Coming to Terms With Critical Thinking 2007 CCRI
advertisement

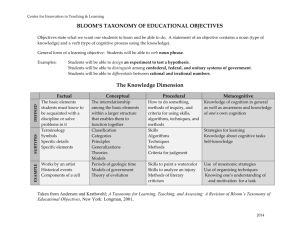
2007 CCRI Critical Thinking Conference Coming to Terms With Critical Thinking Presented By: Daniel J. Donovan, J.D. Professor Legal Studies Coming to Terms with Critical Thinking History of Idea of Critical Thinking Bloom’s Taxonomy Revised Critical Thinking Definitions Elements of Reasoning Educational Terms Definitions Sample Rubrics History of Idea of Critical Thinking Socrates – The Unexamined Life is not worth living – Plato’s Apology – 399 BCE – Socratic Questioning teaching strategy Francis Bacon – Advancement of Learning 1605 concept of “idols” – bad habits of thought John Dewey – How We Think 1910 (rev. 1933) – Reflective or Scientific Thinking Bloom’s Taxonomy Revised Original taxonomy of Educational Objectives - Cognitive Domain 1956 (page 12) Revised Taxonomy – 2001 – Cognitive Domain – 6 processes (page 13) – – Switched order of top two processes Knowledge Domain – 4 types (page 15) Taxonomy Table - two dimensional (page 16) Law of Torts – Example Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify the four elements of all tort actions Explain the concept of vicarious liability in business Apply the elements of the tort “intentional infliction of emotional distress” to given fact patterns Write an evaluation of the law on “social host liability” as it exists in Rhode Island and compare it with Massachusetts law Write a Career Paper detailing your strengths and weaknesses in pursuing your future career as a Paralegal Putting Objectives on the Taxonomy Table Knowledge Dimension A. Factual Knowledge B. Conceptual Knowledge C. Procedural Knowledge D. Metacognitive Knowledge The Cognitive Process Dimension 1. Remember 2. Understand 3. Apply 4. Analyze 5. Evaluate 6. Create E.O. #1 E.O. #2 E.O. #4 E.O. #4 E.O. #5 E.O. #5 E.O.#3 Critical Thinking Definitions Short definition – connects to Bloom’s taxonomy – Critical Thinking is the process of analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action. Delphi Report Definition ( 1990) – page 19 – – – Full report on CT Committee website: http:/www.ccri.edu/learningevidence/ct Contains both cognitive & affective processes Not everything that can be counted counts, and not everything that counts can be counted - Albert Einstein Elements of Reasoning Purpose of the Thinking Question at Issue Assumptions – when you assume… Points of View Information – Relevancy Concepts Inferences or Interpretations (Conclusions) Implications and Consequences See The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking for template Briefing a Court Decision 1. Citation - start with the proper citation to the case - include parallel citations if there are any. 2. Parties - list all parties to an action - the name of the case might not include all the persons involved - “et al.” in the name of a case indicates “and others”. 3. Issues - set forth the legal questions (issues) that the court was addressing in the case. 4. Facts - set out the relevant facts that were needed by the court to come to its opinion. The facts are the events that occurred prior to any court proceeding that led to the prosecution or civil lawsuit involved. 5. Prior Proceedings - set out how this case got to this point - prior proceedings refers to prior court action so essentially the question is what happened in the lower court. 6. Holding - this is the answer or answers the court gave to the issue or issues raised in the case - often the court will use the words “we hold....” but not always. If there is more than one issue in the case then there will be more than one holding. 7. Reasoning - this section will set out the reasons the court gave for reaching its holding or holdings in the case. The holding tells us what legal rules was applied while the reasoning answers the question why this legal rule was applied in this case. If there are two issues, there will be two parts of the reasoning - one for each issue 8. Disposition - what happened to this case on appeal - did the court affirm the lower court decision or did the court reverse the lower court and remand it (send it back) to the lower court for a new trial or entry of judgment? Selected Educational Terms Student Learning Outcomes – – – The student will learn, or be able to, “verb” “noun” For verb, use the Cognitive Domain For Noun, use the Knowledge Domain Information Literacy Stella Awards – bad information replicated on 114 websites Websites – 30 reputable websites on my Law Links Wikipedia – should students we using it for research? Active Learning – – Do students really have an 8 minute attention span? Keep them busy but employ higher order thinking tasks Rubrics or Checklists Rubrics is a scoring tool that lays out your expectations for an assignment Four parts of a standard rubric: – – – – A description of the task to be performed A scale of levels of achievement Dimensions of the assignment Descriptions of what constitutes each level of feedback Sample Rubric Grid Description of the Task Excellent Dimension 1 Dimension 2 Dimension 3 Dimension 4 Dimension 5 Dimension 6 Competent Needs Work Unacceptable