Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Computer & InformationTechnology
advertisement
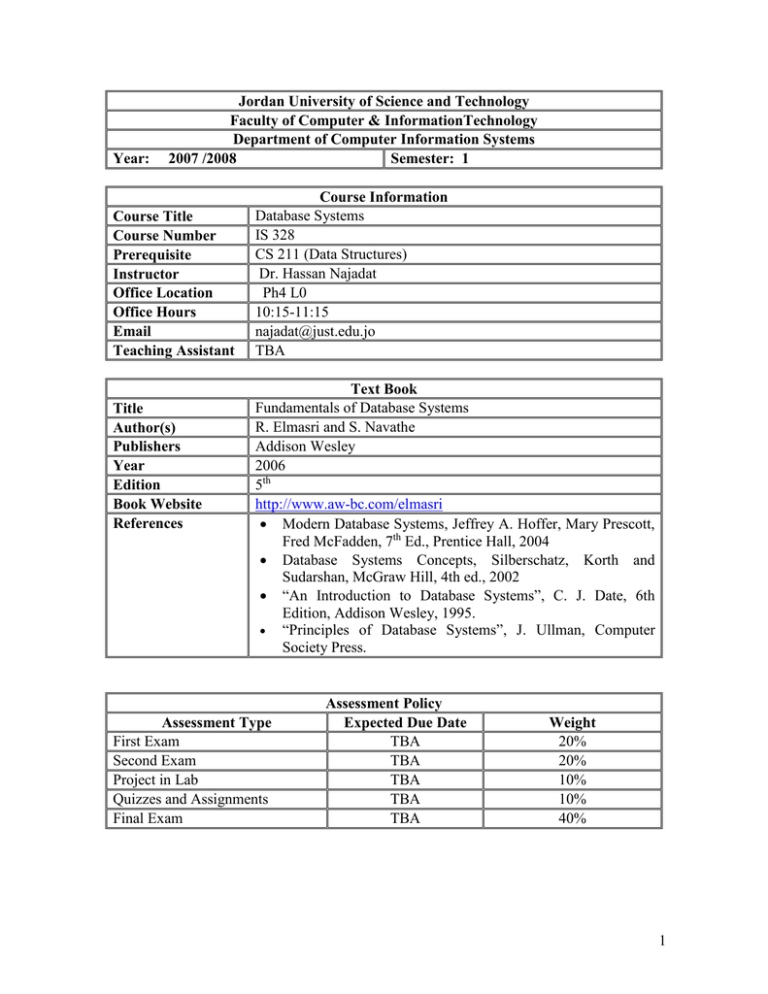
Year: Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Computer & InformationTechnology Department of Computer Information Systems 2007 /2008 Semester: 1 Course Title Course Number Prerequisite Instructor Office Location Office Hours Email Teaching Assistant Title Author(s) Publishers Year Edition Book Website References Course Information Database Systems IS 328 CS 211 (Data Structures) Dr. Hassan Najadat Ph4 L0 10:15-11:15 najadat@just.edu.jo TBA Text Book Fundamentals of Database Systems R. Elmasri and S. Navathe Addison Wesley 2006 5th http://www.aw-bc.com/elmasri Modern Database Systems, Jeffrey A. Hoffer, Mary Prescott, Fred McFadden, 7th Ed., Prentice Hall, 2004 Database Systems Concepts, Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan, McGraw Hill, 4th ed., 2002 “An Introduction to Database Systems”, C. J. Date, 6th Edition, Addison Wesley, 1995. “Principles of Database Systems”, J. Ullman, Computer Society Press. Assessment Type First Exam Second Exam Project in Lab Quizzes and Assignments Final Exam Assessment Policy Expected Due Date TBA TBA TBA TBA TBA Weight 20% 20% 10% 10% 40% 1 Course Objectives The main objective of this course is to provide students with the theoretical background and practical experience relating to the design and implementation of relational databases. Students, during this course, are trained to use SQL to create databases and practice some of the theory taught in class. The main objectives of the course are: 1. Know the terminology associated with the database field. (5%) 2. Know the methodologies to design database systems. (5%) 3. Know some conceptual models (such as ER and EER) (10%) 4. Know the relational model (5%) 5. Know query languages associated with relational models (Relational Algebra and SQL). (20%) 6. Assess the quality of a relational schema (via normalization). (15%) 7. Teach students the principles of database design (10%). 8. Teach students the fundamentals of query processing (10%). 9. Teach students to create database applications using MS-Access (10%) [in lab] Teaching & Learning Methods Class lectures, lecture notes, homework assignments, and projects are designed to achieve the course objectives. You should read the assigned chapters before class, complete assignments on time, participate in class discussions among other things to understand the material. You should ask questions, whether in class or during office hours. You are responsible for all material covered in class. If you have any concerns, please communicate them to the instructor in class, in office or by email. 2 Week 1, 2 2, 3 4, 5 6 7 8, 9 10, 11 12 13, 14 15, 16 Course Contents Topics Databases and Database Users Database System Concepts and Architecture Data Modeling Using the Entity-Relationship Model and Enhanced Entity-Relationship Model The Relational Data Model and Relational Database Constraints ER- and EER-to-Relational Mappings The Relational Algebra SQL - The Relational Database Standard Practical Database Design Methodology Functional Dependencies and Normalization for Relational Databases Relational Database Design Algorithms and Further Dependencies chapter objective 1 2 3, 4 1,2 1,2 5 4 7 6 8 3 5 5 7 12. 1 and 12.2 2, 3 10 6 11 6 Learning Outcomes Upon successful completion of this course, students will have the skills to analyse business requirements and produce a viable model and implementation of a database to meet such requirements. Students Should be able to know basic terms associated with database management systems, such as database, database management system, primary key, foreign key, database administrator, benefits of database systems, factors to consider when buying a DBMS. Should be able to create a conceptual design for a database based on problem specifications and user-requirements. Should be able to model databases using the ER and EER models. Should be able to choose a suitable DBMS; and mapping the conceptual design of a database into the selected DBMS’s format. Should be able to create queries using Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus. Should be able to use and create queries using SQL. Should be able to normalize data and transform it into forms that are most suitable to the applications at hand. 3 Homeworks Makeup Exams Project in Lab Attendance Code of Conduct Additional Notes Homeworks are due at the beginning of class, Late homeworks will not be accepted, All works have to be done independently, Students handing in similar homeworks will receive a grade of 0 (ZERO) and face possible disciplinary actions. In accordance with university regulations, i.e. students should bring a valid excuse authenticated through valid channels in JUST. All works will be done in Lab. Project will be divided into different phases which have to be graded in lab time. Students are expected to attend all classes If a student misses 10% of the classes without an acceptable reason, the student will be assigned a grade of 35, according to the rules of JUST. The assignments, and of course the quizzes, and exams need to be done individually. Copying of another student's work or code, even if changes are subsequently made, is inappropriate, and such work or code will not be accepted. The University has very clear guidelines for academic misconduct, and they will be enforced in this class. 4