Welcome to Biological Anthro! Professor Janaki Natalie Parikh 1
advertisement

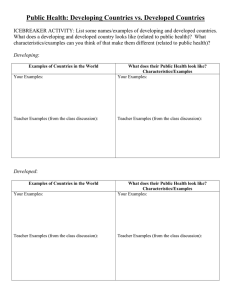
Welcome to Biological Anthro! Professor Janaki Natalie Parikh 1st name pronounced (Jon-uh-key) last name pronounced: (Puh-reekh) profjnp@gmail.com Today’s Agenda • Icebreaker & Introductions: (Note to Petitioners) • Go over syllabus/course outline • Intro lecture Icebreaker Activity Find someone who… – Can do hitch-hiker’s thumb – Has blood type “AB” or “O” – Can name 3 of the 4 types of teeth in our mouths – Can name a specific type of monkey & specific type of ape (descriptions don’t count, such as “gray fur”) – Can identify the type of genetic info that males receive only from their father Icebreaker Answers • Hitch-hikers? • Blood type “AB”s? “O”s? • 4 types of teeth? – Incisors, canines, premolars & molars • Specific type of monkey or ape? • Genetic info from dad to son(s)? • Y-chromosome DNA Interview & present a classmate Now, please interview a fellow classmate regarding: • Name (ask for last name too, I will be checking off roster) • Yr. of study & Course of Study (GWC skip) • Swap e-mail addresses & phone #s if comfortable) • Are they a tongue roller (in other words, can they do taco tongue?) Course Syllabus/Outline • Go over course outline • Recommendations: – put my email address in your address book – Slides are online, print them & bring to class – Books/slides are also on reserve in the library Intro Lecture • What is Anthropology? – Anthropos (Gk.):man – Logos (Gk.): word • Thus, the synthesis would be: Knowledge about mankind or modernized: the science of humankind • Broad definition that could apply to many fields, so what’s unique about anthro? Anthropology • Diversity: many diff’t ways of being human – Studying diversity: making sense of the complex & rich systems of meaning that make up culture • Holistic: what does that mean? – The whole of the human condition: past, present & future – Celebrating the beauty of diversity & human universals – This, of course, is a tall order! – Organized into subfields to manage such an all encompassing focus Anthro Subfields • Archaeology: human cultural diversity in the prehistoric past (midden) • Cultural: human cultural diversity in the present day • Linguistic: focus on lang. as pwr., issues of class, gender, race, sexual orientation w/ lang., not about the history & origins of language • Biological/Physical: human genetic variation, Primatology, human evolution Scientific epistemology • Epistemology: a specific way of acquiring/producing knowledge, a method of gaining knowledge • Science is an epistemology. Is it the only epistemology? • No, there are many difft ways: philosophy, religion, art, etc. • How is science unique as an epistemology? • Characteristics of science: • 1. empirical: based on systematic data collection – What do we call the system/method used? – Scientific method Characteristics (cont’d) • • • • 2. (exclusive ) focus on natural laws & processes Strong avoidance of supernatural realm 3. Addressing q’s of how vs. why? Traditionally has lmtd itself to describing mechanisms, excludes many important & critical q’s as a result • 4. Assumption based: ALL bodies of knowledge make assumptions! Science is not truly objective, neither are scientists, they are part of their cultural context • 5. Provisionality: knowledge is accepted conditionally (temporarily) • Occam’s (Ockham’s) Razor: Law of Parsimony, familiar? Science background (cont’d) • Simplest explanation is best, the one that requires the fewest assumptions • Ex: Newtonian physics, bright guy… • Many of his ideas were replaced, by whom? • Albert Einstein • Science does not prove anything, ideas are tested against avail. evidence, not to be proven, but to be disproved • If it fails to be disproved, it is accepted for the time being, what is it called then? Science • • • • A theory: an idea that has held up against rigorous testing If the theory holds up over time (repeated testing), it becomes? Scientific law: ex.: evolution by natural selection Collection of similarly focused theories, theoretical framework: scientific paradigm • Ex. Mendelian genetics, a scientific paradigm Creationism • • • • • The oxymoron of scientific creationism What is an oxymoron? Pairing concepts that seem mutually exclusive (contradictory) Ex: deafening silence, jumbo shrimp, or, affordable textbooks… Creationism may be an epistemology, but it is not a scientific one since it does not meet the characteristics/requirements of scientific epistemology Evolution as an idea in history • • • • • Antiquity: ancient Greece Plato: Eidos: an ideal type (perfect version) Not found in our world, where is it, then? In the heavens. On Earth we are imperfect copies His student, Aristotle challenged the idea. Suggested that truth is here in this wrld &should be studied in a systematic way, sound familiar? • Birth of scientific empiricism Biblical views of Earth’s Age • Middle Ages: Fixity of species: immutability of living things. Highly static view of nature • Fastfwd in time to 1600s-onward • John Lightfoot: calculations of the Bible to determine when the Earth was created: a date of approx. ~4000 B.C. • Makes the Earth how old? • Only ~6000 years old! • Archbishop Ussher: 9 a.m., Oct. 3rd. 4004 B.C.! • Ussher held a post @ Cambridge & this date happens to be the same as start of fall term, coincidence? You decide! Geologic Age of the Earth • • • • • According to mod. Science, how old is Earth? ~4.5 billion yrs old. How do we know? Geologic evidence, radiometric dating.. Theoretical framework from geology James Hutton: research in geology led him to formulate a geologic theory called uniformitarianism: • This idea was 1st published by a Persian scholar named Avicenna (1027) • Based on uniform processes, what does it mean to be uniform? Geologic Age of the Earth • Uniformitarianism: All the geologic processes on Earth today have been in existence since the beg. Of time & have shaped the Earth to look like it does today • Geologic Processes: • Wind, Rain, Erosion, plate tectonics, etc. • Given ample time, they can have a significant impact. • Key word, TIME! • Sir C. Lyell (Father of Geology) published Hutton’s theory in Principles of Geology • Prompted attempt to counter geolog. evidce being unearthed (‘cuse the pun ;-) & reconcile evidence w/ the Bible • Hence, Cuvier puts forth catastrophism • Sounds like the word? • Catastrophe, what’s a catastrophe? • Momentous tragic event, a disaster • Catastrophism: major disasters caused us to lose many species, particularly a hydraulic event, namely? • The Great Flood (Noah’s ark) • Prob’s: how does this account for changes in fossil forms over time, ex.: crocodile & geese predecessors • • http://chronicle.uchicago.edu/011101/supercroc.shtml http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/09/080926143908.htm • Also, doesn’t account for discovery of brand new species • • • http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/08/080804100258.htm http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/07/080728192930.htm http://species.asu.edu/2011_species02