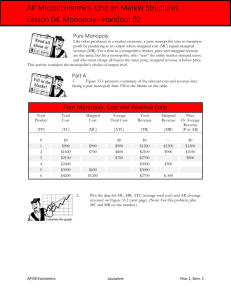
Monopoly A market with a single seller with a product that... differentiated from other products
advertisement

ECO 2023 Chapter 10: Pure Monopoly Monopoly A market with a single seller with a product that is differentiated from other products Characteristics: Single seller o Firm and industry are synonymous No close substitutes o Product is unique in that there are no close substitutes Price maker o Controls the total quantity supplied and thus has considerable control over price o Downward sloping demand curve o Can change price by changing supply Blocked entry o Barriers to entry keep competitors out of the market o Those barriers are Economic Technological Legal Nonprice competition o Standardized or differentiated Inelastic demand Created: M. Mari Fall 2007 Page 1 of 7 ECO 2023 Chapter 10: Pure Monopoly Barriers to Entry Any impediment that prevents new firms from entering an industry and competing on an equal basis with existing firms Types of barriers o Economies of Scale Declining average total cost with added firm size are extensive Long run average total cost will decline over a wide range of output Only a single large firm can achieve low average total costs Protects the firm from competitors Natural monopoly the market demand curve cuts the longrun ATC curve where average total costs are still declining o Legal Restrictions Patent A legal barriers to entry that grants its holder the exclusive right to sell a product for 20 years from the date the patent application is filed Innovation o The process of turning an invention into a marketable product Licenses Governments often confer monopoly status by awarding a single firm the exclusive right to supply a particular good or service o Control of Essential Resource Firms owns all sources of a resource ALCOA – aluminum DeBeers – diamonds Created: M. Mari Fall 2007 Page 2 of 7 ECO 2023 Chapter 10: Pure Monopoly Monopoly Demand Three assumptions o Patents, economies of scale or resource ownership secure our monopolist’s status o No unit of government regulates the firm o Single price monopolist, Demand curve o Downsloping demand curve o Quantity demanded increases as price decreases Implications of Demand Curve Marginal revenue is less than price o The downward sloping demand curve means that it can increase sales by charging a lower price o Marginal revenue is less than price for every level of output o Marginal revenue curve is below the demand curve o Marginal revenue is positive while total revenue is increasing. o When total revenue is decreasing, marginal revenue is negative Price Elastic Unit Elastic Inelastic Demand = Average Revenue Quantity Marginal Revenue Created: M. Mari Fall 2007 Page 3 of 7 ECO 2023 Chapter 10: Pure Monopoly Where demand is price elastic, marginal revenue is positive Therefore: TR as Price Where demand is price inelastic, marginal revenue is negative TR as Price Where demand is unit elastic, marginal revenue is zero, TR is at a maximum, neither increasing nor decreasing Price Maker o When monopolist decides on output level, he determines price. Elastic Region o Monopolist will never choose a price-quantity combination where price reductions cause total revenue to decrease Marginal revenue is NEGATIVE Example: Created: M. Mari Fall 2007 Page 4 of 7 ECO 2023 Chapter 10: Pure Monopoly Outp ut Price Total Revenue Marginal Revenue Average Total Cost PXQ MR ATC TC $ 100.00 $ 190.00 $ 190.00 0 Average Revenue $ 172.00 $ - 1 $ $ 162.00 Q Total Cost $ 162.00 162.00 $ 152.00 $ 304.00 $ 142.00 $ $ 135.00 426.00 $ 132.00 $ $ $ 113.33 528.00 $ $ 100.00 $ 122.00 $ 610.00 6 $ 112.00 $ 672.00 $ 91.67 7 $ 102.00 $ 714.00 $ 91.43 8 $ 92.00 $ 736.00 $ 93.75 $ 9 $ 82.00 $ $ 72.00 $ 720.00 $ 90.00 $ $ 97.78 Graphically: Created: M. Mari Fall 2007 Page 5 of 7 $ 128.00 $ 140.00 $ 122.00 $ 74.00 $ (14.00) 130.00 150.00 $1,030.00 The Firm’s Costs and Profit Maximization A firm that must find the profit maximizing price when the demand curve for its output slopes downward. The monopolist produces the quantity at which total revenue exceeds total cost by the greatest amount. Marginal revenue = marginal cost Short Run Profits 86.00 $ (142.00) $ $ 103.00 $ 110.00 $ 880.00 $ (18.00) 10 80.00 $ 750.00 2.00 738.00 $ $ (34.00) 70.00 $ 640.00 $ 22.00 $ 60.00 $ 550.00 $ 42.00 (28.00) 70.00 $ 470.00 $ 62.00 $ 80.00 $ 400.00 $ $ 94.00 90.00 $ 340.00 $ 82.00 5 TR - TC $ (100.00) $ 270.00 $ 102.00 4 MC $ $ 122.00 3 Profit or Loss $ $ 142.00 2 Marginal Cost $ (310.00) ECO 2023 Chapter 10: Pure Monopoly Price Profit Marginal Cost Average Total Cost P Demand = Average Revenue Q Marginal Revenue Where MR = MC Short Run Losses o If the price covers average variable cost, the firm will produce o If not, the firm will shut down at least in the short run Economic Effects of Monopoly o Long run efficiency in pure competition is P = MC = Minimum ATC o Monopoly MR < P, monopolist will sell smaller output at a higher price than pure competition An efficiency loss occurs because P > MC P > minimum ATC Created: M. Mari Fall 2007 Page 6 of 7 ECO 2023 Chapter 10: Pure Monopoly Long-Run Profit Maximization o If a monopoly is insulated from competition by high barriers that block new entry, economic profit can persist in the long run. Price Discrimination o Increasing profits by charging different groups of consumers different prices when the price differences are not justified by differences in production costs o Conditions for Price Discrimination o Demand must be downward sloping o At least to separate groups of consumers, each with a different price elasticity of demand o The firm must be able to charge each group a different price for essentially the same product. o The firm must be able to prevent those who pay the lower price from reselling the product to those who pay the higher price. o This firm maximizes profit by finding the price in each market that equates marginal revenue with marginal cost Created: M. Mari Fall 2007 Page 7 of 7