.NET Framework & C#
advertisement

.NET Framework
&
C#
.NET Framework
Problem
background
Solution
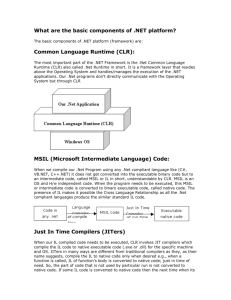
Common
Language Runtime (CLR)
MS Intermediate Language
MSIL
Structure
MSIL and Java bytecode
Introduction to C# language
C#
Structure
C# Features
Problems Background
Good code is hard to write
All system features in any language
COM problems
Platform Interoperability
Automatic memory management
Object-Oriented features in and between all PLs
Safety & Security
Better Access to OS functions
Interoperate with COM (both as client & server)
Solution (Common Language Runtime)
Managed Code in Common Language Runtime
Managed Code
Common Language Runtime
Requests for existing feature
Win 32 OS
New CLR-Only Feature
Solution (Microsoft Intermediate Language)
Different Languages are Compiled into MSIL
Source code :
Any languages
Development
tools
Just-In-Time
MS Intermediate
Language
compiler
Platform specific
code
.Net platform features
Automatic memory management
Explicit Versioning
OO features in any languages
Accessing system functionality throw a
hierarchical namespace
Code security
Interoperability with COM
Costs:
OS got harder to write
More memory and CPU time
CLR structure
Compare with traditional ways
C#
VB
C++
J-script
other
Compiler
Intermediate Language
C++
Compiler
Executable
Existing OS
JIT
econoJIT
Executables
.NET CLR
Machine hardware
PreJIT
A simple example
TimeComponent.vb
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic
' Declare the namespace that clients will use to access
' the classes in this component
Namespace TimeComponentNS
Public Class TimeComponent
Public Function GetTime(ByVal ShowSeconds As Boolean) As String
If (ShowSeconds = True) Then
Return Now.ToLongTimeString
Else
Return Now.ToShortTimeString
End If
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
Timeclient.cs
using System ;
using TimeComponentNS ;
class MainApp
{
public static void Main()
{
// Declare and create a new component of the class
// provided by the VB server we wrote
TimeComponent tc = new TimeComponent ( ) ;
// Call the server's GetTime method. Write its
// resulting string to a console window.
Console.Write (tc.GetTime (true)) ;
}
}
Assembly
A logical collection of one or more exe and dll file
containing an application’s code and resources
It contains
1-Codes in MSIL
2-Manifest
A metadata description of the code and resources
Metadata
What classes and method it contains
What external objects it requires
What version of code it represents
Manifest example (TimeComponent.dll)
.assembly extern mscorlib
{
.publickeytoken = (B7 7A 5C 56 19 34 E0 89 )
.ver 1:0:2411:0
}
.assembly extern Microsoft.VisualBasic
{
.publickeytoken = (B0 3F 5F 7F 11 D5 0A 3A )
.ver 7:0:0:0
}
.assembly TimeComponent
{
.hash algorithm 0x00008004
.ver 0:0:0:0
}
.module TimeComponent.dll
// MVID: {144ACC38-E825-45C4-83A6-C2A9E5A901DD}
.imagebase 0x00400000
.subsystem 0x00000002
.file alignment 512
.corflags 0x00000001
// Image base: 0x032a0000
// .z\V.4..
// .?_....:
Private or Public
Private
In client directory
Public (shared)
In Global Assembly Cache (GAC)
\\winnt\assembly
Namespaces
A logical division within which a name
need to be unique
The best way to handle a large list of
system objects and functions
System namespace (implemented in
several separated DLLs
We can import a namespace
Your code can have its own namespace
Versioning
DLL Hell
Replacing a DLL used by an existing client, with
a newer version (or vice versa)
.NET
provides a standard way to specify
version
Each client assembly uses its own
specified versions of related assemblies
Object oriented programming
Whether to smarten up non-object
oriented languages or dump down OO
languages
.NET provides all languages with
inheritance and constructors features
Virtual Object Model
All .NET classes inherit from the base
class System.Object
Equals
GetHashCode
GetType
ToString
Cross-language inheritance
Because of the standardized IL architecture
you can inherit form a class in another
language
For example:
System.Object
.NET memory management
.NET
CLR provides all languages with
automatic memory management.
Garbage collector automatically removes
unreferenced objects
You can force a garbage collection
manually
Interoperability with COM objects
.NET Supports interoperation with COM object
as client or server via a runtime callable
wrapper or a COM Callable Wrapper
Using COM objects from .NET objects
Using .NET objects from COM objects
Transaction in .NET
Transaction ensure the integrity of
databases during complex operations
Native .NET objects can also participate in
transactions with a simple attribute
Structured exception handling
.NET provides structured exception
handling as a fundamental feature
available in and between all languages
The exception handler can tell exactly
where the exception originated by using a
stack trace
Code access security
Most software comes from web
A user doesn’t know whether a Web code is safe
or not
.NET allows an administrator to specify
privileges that each managed code has.
You can specify these privileges in three level
by modifying XML-based files
Enterprise
Machine
User
\\winnt\microsoft.net\framework\[c.v.]\config\