Advanced Air Interface SCH Architecture 15.3.7.2.1.1 Primary Synchronization Channel (P-SCH) In P-SCH, frequency reuse 1 shall be applied. The time length of P-SCH is 1 Tb and the occupied channel 2 bandwidth is 5 MHz. The P-SCH is used for initial acquisition, superframe synchronization, channel estimation, and sending additional information. 15.3.7.2.1.1.1 P-SCH Modulation Series The length of each P-SCH modulation series is [97]. The modulation and power boosting of P-SCH is FFS. The P-SCH series depends on the sector information, system bandwidth, and carrier information. The series (Wk) used for the P-SCH modulation is defined in Table X-1. Table X-1 includes a set of series in a hexadecimal format. The value of the P-SCH modulation series is obtained by converting the series (Wk) to a binary sequence and mapping the converted sequence starting from the MSB of each symbol to the LSB. (0 mapped to +1 and 1 mapped to –1. For example, Wk = 110000010010..., and the mapping shall follow: –1 –1 +1 +1 +1 +1 +1 –1 +1 +1 –1 +1 ...) The equation (X-1) defines the mapping rule of the sector information, system bandwidth, and carrier information into P-SCH index, IDPSCH as follows: 3 N BW , if NCarrier 0 N , IDP SCH Sector , if NCarrier 1 9 (X-1) where 4 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 - N Sector denotes the sector index with 0, 1, and 2. N BW denotes the bandwidth indication with 0, 1, and 2, and thus, the indices 0, 1, and 2 represent 512FFT, 1024-FFT, and 2048-FFT, respectively. N Carrier represents the carrier type whether this carrier is a fully-configured carrier, i.e., N Carrier 0 , or a partially-configure carrier, i.e., N Carrier 1 . Table X-1 P-SCH modulation series [TBD] IDPSCH Series to modulate (Wk) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 … … … … … … … … … … 15.3.7.2.1.1.2 Transmission of P-SCH Series The subcarrier spacing of P-SCH is four times larger than that of a regular data OFDM symbol. Each subcarrier is modulated using a boosted BPSK modulation with a specific series defined in 15.3.7.2.1.1.1. After inverse FFT, the time domain samples are duplicated into two copies to form one P-SCH. In other words, the P-SCH in the time domain has two repeated waveform. In regular frame header, the subcarrier modulation for P-SCH is provided by the following equation (X-2) Subcarrier ( x) P SCH Wk ( x offset 97), if x offset 4 and x offset 1 W ( x offset ), if x offset and x offset 48 k Wk ( x offset 1), if x offset 50 and x offset 97 , W ( x offset 98), if x offset 98 and x offset 101 k nulled, otherwise (X-2) where Subcarrier(x)P-SCH represents the subcarrier with running index x and Wk(l) represents the lth digit of the modulated P-SCH series. x ranges from 0 to 127 and offset is equal to 15 for the channel bandwidth of 5 MHz; x ranges from 0 to 255 and offset is equal to 79 for the channel bandwidth of 7, 8.75 and 10 MHz; x ranges from 0 to 511 and offset is equal to 207 for the channel bandwidth of 20 MHz. Figure X-2 illustrates an example of PSCH frequency domain structure in regular frame header for channel bandwidths of 5, 10 and 20 MHz. 5 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 DC Tone 0 128 192 203 256 308 319 383 511 49 subcarriers 48 subcarriers 1st Part 128 subcarriers 2nd Part 64 subcarriers 11 subcarriers 64 subcarriers 5 MHz 128 subcarriers 11 subcarriers 1 subcarrier 4 subcarriers 10 MHz 4 subcarriers 20 MHz Figure X-2 Example of P-SCH Frequency Domain Structure in Regular Frame Header In superframe header, the subcarrier modulation for P-SCH is provided by the following equation (X-3) Subcarrier ( x) P SCH Wk ( x offset 4), if x offset 4 and x offset 1 W ( x offset 48), if x offset and x offset 48 k Wk ( x offset 50), if x offset 50 and x offset 97 W ( x offset 5), if x offset 98 and x offset 101 k nulled, otherwise (X-3) , where Subcarrier(x)P-SCH represents the subcarrier with running index x and Wk(l) represents the lth digit of the modulated P-SCH series. x ranges from 0 to 127 and offset is equal to 15 for the channel bandwidth of 5 MHz; x ranges from 0 to 255 and offset is equal to 79 for the channel bandwidth of 7, 8.75 and 10 MHz; x ranges from 0 to 511 and offset is equal to 207 for the channel bandwidth of 20 MHz. Figure X-3 illustrates an example of PSCH frequency domain structure in superframe header for channel bandwidths of 5, 10 and 20 MHz. 6 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 DC Tone 0 128 192 203 256 308 319 383 511 49 subcarriers 48 subcarriers 2nd Part 128 subcarriers 1st Part 64 subcarriers 11 subcarriers 64 subcarriers 5 MHz 128 subcarriers 11 subcarriers 1 subcarrier 4 subcarriers 10 MHz 4 subcarriers 20 MHz Figure X-3 Example of P-SCH Frequency Domain Structure in Superframe Header 15.3.7.2.1.2 Secondary Synchronization Channel (S-SCH) In S-SCH, frequency reuse 3 shall be applied. The time length of S-SCH is Tg 1 Tb and S-SCH occupies full 2 bandwidth. The S-SCH is used for fine synchronization, RSSI measurement, and cell/sector identification (ID). 15.3.7.2.1.2.1 S-SCH Modulation Series The length of each S-SCH modulation series is [67] for any channel bandwidth. Full cell ID information shall be carried inside the minimal supported channel bandwidth – 5 MHz. The modulation and power boosting of SSCH is FFS. The S-SCH series modulating the subcarriers is generated from Zadoff-Chu sequences with parameters u and S defined in Table X-2.1~2.4, where Table X-2.4 is for femtocells only. Table X-2.1 S-SCH modulation series [FFS] Cell ID Segment 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 0 u 1 1 1 1 S 0 5 10 15 Cell ID Segment 60 0 61 1 62 2 63 0 7 u 9 9 9 9 S 0 5 10 15 Cell ID Segment 120 0 121 1 122 2 123 0 u 17 17 17 17 S 0 5 10 15 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 8 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 1 17 20 2 17 25 0 17 30 1 17 35 2 17 40 0 17 45 1 17 50 2 17 55 0 18 0 1 18 5 2 18 10 0 18 15 1 18 20 2 18 25 0 18 30 1 18 35 2 18 40 0 18 45 1 18 50 2 18 55 0 21 0 1 21 5 2 21 10 0 21 15 1 21 20 2 21 25 0 21 30 1 21 35 2 21 40 0 21 45 1 21 50 2 21 55 0 22 0 1 22 5 2 22 10 0 22 15 1 22 20 2 22 25 0 22 30 1 22 35 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 4 4 4 4 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 14 14 14 14 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 2 22 40 0 22 45 1 22 50 2 22 55 0 24 0 1 24 5 2 24 10 0 24 15 1 24 20 2 24 25 0 24 30 1 24 35 2 24 40 0 24 45 1 24 50 2 24 55 Table X-2.2 S-SCH modulation series [FFS] Cell ID Segment 180 0 181 1 182 2 183 0 184 1 185 2 186 0 187 1 188 2 189 0 190 1 191 2 192 0 193 1 194 2 195 0 196 1 197 2 198 0 199 1 u 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 28 28 28 28 28 28 28 28 S 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Cell ID Segment 240 0 241 1 242 2 243 0 244 1 245 2 246 0 247 1 248 2 249 0 250 1 251 2 252 0 253 1 254 2 255 0 256 1 257 2 258 0 259 1 9 u 34 34 34 34 34 34 34 34 34 34 34 34 35 35 35 35 35 35 35 35 S 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Cell ID Segment 300 0 301 1 302 2 303 0 304 1 305 2 306 0 307 1 308 2 309 0 310 1 311 2 312 0 313 1 314 2 315 0 316 1 317 2 318 0 319 1 u 43 43 43 43 43 43 43 43 43 43 43 43 45 45 45 45 45 45 45 45 S 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 28 28 28 28 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 33 33 33 33 33 33 33 33 33 33 33 33 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 35 35 35 35 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 39 39 39 39 39 39 39 39 39 39 39 39 41 41 41 41 41 41 41 41 41 41 41 41 10 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 2 45 40 0 45 45 1 45 50 2 45 55 0 46 0 1 46 5 2 46 10 0 46 15 1 46 20 2 46 25 0 46 30 1 46 35 2 46 40 0 46 45 1 46 50 2 46 55 0 49 0 1 49 5 2 49 10 0 49 15 1 49 20 2 49 25 0 49 30 1 49 35 2 49 40 0 49 45 1 49 50 2 49 55 0 50 0 1 50 5 2 50 10 0 50 15 1 50 20 2 50 25 0 50 30 1 50 35 2 50 40 0 50 45 1 50 50 2 50 55 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 Table X-2.3 S-SCH modulation series [FFS] Cell ID Segment 360 0 361 1 362 2 363 0 364 1 365 2 366 0 367 1 368 2 369 0 370 1 371 2 372 0 373 1 374 2 375 0 376 1 377 2 378 0 379 1 u 51 51 51 51 51 51 51 51 51 51 51 51 53 53 53 53 53 53 53 53 S 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Cell ID Segment 380 2 381 0 382 1 383 2 384 0 385 1 386 2 387 0 388 1 389 2 390 0 391 1 392 2 393 0 394 1 395 2 396 0 397 1 398 2 399 0 u 53 53 53 53 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 57 57 57 57 S 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 Cell ID Segment 400 1 401 2 402 0 403 1 404 2 405 0 406 1 407 2 408 0 409 1 410 2 411 0 412 1 413 2 414 0 415 1 416 2 417 0 418 1 419 2 u 57 57 57 57 57 57 57 57 58 58 58 58 58 58 58 58 58 58 58 58 S 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 u 14 16 17 18 21 22 24 26 28 30 S 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 Table X-2.4 S-SCH modulation series for femtocells [FFS] Cell ID Segment 420 0 421 1 422 2 423 0 424 1 425 2 426 0 427 1 428 2 429 0 u 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 S 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 Cell ID Segment 454 1 455 2 456 0 457 1 458 2 459 0 460 1 461 2 462 0 463 1 11 u 64 64 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 S 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Cell ID Segment 488 2 489 0 490 1 491 2 492 0 493 1 494 2 495 0 496 1 497 2 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 60 60 63 63 63 63 63 63 63 63 63 63 63 63 64 64 64 64 64 64 64 64 64 64 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 65 65 65 65 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 1 2 3 4 7 9 10 12 40 45 50 55 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 0 32 60 1 33 60 2 34 60 0 35 60 1 37 60 2 39 60 0 41 60 1 43 60 2 45 60 0 46 60 1 49 60 2 50 60 0 51 60 1 53 60 2 55 60 0 57 60 1 58 60 2 60 60 0 63 60 1 64 60 2 65 60 0 66 60 15.3.7.2.1.2.2 Transmission of S-SCH Series The subcarrier spacing of S-SCH is two times larger than that of a regular data OFDM symbol. Every third subcarrier is modulated using a boosted value with a specific series defined in 15.3.7.2.1.2.1. The subcarrier modulation for S-SCH is provided by the following equations, which are FFS. DC tone shall be nulled. Figure X-4 illustrates an example of S-SCH frequency domain structure for channel bandwidths of 5, 10 and 20 MHz. 12 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 DC Tone 0 88 256 301 384 412 512 615 639 723 767 936 1023 99 subcarriers 102 subcarriers 2nd Part 1st Part 2nd Part 1st Part 2nd Part 1st Part 2nd Part 1st Part 88 subcarriers 87 subcarriers 5 MHz 6 subcarriers 9 subcarriers 10 MHz 3 subcarriers 6 subcarriers 9 subcarriers 20 MHz Segment 1 Segment 2 Segment 3 Figure X-4 Example of S-SCH Frequency Domain Structure For the deployment of femtocells, interferences between femtocells and other cells in S-SCH shall be mitigated. The interference mitigation scheme is FFS. 15.3.7.2.1.3 Support of WirelessMAN-OFDMA Advanced Air Interface shall exist in both green field and mixed deployments. In mixed deployments, the WirelessMAN-OFDMA preamble shall be always present. The Advanced Air Interface SCH shall enable AMSs to synchronize in frequency and time without requiring WirelessMAN-OFDMA preamble. Figure X-5 shows an example of Advanced Air Interface SCH architecture in mixed deployments. 13 IEEE C802.16m-09/0272 WirelessMAN-OFDMA Frame Advanced Air Interface Superframe Advanced Air Interface Frame D FDD Mode TDD Mode D D D Frame Offset D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D U U U U Frame Offset D D D U U U D D D D U U U D D D D U U U D D D D U U U D WirelessMAN-OFDMA preamble Idle Time Advanced Air Interface SCH Figure X-5 Advanced Air Interface SCH Architecture Supporting WirelessMAN-OFDMA -----------------------------------------------------------End of the Text--------------------------------------------------------- 14