Risk management By the name of the god Dr. Lo’ai Tawalbeh DONE BY:
advertisement

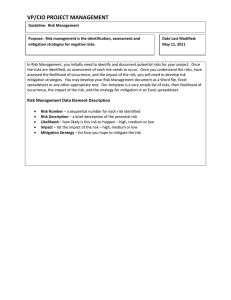
By the name of the god Risk management Dr. Lo’ai Tawalbeh DONE BY: AMNA ISMAIL RASHAN 1 The elements of risk 1) asset is anything within an environment that should be protected 2) Threat: is any potential danger to information, or systems (e.g. fire) 2 The elements of risk 3) Vulnerability: is a software, hardware, or procedural weakness that may provide an attacker the open door to enter a system. 4) Exposure: It means that, if there is a vulnerability and a threat that can exploit it, there is the possibility that a threat event can occur. 3 The elements of risk 5) Risk: is the possibility that any specific threat will exploit a specific vulnerability to cause harm to an asset. risk = threat + vulnerability. 6) safeguard: or countermeasure, is anything that removes a vulnerability or protects against one or more specific threats. Safeguards and counter-measures are the only means by which risk is mitigated or removed. 4 Sources of risk A) Internal: * Changes in budget * change of initial requirement * disruption to day to day operation of the organization * key staff leaving * equipment failure. B) External: * Hardware/software not delivered * supplier becomes insolvent * unauthorised access into systems * disruption through power/communication 5 Parts of risk Risk event: the adverse event that results in a risk. Risk probability: the likelihood or uncertainty of a risk to occur. Risk impact: the loss or extent of damage caused by a risk. 6 Types of risk 1. Technical risk 2. Managerial risk 3. Operational risk 4. Environment risk 5. Testing risk 7 Types of risk (1)Do we really know what the problem is? (2) Is the problem solvable? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Technical risk Managerial risk Operational risk Environment risk Testing risk Types of risk * * * * Schedule risk; Financial risk; Personnel risk; Quality risk; 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Technical risk Managerial risk Operational risk Environment risk Testing risk Types of risk * Inadequate user education or training; * Software Misuse; * Inadequate maintenance of the product. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Technical risk Managerial risk Operational risk Environment risk Testing risk Types of risk physical risks that may threaten a particular data center as: Fire, water 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Technical risk Managerial risk Operational risk Environment risk Testing risk Types of risk The quality control practitioner plays a key role in addressing the testing of risk 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Technical risk Managerial risk Operational risk Environment risk Testing risk Risk Management is the process of controlling risk and monitoring the effectiveness of the control mechanisms. The goal of RM: is to preserve the quality and integrity of a project by reducing cost escalation and project slippage. 13 Risk management process 1) Identifying the risk; 2) Assessing the risk's magnitude; 3) Determining the response to the risk; 4) Planning for the addressing of, and reporting on, the risk if encountered 14 Risk assessment The cost potential of the risk's occurrence; The probability of the risk occurring; The risk exposure; The cost to respond to the risk. 15 Risk response 1) Elimination; 2) Avoidance; 3) Mitigation; 4) Acceptance. 16 Risk Analysis the process of identifying, estimating, and evaluating risk. 17 Risk Analysis Benefits of RA • Ease of data comprehension. • Identification and prioritization of critical activities and functions • Identification of areas where policies and procedures need to be enhanced and implemented Justification of cost of implementation of measures • Assessment of the preparedness of an organization with respect to the risks. • Assessment of the security awareness among employees 18 Risk Analysis 1) Software Risk Analysis 2) Planning Risks and Contingencies The purpose of software risk analysis: to determine what to test, the testing priority, and the depth of testing. 19 Risk Analysis Who Should Do the Analysis? The risk analysis should be done by a team of experts from various groups within the organization include developers, testers, users, customers, marketers, and other interested, willing, and able contributors. When Should It Be Done? A risk analysis should be done as early as possible in the software lifecycle. A first cut at a risk analysis can usually be done as soon as the high-level requirements are known. 20 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 1: Form a Brainstorming Team Step 2: Compile a List of Features Step 3: Determine the Likelihood Step 4: Determine the Impact Step 5: Assign Numerical Values Step 6: Compute the Risk Priority Step 7: Review/Modify the Values Step 8: Prioritize the Features Step 9: Determine the "Cut Line“ Step 10: Consider Mitigation 21 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 1: Form a Brainstorming Team Include: users (such as business analysts) developers testers marketers customer service representatives support personnel and anyone else that has knowledge of the business and/or product, and is willing and able to participate. 22 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 2: Compile a List of Features Compile an inventory of features, attributes, or business functions for the entire system. Global attributes include: Accessibility, availability, compatibility, maintainability, performance, reliability, scalability, security, and usability. 23 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 3: Determine the Likelihood Assign an indicator for the relative likelihood of failure. 24 Table 2: Likelihood of Failure for ATM Features/Attributes ATM Software Features Likelihood Attributes Withdraw cash High Deposit cash Medium Check account balance Low Transfer funds Medium Purchase stamps High Make a loan payment Low Usability Medium Performance Low Security Medium 25 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 4: Determine the Impact What would be the impact on the user if this feature or attribute failed to operate correctly? 26 Table 3: Impact of Failure for ATM Features/Attributes ATM Software Likelihood Impact Withdraw cash High High Deposit cash Medium High Features Attributes Check account balance Low Medium Transfer funds Medium Medium Purchase stamps High Make a loan payment Low Low Medium Usability Performance Security Medium High Low Medium Medium High Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 5: Assign Numerical Values Brainstorming team should assign numerical values for H, M, and L for both likelihood and impact. Usually assign a value of 3 for H, 2 for M, and 1 for L. 28 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 6: Compute the Risk Priority The values assigned to the likelihood of failure and the impact of failure should be added together. 29 Table 4: Summed Priorities for ATM Features/Attributes ATM Software Likelihood Features Check Impact Priority Attributes Withdraw cash High High 6 Deposit cash Medium High 5 account balance Low Medium 3 Transfer funds Medium Medium 4 Purchase stamps High Make a loan payment Usability Performance Security Low 4 Low Medium 3 Medium High 5 Low Medium 3 Medium High 5 30 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 7: Review/Modify the Values Values of the likelihood of failure for each feature may be modified based on additional information or analyses that may be available. 31 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 8: Prioritize the Features The brainstorming team should reorganize their list of features and attributes in order of risk priority. 32 Table 5: Sorted Priorities for ATM Features/Attributes ATM Software Likelihood Impact Priority Withdraw cash High High 6 Deposit cash Medium High 5 Usability Medium High 5 Security Medium High 5 Transfer funds Medium Medium 4 Purchase stamps High Low 4 Make a loan payment Low Medium 3 Check account balance Low Medium 3 Low Medium 3 Features Attributes Performance Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 9: Determine the "Cut Line“ To indicate the line below which features will not be tested (if any) or tested less. In order to do that, it's necessary to estimate the amount of testing that is possible with the available time and resources. 34 Table 6 "Cut Line" for ATM Features/Attributes ATM Software Likelihood Impact Priority Withdraw cash High High 6 Deposit cash Medium High 5 Medium High 5 Transfer funds Medium Medium 4 Purchase stamps High Low 4 Low High 4 Make a loan payment Low Medium 3 Check account balance Low Medium 3 Low Medium 3 Features Attributes Usability Security Performance To Be Tested Not to Be Tested (or tested less) 35 Software Risk Analysis Process How Should It Be Done Step 10: Consider Mitigation The mitigation activities may require action by developers, users, testers, or others. Risk mitigation helps reduce the likelihood of a failure, but does not affect the impact. 36 Table 7: Mitigated List of Priorities for ATM Features/Attributes ATM Software Likelihood Impact Withdraw cash High High 6 Code inspection Deposit cash Medium High 5 Early prototype Usability Medium High 5 Early Security Medium High 5 Transfer funds Medium Medium 4 Purchase stamps High Low 4 Features Priority Mitigation Attributes Make a loan payment Low Medium 3 Check account balance Low Medium 3 Low Medium 3 Performance user feedback 2) Planning Risks and Contingencies Purpose: To determine the best contingencies in the event that one of the planning risks occurs. This is important because the scope and nature of a project almost always change as the project progresses. The planning risks help us to do the "What if…" and develop contingencies. 38 39




![School Risk Register [DOCX 19.62KB]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/014980461_1-ba10a32430c2d15ad9059905353624b0-300x300.png)
