Seasonal and Site Fluctuations of Chloride Levels in the Saratoga Lake Watershed
advertisement

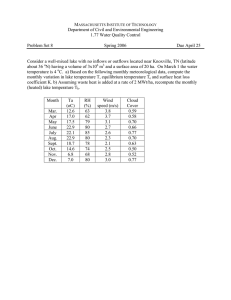
Seasonal and Site Fluctuations of Chloride Levels in the Saratoga Lake Watershed Environmental Studies Capstone Project 2007 What is Salt? Chemical composition of salt (NaCl) Used as a deicer on roadways (NaCl, KCl, MgCl, CaCl) (RiverSides, 2005) (www.rbwm.gov.uk, www.newyorkwater.org, www.earthhopenetwork.net, www.gurnee.il.us) Impacts of Salt on the Environment Impacts on aquatic communities Invertebrates and plants Impacts on terrestrial communities Can affect areas up to 1 km away from roadways (Habron et al., 2004) Colonization of invasive species Impacts on water Affects smaller waterways most (Trombulak and Frissell, 2000) Impacts of Salt on Humans Impacts on humans debatable Can’t remove salt at water treatment plant → hypertension (Special Report 235, 1991) Metal Corrosion Property Damage Trace metals (Hg, As, Cr, Pb) (Fischel, 2001) Saratoga Lake Watershed Sampling Sites Upper Kayaderosseras D 50 RT I8 7 RT 9 RT 9N DANIEL S RD RT 29 Clover Mill Creek E WEST AV D 2 RT 9 RT 9 P Lake Lonely Outlet C R ES Main Kayaderosseras D AVE 0 I 87 RT 43 MP RA RT 45 RT 5 D RT 47 CENT RT 6 RT 59 RT 4 RT 67 Kristina Connolly and Ashley Hellman ES Capstone Spring 2007 RT 67 3 23 Aerial Photo of Lake Lonely Outlet Collection Site Co un ty H igh wa y2 2 Vista Kayd eros s Av enue East Poe Waner Hypothesis We anticipated differences in chloride & conductivity levels from: Upstream & Downstream Site to Site Season to Season Sampling Four sampling dates: 2/24/07, 3/3/07, 3/24/07, 4/6/07 Conductivity measurements for all four dates Water samples on 2/24/07 and 4/6/07 Conductivity & Chloride Explained 350 300 Chloride (ppm) Conductivity (µS) 250 200 Chloride Conductivity 150 100 50 0 Upper Kayaderosseras Clover Mill Creek Main Kayaderosseras Lake Lonely Outlet Conductivity: a measure of the ability of a given substance to conduct electric current (www.dictionary.com) Comparison of Average Upstream and Downstream Conductivity Levels for Each Site 350 300 Conductivity (µS) 250 200 Upstream Downstream 150 100 50 0 Upper Kayaderosseras Clover Mill Creek Main Kayaderosseras Lake Lonely Outlet Across Date Comparison of Average Conductivity Levels by Site 350 Conductivity (µS) 300 250 200 2/24/2007 150 3/3/2007 100 3/24/2007 4/6/2007 50 0 Upper Kayaderosseras Clover Mill Creek Main Kayaderosseras Lake Lonely Outlet Saratoga Lake Watershed Sampling Sites Upper Kayaderosseras D 50 RT I8 7 RT 9 RT 9N DANIEL S RD RT 29 Clover Mill Creek E WEST AV D 2 RT 9 RT 9 P Lake Lonely Outlet C R ES Main Kayaderosseras D AVE 0 I 87 RT 43 MP RA RT 45 RT 5 D RT 47 CENT RT 6 RT 59 RT 4 RT 67 Kristina Connolly and Ashley Hellman ES Capstone Spring 2007 RT 67 3 23 Land Uses in the Saratoga Lake Watershed Upper Kayaderosseras D Land Use Types Water Low Intensity Development High Intensity Development Undeveloped Clover Mill Creek D Agriculture Lake Lonely Outlet Main Kayaderosseras D Kristina Connolly and Ashley Hellman ES Capstone Spring 2007 D Population Density by Square Mile in the Saratoga Lake Watershed D Upper Kayaderosseras Population Density Number of People Per Square Mile 24.7 - 25.0 25.1 - 50.0 50.1 - 100.0 100.1 - 500.0 D Lake Lonely Outlet Clover Mill Creek D 500.1 - 1000.0 1000.1 - 21150.0 D Main Kayaderosseras Kristina Connolly and Ashley Hellman ES Capstone Spring 2007 What it means… The Saratoga Lake Watershed and the Future • Highest levels in Lake Lonely Outlet large roads • Lowest levels in Upper Kayaderosseras small roads • Use data as a component of long-term consistent data for future studies • Political officials in Saratoga County can use data for future road salt debates Acknowledgments • • • • Skidmore College Environmental Studies Program Water Resources Initiative Karen Kellogg, Judy Halstead, Bob Turner, Bob Jones, Cathy Gibson, and Conor Taff • Jim Turner (for the use of his land) • Dominick Gabriel and Peter van Kuren • Our Parents References 2005. The Weight of Evidence. RiverSides: Where Water Quality Begins. http://www.riversides.org/index.php?cat=3&page1=8&page2=36 Committee on the Comparative Costs of Rock Salt and Calcium Magnesium Acetate (CMA) for Highway Deicing. 1991. Highway Deicing: Comparing Salt and Calcium Magnesium Acetate. Special Report 235, Transportation Research Board, National Research Council, Washington, D.C., USA. Demers, C. L., and R. W. Sage Jr. 1989. Effects of Road Deicing Salt on Chloride Levels in Four Adirondack Streams. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 49: 369-373. Habron, G.B., M.D. Kaplowitz, and R.L. Levine. 2004. A Soft Systems Approach to Watershed Management: A Road Salt Case Study. Environmental Management 33(6):776-787. Trombulak, S. C., and C. A. Frissell. 1999. Review of Ecological Effects of Roads on Terrestrial and Aquatic Communities. Conservation Biology 14(1): 18-30. www.dictionary.com, www.earthhopenetwork.net, www.gurnee.il.us, www.newyorkwater.org, www.rbwm.gov.uk