IEEE P802.20 Mobile Broadband Wireless Access
advertisement

IEEE P802.20
Mobile Broadband Wireless Access
Project
IEEE P802.20 Working Group for Mobile Broadband Wireless Access (MBWA)
Correspondence Group on Requirements
Title
802.20 Technical Requirements
Date
Submitted
9 June 2003
Source
Jim Tomcik
Ayman Naguib
Arak Sutivong
jtomcik@qualcomm.com
anaguib@qualcomm.com
asutivon@qualcomm.com
Re:
Abstract
As requested in the Requirements Correspondence Group conference call of June
4, 2003, this contribution re-casts contribution 802.20-03/44 into the format of the
new TOC discussed.
Purpose
The intent of this contribution is to establish a working document that will become
the repository for the terms, definitions and high level requirements to be used in
the selection process for a Draft Standard for 802.20.
Notice
This document has been prepared to assist the IEEE P802.20. It is offered as a
basis for discussion and is not binding on the contributing individual(s) or
organization(s). The material in this document is subject to change in form and
content after further study. The contributor(s) reserve(s) the right to add, amend or
withdraw material contained herein.
Release
The contributor acknowledges and accepts that this contribution becomes the
property of IEEE and may be made publicly available by P802.20.
{INSERT DATE}
P<designation>D<number>
IEEE P 802.20™/PD<insert PD Number>/V<insert version number>
Date: <June 04.2003>
Draft 802.20 Permanent Document
<802.20 Requirements Document >
This document is a Draft Permanent Document of IEEE Working Group 802.20. Permanent Documents
(PD) are used in facilitating the work of the WG and contain information that provides guidance for the
development of 802.20 standards. This document is work in progress and is subject to change.
1
2
2
{May 29, 2003}
3
Contents
4
1
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 11
5
1.1
Scope ............................................................................................................................................. 11
6
1.2
Purpose .......................................................................................................................................... 11
7
1.3
PAR Summary ............................................................................................................................... 11
8
9
10
2
Services and Applications...................................................................................................................... 11
2.1
Data Communications Applications .............................................................................................. 11
2.1.1
World Wide Web Browsing .................................................................................................. 11
11
2.1.1.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 11
12
2.1.1.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 11
13
2.1.2
Electronic Mail Transmission and Retrieval .......................................................................... 11
14
2.1.2.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 11
15
2.1.2.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 11
16
2.1.3
Instant Messaging .................................................................................................................. 11
17
2.1.3.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 11
18
2.1.3.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 11
19
20
2.2
Telecommunications Applications ................................................................................................. 11
2.2.1
Voice Services ....................................................................................................................... 11
21
2.2.1.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 12
22
2.2.1.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 12
23
2.2.2
Supplementary Services ......................................................................................................... 12
24
2.2.2.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 12
25
2.2.2.2
Minimum Requirements..................................................................................................... 12
26
2.2.3
Multimedia Applications ....................................................................................................... 12
27
2.2.3.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 12
28
2.2.3.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 12
29
2.2.4
Telematics Applications ........................................................................................................ 12
iii
{May 29, 2003}
30
2.2.5
31
2.2.5.1
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
E911 Services ........................................................................................................................ 12
Location Services .............................................................................................................. 12
32
2.2.5.1.1
Definition and Characteristics ..................................................................................... 12
33
2.2.5.1.2
Requirements on MBWA............................................................................................ 12
34
2.2.5.2
Priority Access ................................................................................................................... 13
35
2.2.5.2.1
Definition and Characteristics ..................................................................................... 13
36
2.2.5.2.2
Requirements on MBWA............................................................................................ 13
37
2.2.6
38
2.2.6.1
1.5 Messaging Services.......................................................................................................... 13
SMS Messaging ................................................................................................................. 13
39
2.2.6.1.1
Definition and Characteristics ..................................................................................... 13
40
2.2.6.1.2
Requirements .............................................................................................................. 13
41
2.2.7
3G Service Application Extensions for MBWA .................................................................... 13
42
2.2.7.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 13
43
2.2.7.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 13
44
3
45
System Reference Architecture .............................................................................................................. 13
3.1
System Architecture ....................................................................................................................... 13
46
3.1.1
System Context Diagram ....................................................................................................... 13
47
3.1.2
MBWA-Specific Reference Model ........................................................................................ 13
48
49
3.2
4
Definition of Interfaces .................................................................................................................. 15
System Requirements............................................................................................................................. 15
50
4.1
System Aggregate Data Rates – Downlink & Uplink .................................................................... 15
51
4.2
User Data Rates - – Downlink & Uplink ....................................................................................... 15
52
4.2.1
Peak User Data Rates............................................................................................................. 15
53
4.2.1.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 15
54
4.2.1.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 15
55
4.2.2
Average User Data Rates ....................................................................................................... 15
56
4.2.2.1
Definition and Characteristics ............................................................................................ 15
57
4.2.2.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 15
iv
{May 29, 2003}
58
4.3
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
Spectral Efficiency (bps/Hz/sector) ............................................................................................... 15
59
4.3.1
Definition and Characteristics ................................................................................................ 15
60
4.3.2
Requirements ......................................................................................................................... 15
61
4.4
QOS ............................................................................................................................................... 15
62
4.5
Number of Simultaneous Sessions ................................................................................................. 15
63
4.5.1
Definitions ............................................................................................................................. 15
64
4.5.2
Requirements ......................................................................................................................... 15
65
4.6
Packet Error Rate ........................................................................................................................... 16
66
4.7
System Link Budget ....................................................................................................................... 16
67
4.8
Air-link reliability .......................................................................................................................... 16
68
4.9
Max tolerable delay spread ............................................................................................................ 16
69
4.10
Mobility ......................................................................................................................................... 16
70
4.11
Security .......................................................................................................................................... 16
71
4.11.1
Access Control ....................................................................................................................... 16
72
4.11.1.1
Definitions and Characteristics ...................................................................................... 16
73
4.11.1.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 16
74
4.11.2
Privacy Methods .................................................................................................................... 16
75
4.11.2.1
Definitions and Characteristics ...................................................................................... 16
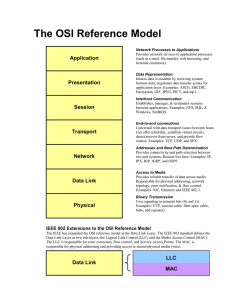
76
4.11.2.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 16
77
4.11.3
Billing Considerations ........................................................................................................... 16
78
4.11.3.1
Definitions and Characteristics ...................................................................................... 16
79
4.11.3.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 16
80
4.11.4
Authorization ......................................................................................................................... 16
81
4.11.4.1
Definitions and Characteristics ...................................................................................... 16
82
4.11.4.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 16
83
4.12
OA&M ........................................................................................................................................... 16
84
4.13
Signaling Requirements ................................................................................................................. 16
85
4.13.1
Signaling Subchannels ........................................................................................................... 17
v
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
86
4.13.1.1
Definition and Characteristics ........................................................................................ 17
87
4.13.1.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 17
88
4.13.2
Signaling Subchannel Reliability ........................................................................................... 17
89
4.13.2.1
Definition and Characteristics ........................................................................................ 17
90
4.13.2.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 17
91
4.13.3
Signaling Subchannel Latency and Data Rates ...................................................................... 17
92
4.13.3.1
Definitions and Characteristics ...................................................................................... 17
93
4.13.3.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 17
94
4.14
95
Handoff Support ............................................................................................................................ 17
4.14.1
Soft Handoff .......................................................................................................................... 18
96
4.14.1.1
Definitions and Characteristics ...................................................................................... 18
97
4.14.1.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 18
98
4.14.2
99
Hard Handoff ......................................................................................................................... 18
4.14.2.1
Hard Handoff Between Similar MBWA Systems .......................................................... 18
100
4.14.2.1.1
Definition and Characteristics ................................................................................... 18
101
4.14.2.1.2
Requirements ............................................................................................................ 18
102
4.14.2.2
Hard Handoff Between Frequencies .............................................................................. 18
103
4.14.2.2.1
Definition and Characteristics ................................................................................... 18
104
4.14.2.2.2
Requirements ............................................................................................................ 18
105
4.14.2.3
Hard Handoff Between MBWA and 3G Systems .......................................................... 18
106
4.14.2.3.1
Definitions and Characteristics ................................................................................. 18
107
4.14.2.3.2
Requirements ............................................................................................................ 18
108
4.14.3
IP-Level Handoff ................................................................................................................... 18
109
4.14.3.1
Definitions and Characteristics ...................................................................................... 19
110
4.14.3.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 19
111
112
113
5
Functional Requirements ....................................................................................................................... 19
5.1
Layer 1 RF/PHY ............................................................................................................................ 19
5.1.1
Duplexing – FDD & TDD ..................................................................................................... 19
vi
{May 29, 2003}
114
5.1.2
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
RF Channelization ................................................................................................................. 19
115
5.1.2.1
Bands of Applicability ....................................................................................................... 19
116
5.1.2.2
Spectral Masks ................................................................................................................... 19
117
5.1.3
Link Budget ........................................................................................................................... 19
118
5.1.4
Spectral Efficiency................................................................................................................. 19
119
5.1.4.1
Definitions and Conditions ................................................................................................ 19
120
5.1.4.2
Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 19
121
5.1.5
Channel Characteristics ......................................................................................................... 19
122
5.1.6
Adaptive Modulation ............................................................................................................. 19
123
5.1.7
Adaptive Coding .................................................................................................................... 19
124
5.1.8
Layer 1 to Layer 2 Inter-working ........................................................................................... 19
125
5.1.9
Mobility and PHY.................................................................................................................. 19
126
5.1.10
Space-Time Processing hooks & Multiple Antenna Capabilities .......................................... 19
127
5.1.11
Encryption ............................................................................................................................. 19
128
5.1.12
Antenna Configurations ......................................................................................................... 19
129
130
5.2
Layer 2 MAC ................................................................................................................................. 19
5.2.1
MAC Modes of Operation ..................................................................................................... 19
131
5.2.1.1
Random Access MAC........................................................................................................ 19
132
5.2.1.2
Polled MAC ....................................................................................................................... 19
133
5.2.2
Adaptive Coding .................................................................................................................... 19
134
5.2.3
Scheduler ............................................................................................................................... 19
135
5.2.4
Quality of Service and The MAC .......................................................................................... 20
136
5.2.4.1
Cos/QoS Matched-Criteria................................................................................................. 20
137
5.2.4.1.1
Protocol field mapping ................................................................................................ 20
138
5.2.4.1.2
Hardware mapping ...................................................................................................... 20
139
5.2.4.2
CoS/QoS Enforcement ....................................................................................................... 20
140
5.2.4.2.1
Inter-packet delay variation......................................................................................... 20
141
5.2.4.2.2
One-way, round-trip delay .......................................................................................... 20
vii
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
142
5.2.4.2.3
Prioritization ............................................................................................................... 20
143
5.2.4.2.4
Error correction ........................................................................................................... 20
144
5.2.4.2.5
Queuing ....................................................................................................................... 20
145
5.2.4.2.6
Suppression ................................................................................................................. 20
146
5.2.5
ARQ/Retransmission ............................................................................................................. 20
147
5.2.6
MAC Error Performance ....................................................................................................... 20
148
5.2.7
Latency .................................................................................................................................. 20
149
5.2.7.1
End to End Latency............................................................................................................ 20
150
5.2.7.2
End to End Latency Variation ............................................................................................ 20
151
5.2.8
Protocol Support .................................................................................................................... 20
152
5.2.9
Addressing ............................................................................................................................. 20
153
5.2.10
Mobility and the MAC ........................................................................................................... 20
154
5.2.10.1
Definitions and Characteristics ...................................................................................... 21
155
5.2.10.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 21
156
5.2.11
MAC Complexity Measures .................................................................................................. 21
157
5.2.11.1
Definition and Characteristics ........................................................................................ 21
158
5.2.11.2
Requirements ................................................................................................................. 21
159
5.2.12
160
5.3
Additional IP Offerings ......................................................................................................... 21
Layer 3+ Support ........................................................................................................................... 21
161
6
162
Appendix A
Definition of Terms .......................................................................................................... 22
163
Appendix B
Unresolved issues ............................................................................................................. 23
164
7
165
166
References ............................................................................................................................................. 21
Coexistence and Interference Resistance ............................................................................................... 23
7.1
5.1 Coexistence Scenarios ............................................................................................................. 23
7.1.1
FDD Deployments ................................................................................................................. 23
167
7.1.1.1
802.20 and AMPS.............................................................................................................. 23
168
7.1.1.2
802.20 and IS-95................................................................................................................ 23
169
7.1.1.3
802.20 and GSM ................................................................................................................ 23
viii
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
170
7.1.1.4
802.20 and LMR ................................................................................................................ 23
171
7.1.1.5
802.20 and CDMA2000..................................................................................................... 23
172
7.1.1.6
802.20 and WCDMA ......................................................................................................... 23
173
7.1.1.7
802.20 and 1xEVDO ......................................................................................................... 23
174
7.1.1.8
802.20 and HSDPA ........................................................................................................... 23
175
7.1.1.9
802.20 and 1xEV/DV ........................................................................................................ 23
176
7.1.2
5.1.2 TDD Deployments ........................................................................................................ 23
177
7.1.2.1
802.20 and AMPS.............................................................................................................. 24
178
7.1.2.2
802.20 and IS-95................................................................................................................ 24
179
7.1.2.3
802.20 and GSM ................................................................................................................ 24
180
7.1.2.4
802.20 and LMR ................................................................................................................ 24
181
7.1.2.5
802.20 and CDMA2000..................................................................................................... 24
182
7.1.2.6
802.20 and WCDMA ......................................................................................................... 24
183
7.1.2.7
802.20 and 1xEVDO ......................................................................................................... 24
184
7.1.2.8
802.20 and HSDPA ........................................................................................................... 24
185
7.1.2.9
802.20 and 1xEV/DV ........................................................................................................ 24
186
7.2
Adjacent Channel Interference ...................................................................................................... 24
187
7.2.1
Definitions and Characteristics .............................................................................................. 24
188
7.2.2
Requirements ......................................................................................................................... 24
189
7.3
Co-channel Interference ................................................................................................................. 24
190
7.3.1
Definitions and Characteristics .............................................................................................. 24
191
7.3.2
Requirements ......................................................................................................................... 24
192
7.4
TDD Interference in Traditionally FDD Bands ............................................................................. 24
193
7.4.1
Definition and Characteristics ................................................................................................ 24
194
7.4.2
Requirements ......................................................................................................................... 24
195
ix
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
196
1
197
1.1
Scope
198
1.2
Purpose
199
1.3
PAR Summary
200
2
201
202
203
204
This section provides definitions of anticipated traffic types. The section is arranged to cover likely
applications from traditional “data communications” as well as emerging applications and traffic types.
Since 802.20 may be deployed as a service extension of 3G networks, we also include a section on
extending 3G services to 802.20.
205
2.1
206
207
This section will describe the anticipated Data Communications applications for MBWA and associated
requirements.
Overview
Services and Applications
Data Communications Applications
208
209
2.1.1
210
2.1.1.1
Definition and Characteristics
211
2.1.1.2
Requirements
212
2.1.2
213
2.1.2.1
Definition and Characteristics
214
2.1.2.2
Requirements
215
2.1.3
216
2.1.3.1
Definition and Characteristics
217
2.1.3.2
Requirements
World Wide Web Browsing
Electronic Mail Transmission and Retrieval
Instant Messaging
218
219
2.2
220
2.2.1
221
222
Voice Services are currently among the most profitable services available to the cellular and PCS service
providers. These services are highly optimized to provide high quality at very minimal cost to provide. It is
Telecommunications Applications
Voice Services
11
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
223
224
expected that MBWA will need to make some accommodation to provide voice services as an integral part
of any service offering.
225
2.2.1.1
Definition and Characteristics
226
2.2.1.2
Requirements
227
2.2.2
228
2.2.2.1
229
230
231
To complement a basic point to point voice service offering, service providers normally provide several
“supplementary” services, such as Call Forwarding, Calling Number Identification. Some approach should
be adopted so that MBWA access can accommodate these basic services.
232
2.2.2.2
Supplementary Services
Definition and Characteristics
Minimum Requirements
233
234
2.2.3
235
Multimedia Applications are perceived as those of great interest for the future.
236
2.2.3.1
Definition and Characteristics
237
2.2.3.2
Requirements
238
2.2.4
239
240
241
242
243
Telematics is an emerging area that is expected to become a popular application for macro-cellular systems
in the next few years. Delivering services to vehicles such as positioning, location based services,
electronic toll tags and others are currently proving to be one of the more challenging areas. This section is
meant to capture anticipated services and to act as a repository for requirements that may affect the 802.20
specification.
244
2.2.5
245
246
247
Current systems implementing mobile access are required to implement FCC-mandated emergence services,
called E911 services, these typically consist of a positioning service as well as mechanisms to activate
priority access in times of emergency.
248
2.2.5.1
249
2.2.5.1.1
Definition and Characteristics
250
2.2.5.1.2
Requirements on MBWA
Multimedia Applications
Telematics Applications
E911 Services
Location Services
251
12
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
252
2.2.5.2
253
2.2.5.2.1
Definition and Characteristics
254
2.2.5.2.2
Requirements on MBWA
255
2.2.6
256
257
258
These services are Data-Like services, but currently are not implemented as true “data services.” Examples
of these services are the current SMS offerings of GSM and CDMA2000 networks, as well as the “instant
messaging” type services provided by independent service providers.
259
2.2.6.1
260
2.2.6.1.1
261
262
263
“Classic” SMS messaging was first described for 2G systems such as GSM and IS-95 and currently are
implemented directly over the cellular infrastructure, without need of data communication networking
infrastructure. Several different variations of these services exist, to be described as part of this section.
264
2.2.6.1.2
265
2.2.7
266
2.2.7.1
Definition and Characteristics
267
2.2.7.2
Requirements
268
3
269
3.1
270
3.1.1
271
272
273
274
This section presents a high level context diagram of the MBWA technology, and how such technology will
“fit into” the overall infrastructure of the network. It should include data paths, wired network connectivity,
AAA functionality as necessary, and inter-system interfaces. Major System Interfaces should be included in
this diagram.
275
3.1.2
276
277
278
To aid the discussion in this document and in the 802.20 specification, a strawman Reference Partitioning
of the 802.20 functionality is shown in Figure 1. This reference partitioning model is similar to those used
in other 802 groups.
279
280
The 802.20 reference model consists of two major functional layers, the Data Link Layer (DLL) and the
Physical Layer (PHY).
281
282
283
284
285
286
The Data Link Layer is functionally responsible for a mobile station’s method of gaining access to the overthe-air resource. The Data Link Layer consists of the MAC Sublayer, and the MAC Management Sublayer.
The MAC Sublayer is responsible for the proper formatting of data, as well as requesting access to the overthe-air resource. The MAC Management Sublayer is responsible for provisioning of MAC Layer
Parameters and the extraction of MAC monitoring information which can be of use in network
management.
Priority Access
Messaging Services
SMS Messaging
Definition and Characteristics
Requirements
3G Service Application Extensions for MBWA
System Reference Architecture
System Architecture
System Context Diagram
MBWA-Specific Reference Model
13
{May 29, 2003}
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
The Physical Layer consists of the Physical Layer Convergence Protocol, the Physical Medium Dependent,
and the Physical Layer Management Sublayers. The Physical Layer Convergence Protocol Sublayer is
responsible for the formatting of data received from the MAC Sublayer into data objects suitable for over
the air transmission, and for the deformatting of data received by the station. The Physical Medium
Dependent Sublayer is responsible for the transmission and reception of data to/from the over-the-air
resource. The Physical Layer Management sublayer is responsible for provisioning of the Physical Layer
parameters, and for the extraction of PHY monitoring information which can be of use in network
management.
295
296
297
298
MAC_SAP: MAC Service Access Point
PHY_SAP: PHY Service Access Point
Protocol contains FEC
PLCP: PHY Layer Convergence Protocol,
PMD: Physical Medium Dependent (radio)
Figure 1 – Reference partitioning
299
300
301
302
14
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
303
3.2
304
4
305
4.1
System Aggregate Data Rates – Downlink & Uplink
306
4.2
User Data Rates - – Downlink & Uplink
307
4.2.1
308
4.2.1.1
Definition and Characteristics
309
4.2.1.2
Requirements
310
4.2.2
311
4.2.2.1
Definition and Characteristics
312
4.2.2.2
Requirements
313
4.3
314
315
316
The 802.20 PAR indicates that the MBWA technology shall have a much greater spectral efficiency than
“existing systems”. This section defines the fundamentals of Spectral Efficiency in terms of “achievable”
and “maximum” spectral efficiency and the necessary requirements for the concept of “much greater.”
317
4.3.1
Definition and Characteristics
318
4.3.2
Requirements
319
4.4
QOS
320
4.5
Number of Simultaneous Sessions
321
4.5.1
Definitions
322
4.5.2
Requirements
Definition of Interfaces
System Requirements
Peak User Data Rates
Average User Data Rates
Spectral Efficiency (bps/Hz/sector)
323
15
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
324
4.6
Packet Error Rate
325
4.7
System Link Budget
326
4.8
Air-link reliability
327
4.9
Max tolerable delay spread
328
4.10 Mobility
329
4.11 Security
330
331
332
333
Network security in MBWA systems is assumed to have goals similar to those in cellular or PCS systems.
These goals are to protect the service provider from theft of service, and to protect the user’s privacy and
mitigate against denial of service attacks. Security for these systems is generally broken into Access
control, privacy methods, billing and authorization.
334
4.11.1 Access Control
335
4.11.1.1 Definitions and Characteristics
336
4.11.1.2 Requirements
337
4.11.2 Privacy Methods
338
4.11.2.1 Definitions and Characteristics
339
4.11.2.2 Requirements
340
4.11.3 Billing Considerations
341
4.11.3.1 Definitions and Characteristics
342
4.11.3.2 Requirements
343
4.11.4 Authorization
344
4.11.4.1 Definitions and Characteristics
345
4.11.4.2 Requirements
346
4.12 OA&M
347
4.13 Signaling Requirements
348
349
350
A signaling system for MBWA is key to providing services over the system and tying these services into
currently existing 2.5G and 3G infrastructure. This section presents requirements for signaling channels,
latencies and other items of interest.
16
{May 29, 2003}
351
4.13.1 Signaling Subchannels
352
4.13.1.1 Definition and Characteristics
353
4.13.1.2 Requirements
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
354
355
4.13.2 Signaling Subchannel Reliability
356
4.13.2.1 Definition and Characteristics
357
4.13.2.2 Requirements
358
359
4.13.3 Signaling Subchannel Latency and Data Rates
360
4.13.3.1 Definitions and Characteristics
361
4.13.3.2 Requirements
362
4.14 Handoff Support
363
364
365
366
367
368
Handoff methods are required in MBWA systems to facilitate providing continuous service for a population
of moving Mobile Stations. Mobile stations may move between cells, between systems, between
frequencies, and at the higher layer between IP Subnets. At the lowest layers, handoffs can be classified as
either soft or hard handoffs, depending on whether there is a momentary service disruption or not.
Handoffs to and from 3G technology are assumed to be important in this context as well, since MBWA is
being designed to co-exist with current 3G systems.
369
17
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
370
4.14.1 Soft Handoff
371
4.14.1.1 Definitions and Characteristics
372
4.14.1.2 Requirements
373
4.14.2 Hard Handoff
374
4.14.2.1 Hard Handoff Between Similar MBWA Systems
375
4.14.2.1.1 Definition and Characteristics
376
4.14.2.1.2 Requirements
377
4.14.2.2 Hard Handoff Between Frequencies
378
4.14.2.2.1 Definition and Characteristics
379
4.14.2.2.2 Requirements
380
4.14.2.3 Hard Handoff Between MBWA and 3G Systems
381
4.14.2.3.1 Definitions and Characteristics
382
4.14.2.3.2 Requirements
383
384
4.14.3 IP-Level Handoff
385
386
Regardless of the lower layer handoff types required, it is expected that a higher level handoff utilizing a
mechanism such as Mobile IP will be required for MBWA systems.
18
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
387
4.14.3.1 Definitions and Characteristics
388
4.14.3.2 Requirements
389
5
390
5.1
391
5.1.1
Duplexing – FDD & TDD
392
5.1.2
RF Channelization
393
5.1.2.1
Bands of Applicability
394
5.1.2.2
Spectral Masks
395
5.1.3
Link Budget
396
5.1.4
Spectral Efficiency
397
5.1.4.1
Definitions and Conditions
398
5.1.4.2
Requirements
399
5.1.5
Channel Characteristics
400
5.1.6
Adaptive Modulation
401
5.1.7
Adaptive Coding
402
5.1.8
Layer 1 to Layer 2 Inter-working
403
5.1.9
Mobility and PHY
404
5.1.10 Space-Time Processing hooks & Multiple Antenna Capabilities
405
5.1.11 Encryption
406
5.1.12 Antenna Configurations
407
5.2
408
5.2.1
409
5.2.1.1
Random Access MAC
410
5.2.1.2
Polled MAC
411
5.2.2
Adaptive Coding
412
5.2.3
Scheduler
Functional Requirements
Layer 1 RF/PHY
Layer 2 MAC
MAC Modes of Operation
19
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
413
5.2.4
414
415
416
417
418
Many emerging service concepts such as multimedia applications, video on demand, and others require that
data transmission and delivery performance be bounded to provide a good user experience. To achieve this,
there are many efforts in progress to define a Quality of Service “framework” and from that framework to
define requirements to assure that such services can be offered. This section is meant to capture relevant
QoS work, and to derive appropriate requirements for the 802.20 technology.
419
5.2.4.1
420
Definition of Cos??
421
5.2.4.1.1
Protocol field mapping
422
5.2.4.1.2
Hardware mapping
423
5.2.4.2
424
5.2.4.2.1
Inter-packet delay variation
425
5.2.4.2.2
One-way, round-trip delay
426
5.2.4.2.3
Prioritization
427
5.2.4.2.4
Error correction
428
5.2.4.2.5
Queuing
429
5.2.4.2.6
Suppression
430
5.2.5
ARQ/Retransmission
431
5.2.6
MAC Error Performance
432
5.2.7
Latency
433
5.2.7.1
End to End Latency
434
5.2.7.2
End to End Latency Variation
435
5.2.8
Protocol Support
436
5.2.9
Addressing
437
5.2.10 Mobility and the MAC
438
439
440
As listed in the PAR, the 802.20 specification should provide robust communications under vehicular
mobility conditions up to 250 Km/hr. This section seeks to parameterize this requirement and to derive
MAC layer requirements to meet the goal of a robust air interface in these mobility conditions.
Quality of Service and The MAC
Cos/QoS Matched-Criteria
CoS/QoS Enforcement
20
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
441
5.2.10.1 Definitions and Characteristics
442
5.2.10.2 Requirements
443
5.2.11 MAC Complexity Measures
444
445
446
To make the MBWA technology commercially feasible, it is necessary the complexity is minimized at the
MAC, consistent with the goals defined for the technologies. This section defines complexity measures to
be used in estimating MAC complexity.\
447
5.2.11.1 Definition and Characteristics
448
5.2.11.2 Requirements
449
450
5.2.12 Additional IP Offerings
451
5.3
452
453
6
Layer 3+ Support
References
21
{May 29, 2003}
454
455
Appendix A
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
Definition of Terms
22
{May 29, 2003}
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
456
Appendix B
457
7
458
459
460
461
462
Since MBWA technology will be operative in licensed bands some of which are currently being utilized by
other technologies, it is important that coexistence and interference issues be considered from the outset,
unlike the situation in unlicensed spectrum where there is much more freedom of design. Of particular
interest is adjacent channel interference; if MBWA is deployed adjacent to any of a number of technologies,
the development effort should evaluate potential effects.
463
464
465
466
Interference can be grouped as co-channel and adjacent channel interference; evaluation of all combinations
of technologies likely to be encountered should be part of the 802.20 process. Furthermore, 802.20
technology is described in the PAR to encompass both TDD and FDD techniques. These should be
evaluated separately, and requirements provided below.
467
7.1
468
7.1.1
469
470
In this section, scenarios should be developed with 802.20 deployed as FDD, following the FDD “rules” for
each of the 2G and 3G technologies likely to be encountered in practice.
Unresolved issues
Coexistence and Interference Resistance
5.1 Coexistence Scenarios
FDD Deployments
471
472
7.1.1.1
802.20 and AMPS
473
7.1.1.2
802.20 and IS-95
474
7.1.1.3
802.20 and GSM
475
7.1.1.4
802.20 and LMR
476
7.1.1.5
802.20 and CDMA2000
477
7.1.1.6
802.20 and WCDMA
478
7.1.1.7
802.20 and 1xEVDO
479
7.1.1.8
802.20 and HSDPA
480
7.1.1.9
802.20 and 1xEV/DV
481
7.1.2
482
483
484
485
In this section, scenarios should be developed with 802.20 deployed as TDD, following any TDD “rules”
for each of the 2G and 3G technologies likely to be encountered in practice. Since the majority of existing
technologies are deployed as FDD solutions, some new ground is being explored here, and it will be
necessary to make sure that the 802.20 technology will not seriously impact the existing services.
5.1.2 TDD Deployments
23
{May 29, 2003}
486
7.1.2.1
802.20 and AMPS
487
7.1.2.2
802.20 and IS-95
488
7.1.2.3
802.20 and GSM
489
7.1.2.4
802.20 and LMR
490
7.1.2.5
802.20 and CDMA2000
491
7.1.2.6
802.20 and WCDMA
492
7.1.2.7
802.20 and 1xEVDO
493
7.1.2.8
802.20 and HSDPA
494
7.1.2.9
802.20 and 1xEV/DV
495
7.2
496
7.2.1
Definitions and Characteristics
497
7.2.2
Requirements
498
7.3
499
7.3.1
Definitions and Characteristics
500
7.3.2
Requirements
IEEE P802.20-PD<number>/V<number>
Adjacent Channel Interference
Co-channel Interference
501
502
7.4
503
504
505
506
Since 802.20 is listed as being both TDD and FDD, it should be evaluated in a scenario where TDD 802.20
technology is deployed in a traditionally FDD frequency band. 802.20 should develop appropriate
scenarios and requirements so that the new technology meets all necessary coexistence requirements that
may be placed upon it.
507
7.4.1
Definition and Characteristics
508
7.4.2
Requirements
TDD Interference in Traditionally FDD Bands
509
510
511
Interworking
24