ZOO 1010 Study Guide Chapter 3 Chapter 3 – Animal Architecture
advertisement

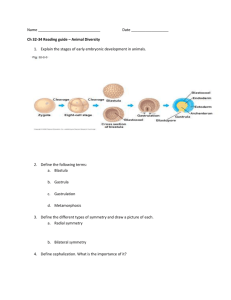
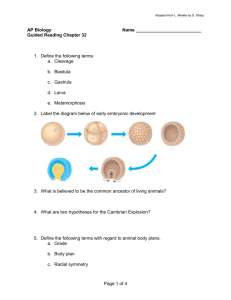
ZOO 1010 Study Guide Chapter 3 Chapter 3 – Animal Architecture 1. How are animal cells/tissues organized in terms of complexity? cellular level vs. cell-tissue level vs. tissue-organ vs. organ-system 2. Differentiate between radial and bilateral symmetry. 3. What terminology do we use to differentiate between different regions and/or directions around the animal body? 4. What are the developmental stages of an animal as it goes from zygote to adult? 5. How do we differentiate between radial and spiral cleavage? Regulative vs. mosaic development? Deuterostome vs. protostome? 6. How do we differentiate between an acoelomate, psuedocoelomate, and coelomate (eucoelomate) body cavity? Which basic groups of animals possess which? Which type of body cavity is more advantageous from an evolutionary standpoint and why? 7. What is a tissue? What are the four types of tissues? What are the basic characteristics of each tissue and their functions? What are examples of specialized cells comprising each of the tissues (to the extent they are covered in your textbook)? 8. What are the extracellular components of the animal body? 9. How does body size affect surface area vs. volume? What advantages/disadvantages may this relationship provide for animals? Key Terms – aboral, anterior, posterior, dorsal, ventral, medial, distal, proximal, frontal plane, sagittal plane, transverse plane, Bilateria, cephalization, zygote, cleavage, mosaic development, regulative development, homeotic genes, Hox genes, radial cleavage, spiral cleavage, ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm, blastula, blastocoel, gastrula, gastrocoel, parenchyma, histology, epithelium, collagen, ground substance, matrix, lymph, interstitial fluid, cartilage, neurons, neuroglia, intracellular space, axon, dendrites Note: This study guide may not be all inclusive of material covered. The student is responsible for learning all material covered in lecture and as expected as part of this course.