The Economic Perspective Chapter 1
advertisement

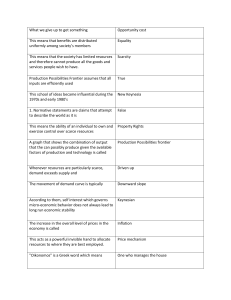
The Economic Perspective Chapter 1 Economic Problem • The problem is that, although your wants, or desires, are virtually unlimited, the resources available to satisfy these wants are scarce. Scarcity All resources are scarce Scarcity • Means limited goods and services • Restricts options and demands choices • Price > ZERO Rational Self-Interest • Means that individuals try to maximize the expected benefit achieved with a given cost or to minimize the expected cost of achieving a given benefit Making decisions at the margin • Margin: the cutoff point; decision making at the margin refers to deciding on one more or one less of something • Weighing and balancing of alternatives – Marginal benefit – Marginal cost – Benefits > Costs Scientific Method • Elements – Observation of real-world behavior and outcomes – Formulation of hypothesis – Testing of this explanation by comparing the outcomes of specific events to predict outcome – The acceptance, rejection, or modification of the hypothesis – The continued testing of the hypothesis against the facts. Microeconomics • Analyzes the individual components of the economy, such as the choices made by people, firms, and industries. • Markets – make possible the voluntary exchange of resources, goods and services; can take physical, electronic, and other forms. • Market prices – serve as signals that guide the allocation of resources Macroeconomics • Analyzes economic aggregates such as aggregate employment, output, growth, and inflation • Most important is GDP – Gross domestic product Normative Economics • A statement that represents an opinion, which cannot be proved or disproved • What ought to be • Ethical value judgments Positive Economics • A statement that can be proved or disproved by reference to facts • What is • Scientific portion Society’s Economizing Problem • The need to make choices because economic wants exceed economic means Scarce resources • Society has limited economic resources Resources • The inputs, or factors of production, used to produce the goods and services that people want resources • Also called factors of production Land • Includes all the natural resources used in the production process Labor • The physical and mental effort used to produce goods and services Labor - mental • Mental effort – Consists of the knowledge and skill people acquire to enhance their productivity Capital • The buildings, equipment, and human skill used to produce goods and services – Physical capital – Human capital Capital • Physical capital – Consists of factories, machines, tools, buildings, airports, highways, and other human creation Entrepreneurial Ability • Managerial and organizational skills needed to start a firm, combined with the willingness to take risks Functions of Entrepreneur • Entrepreneur takes the initiative in combining the resources of land, labor, and capital • The entrepreneur makes the strategic business decisions that set the course of an enterprise • Innovator • Risk bearer Entrepreneurs • Pick Anita Roddick William H. Gates Payments to Resources • Wages – Payment to resource owners for their labor • Interest – Payment to resource owners for the use of their capital • Rent – Payment to resource owners for the use of their natural resources. • Profits – The reward for entrepreneurial ability. Production Possibilities Frontier • Assumptions – Output is limited to two products: consumer goods and capital goods – Resources are FIXED in both quantity and quality during that period – Technology does not change – Full employment Production Possibilities Frontier • A curve showing alternative combinations of goods that can be produced when available resources are used fully and efficiently. Product A B C D E Consumer 0 1 2 3 4 Capital 10 9 7 4 0 Production Possibilities Frontier Consumer goods Points on line are efficient 0 D. A C Inefficient Unattainable B Production possibilities curve Capital Goods Production Possibilities Frontier • Efficient points – Any point found on the production possibilities frontier such as A and B • Inefficient points – Inside the curve • Unattainable – Outside the curve Economic growth • An increase in the economy’s ability to produce goods and services • An outward shift of the production possibilities frontier • Caused by – Changes in resource availability – Increases in capital stock – Technological change Economic Growth Caused by – Increases in capital stock – Technological change Economic Growth Consumer goods Shift in PPF 0 Production possibilities curve Capital Goods Economic Analysis • Fallacy of composition – What is true at the micro level is also true at the macro level • What is true for the individual is true for the whole • Fallacy of that association is causation – The incorrect idea that if two variables are associated in time, one must necessarily cause the other Economic Analysis • Secondary Effects – Unintended consequences of economic actions that may develop slowly over time as people react to events.