Thermal chemistry is study of the transfer of heat in
advertisement

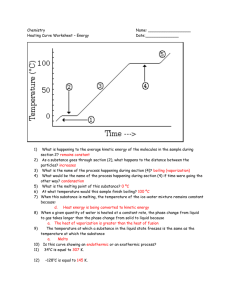
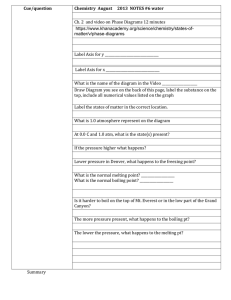
Thermal chemistry is study of the transfer of heat in chemical reactions and physical changes. Student will learn: 1. to read Phase diagrams 2. math calculations of energy for melting, freezing, vaporization, condensing or raising temperature of a compound or element. 3. how to read heating cooling curves Thermal Chemistry Phase: any part of a system that has uniform composition and properties. ( solid, liquid, gas) Overhead Fluid: gas or liquid: a substance that can flow and take shape of the container. Diffuse: ability to mix with other liquids or gases (p.364 food coloring, perfume) Vaporization: process - liquid or solid changes into a gas. “you have added energy and vaporized it” Evaporization: process - particles escape from the surface of a non boiling liquid and become gas. “naturally evaporated” Volatile liquids: liquids that evaporate readily “finger nail polish remover” Condensation: process which a gas becomes a liquid “ rain, water drops on out side of glass of cold drink” Boiling: conversion of a liquid to a gas within the liquid as well as the surface. Boiling Point: Temperature which vapor pressure of the liquid equals the atmospheric pressure. Freezing or solidification: physical change of liquid to a solid by removal of heat or energy Freezing Point: Temperature which liquid and solid have same average kinetic energy. Melting: physical change of a solid to a liquid by the addition of energy. Melting point: the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. Sublimation: change of a solid directly to a gas. “CO2.. Dry ice, Iodine, frost free freezer” Deposition: change of a gas directly to a solid. “ frost on grass or car windshield ” Phase Diagrams graph which shows conditions of phase changes Triple point = solid, liquid, gas coexist at equilibrium. Critical Temperature point = cannot exist as a liquid regardless of pressure. o The critical temperature point of water is 373.99 c. Above this temperature, water cannot be liquefied, no matter how much pressure is applied. Critical Pressure point = lowest pressure at which the substance can exist as liquid @ critical temp. The lowest pressure at which water can exist as a liquid is 217.75 atm @ the critical temperature point. Phase Diagram Describe all phase changes that would occur when heating the chemical from -80o to 20o at a constant pressure of 10atm. At room temperature what is the phase of this chemical? Phase Diagram What are the phase changes at 16atm from -100o to 40o and their corresponding temperatures? At room temperature what is the phase of this chemical? Phase Diagram Given a sample of this chemical, how would you phase change the liquid into a gas without changing the temperature? Where is the triple point? Where is the critical point? Thermal Chemistry study of transfer of heat in chemical reactions and physical changes. What is the difference? Temperature Heat Thermal energy Temperature: measurement of motion… measurement of kinetic energy of the molecules …. Wood… …. cold (vs) hot water ……. Fever of 105 Normally use a thermometer Heat: The transfer of thermal energy. The energy that ‘flows’ from higher Temperature to lower temperature. … standing beside the burning wood and feeling the warmth… Thermal energy = total energy of matter… measured in joules… Q = thermal energy Heat of Fusion: energy required to melt solid to a liquid Q = m Hf Q = energy M = mass Hf = heat of fusion Heat of Vaporization: energy required to vaporize a liquid Q = m Hv Q = energy m = mass Hv = heat of vapor 1. Calculate the amount of energy required to melt a small ice cube weighing 24 grams. 2. Calculate the amount of energy required to produce steam from 100 mL of water. 3. Find the molar heat of vaporization for a substance, given that 4.22 mol of the substance absorbs 32.8 kJ of energy when it changes from a liquid to a gas. 4. Aluminum is used in manufacturing Pepsi-cola cans. How much heat energy does the factory need to provide to melt the 3 grams of aluminum needed per can? The factory produces 3,000 cans per hour. How much energy is needed per hour? Aluminum’s melting point is 660 degrees Celsius. 5. Copper is vaporized so it may be infused onto a fabric for hospital use in fighting germs. Calculate the energy required for processing 5 grams of Copper. Copper melting point is 1083 degrees. 6. Zinc is used in making brass. Zinc melts at 420 degrees celsius. Calculate the energy needed to melt 150kg of Zinc. 7. The molar heat of vaporization of carbon disulfide is 28.4 KJ/mol at its normal boiling point of 45oC. How much energy is required to vaporize 12 grams of CS2 ? 8. Twenty three thousand two hundred an twenty nine Joules of energy was used to melt 85 grams of an unknown metal. Calculate its heat of fusion and determine if the metal was iron or lead or platinum. 9. The heat of fusion of a metal is 7.35 J/g at its freezing point of -39oC. Calculate the amount in grams of this solid metal that can be melted if 5500 J of energy are available. 10. Turning mercury into a vapor is not easy. But for some reason your evil boss wants it done. You are beginning to think he has diabolic plans to eliminate the employees. How much energy will be needed to accomplish this for 5 grams of mercury? Thermal chemistry is study of the transfer of heat in chemical reactions and physical changes. Student will learn: 1. Heat of Fusion math calculations of energy for melting or freezing a substance. 2. Heat of Vaporization math calculations of energy for vaporizing or condensing a substance. Calculate the energy required to turn 45mL of water into steam. Answer in Kj 0 of 30 Thermal chemistry is study of the transfer of heat in chemical reactions and physical changes. Student will learn: 1. math calculations of energy condensing or raising temperature of a compound or element. Q = m Cp t Substanc e Specific Heat J/gOC Aluminum 0.897 Copper 0.385 Gold 0.129 Iron 0.449 Lead 0.129 Magnesium 1.023 Mercury 0.140 Nickel 0.444 Titanium 0.523 Zinc 0.388 Water gas 2.02 Water liquid 4.18 Water solid 2.05 Specific Heat = amount of energy required to raise 1gram of substance by 1 degree Q = m Cp t Which requires the most heat to heat up? iron pipe or lead pipe Which requires least amount of heat to heat up? magnesium or gold Which requires least amount of heat to heat up? Fe, Zn, Ti WS17.2 1. How much heat is needed to raise the temperature of a 20g aluminum Pepsi-cola can 35 degrees? 2. Calculate the heat lost from a 5g copper o o penny if cooled from 25 c to 3 c in the freezer. 3. Calculate the mass of water that uses 2508J of energy in raising its temperature from 80oC to 100oC. 4. Calculate the temperature rise if 224.25J of heat energy was added to a 30gram ice cube. 5. How much energy is needed to raise the temperature of a gold necklace with a mass 83.0g from 15oC to 39oC? 6. If 66kj of heat energy is absorbed by 9.0kg of nickel that has an initial temperature of 25oC, what will be the final temperature after heating? 7. Calculate the specific heat of this unknown metal that absorbed 450.J of energy, weighed 10 grams, and the temperature increased 100oC. Identify this metal. 8. How much energy is needed to raise the temperature 30 degrees of 908.0 kg (2 tons) of Zinc? 9. Calculate the amount of energy to be extracted to cool down a 2 ton solid iron turbine engine from 150oC to 80oC. 10. Calculate how much more energy it would take to increase 150oC steam to 400oC steam having a mass of 200grams. Thermal chemistry is study of the transfer of heat in chemical reactions and physical changes. Student will learn: 1. math calculations of energy condensing or raising temperature of a compound or element. Q = m Cp t Ws. 17.3 3.5Kj of heat are added to a 28.2 gram sample of Fe @20oC. Calculate final Temperature of the FE. 0 of 30 * HEATING CURVES VS COOLING CURVES HANDOUT CURVE SHEET Thermal chemistry is study of the transfer of heat in chemical reactions and physical changes. Student will learn: 1. how to read heating cooling curves Label : 60oc 50oc 40oc 30oc 20oc 10oc 0c -10oc -20oc -30oc 0 kj 25 kj 50 kj 75 kj 100kj 125kj 150kj 175kj 200kj 225kj Heating-Cooling curve ( Enthalpy of Fusion and Vaporization 250kj Theory pt.1: The quantity of heat absorbed to melt a solid = the quantity of heat released to solidify the liquid. 60oc 50oc 40oc 30oc 20oc 10oc 0c -10oc -20oc -30oc 0 kj 25 kj 50 kj 75 kj 100kj 125kj 150kj 175kj 200kj 225kj 250kj Theory pt.2: The quantity of heat absorbed to vaporize a liquid = the quantity of heat released to condensate the vapor. 60oc 50oc 40oc 30oc 20oc 10oc 0c -10oc -20oc -30oc 0 kj 25 kj 50 kj 75 kj 100kj 125kj 150kj 175kj 200kj 225kj 250kj Theory pt.3: All solids absorb heat as they melt . This causes a phase change rather than a temperature change. 60oc 50oc 40oc 30oc 20oc 10oc 0c -10oc -20oc -30oc 0 kj 25 kj 50 kj 75 kj 100kj 125kj 150kj 175kj 200kj 225kj 250kj Ex) ice melting: Temperature remains constant until all ice has melted….. The temperature of water will increase only after all ice has melted. Ex) boiling water. 1. Which segments on the curve represent constant temperature? 2. What is the boiling point of this substance? 3. How much energy is needed for vaporization? 4. If this chart is based on 2 grams of substance how much energy is needed to melt 10 grams of the substance. 60oc 50oc 40oc 30oc 20oc 10oc 0c -10oc -20oc -30oc 0 kj 25 kj 50 kj 75 kj 100kj 125kj 150kj 175kj 200kj 225kj 250kj 1. What temperatures do phase changes occur? 2. Which portion represents an decrease in heat absorbed while kinetic energy remains constant? 3. What is the quantity of the Heat of Vaporization? 4. What temperature is condensation? TIME 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 29 30 32 34 36 TEMPERATURE 25 30 35 40 45 45 45 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 75 75 75 80 85 What is the melting Temperature? How many minutes does this take to melt? What is the boiling point? Ws. 17.4 Use the chart above to complete the following essay At the start of the experiment, point A and point B the substance is a ___________________. Its melting point in degrees is ______________. It takes ________ minutes for this substance to melt. Point D is called the Heat of Fusion. The mathematical formula for point D is _________________. Point D is a phase change. The ____________________stays constant during a phase change. The temperature begins to rise during the liquid phase for ______ minutes. The boiling temperature for this substance is _______. It takes _________minutes and _________ joules of energy to vaporize this substance from its liquid phase. The math formula for the slant lines at B, F, and J is ____________________? This substance is a___________ at point J. At point K the temperature may continue to rise that is one reason why steam will burn you much quicker than boiling liquids. When gaseous substances are cooled, energy is released. The cooling curve will be the opposite of the heating curve. Energy is released as the substance changes phases from _______ to _______________ and again when it changes from ____________ to __________________. Segments _____ and _____ on the cooling curve represent fix points on a thermometer. If the chart above is based on 4 grams of Gold, how much energy does it take to melt 12 grams of Gold? ___________. How long would it take to melt 4 grams? _____________. How long it would it probably take to melt 12 grams? ________________________. When water freezes, each gram loses an amount of heat equal to its heat of 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Vaporization Sublimation Reaction Melting point Freezing point Fusion The phase change represented by the following reaction is… I2(s) I2(g) 1. 2. 3. 4. Sublimation Condensation Melting boiling Thermal chemistry is study of the transfer of heat in chemical reactions and physical changes. Student will learn: 1. how to read heating cooling curves