Document 17624703
advertisement

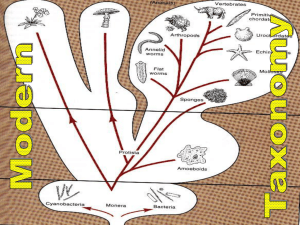
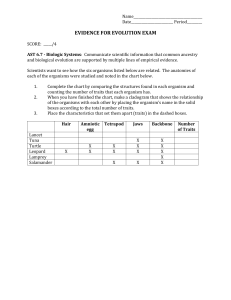
• Taxonomy: grouping life according to shared traits – not just physical traits anymore • Phylogeny: Evolutionary history of an organism • Morphology – Defined: studying the form and structure of organisms – Comparing the morphology (traits) of different species shows similarities and/or differences Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Morphology Shows Non-Relationships Also! • Homologous structures – Defined: body parts that have a similar structure, but different function – Comparing homologous structures of different organisms can show relationships • Conclusion: similar structures shows relationships • Biochemical evidence – Comparing DNA, RNA, amino acids, & proteins – Similarities and differences can be found • DNA mutates at known rates – More time that has passed = more mutations • Conclusion: Organisms with similar DNA are more closely related • Chromosome Evidence – Chromosomes of different species are examined for similarities and differences (size, shape, gene sequences) – Ex Above: human, orangutan, gorilla, pygmy chimp • Conclusion: related organisms have chromosome similarities • Embryo Development – Blastula (ball of cells) forms early in development – Blastopore (small indentation) begins to form digestive system – Blastopore develops into the anus of some animals and mouth of others • Conclusion: Similar development indicates relationship Which two organisms are more closely related to one another? In both humans and starfish, the blastopore becomes our anus…. In insects, the blastopore becomes their mouth. • Defined: branching diagram used to show evolutionary relationships – Try to group life according to similar traits • Shows phylogeny • Q: List 2 characteristics of a salamander. • Q: From the diagram, which organism is most closely related to the Chimp? Silly example of a cladogram Cladogram Practice • 1) What does an amphibian & crocodile have in common? Vertebrae, Bony skeleton, Four limbs • 2) List the traits of a ray-finned fish. Bony skeleton, has vertebrae Review 1) 2) 3) 4) What is morphology and how can it be used to help classify organisms? What are homologous structures and how is it used to help classification? How can molecular evidence like DNA and chromosomes be used to classify life? What does it mean if two different organisms develop along similar pattern? Different patterns? Examine the cladogram to answer the questions: 5) List the traits of organism 4. 6) What does organism 2 and 5 have in common? 7) Which trait separates organism 1 from the rest?