Vocabulary Chapter 7 Energy: Photosynthesis
advertisement

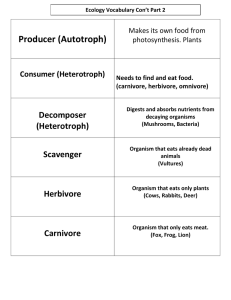
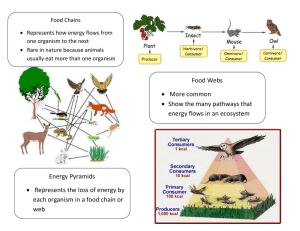
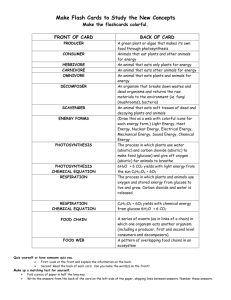
Vocabulary Chapter 7 Energy: Ability to do work or cause change Photosynthesis: A series of reactions where plants, algae and some bacteria absorb sunlight to make food and store energy. Enzymes: Protein made by an organism that is used as a catalyst in specific biochemical reactions. Catalyze: To speed up a reaction. Cellular respiration: A series of reactions where a living cell breaks down carbohydrates or other organic compounds to release energy. Chemical energy: Energy stored in a chemical bond Chemical equation: Mathematical model for a chemical reaction Reactant: The substance that goes into a reaction Product: The substance that comes out of a chemical reaction Endothermic reaction: A reaction that absorbs energy. Exothermic reaction: A reaction that releases energy. Aerobic respiration: Cellular respiration that requires oxygen Anaerobic respiration: Cellular respiration that does not require oxygen. Producer: Organism that makes its own food Consumer: Organism that eats other organisms Herbivore: Animal that eats plants. Omnivore: Animal that eats plants and animals. Carnivore: Animal that eats other animals. Heterotroph: Organism that obtains energy from other organisms-living or dead. (Animals, fungi and bacteria) Autotroph: Organism that obtain energy and matter from non-living things like the sun, air. (Plants, algae and some bacteria) Metabolism: A term for all collective chemical activities and changes that take place in a cell or organism. Biosynthesis: A synthesis reaction where smaller molecules are built into larger more complex ones. Digestion: A decomposition reaction where larger, more complex molecules are broken down into more simple molecules. Carbon….its what’s for dinner!