Terminology
advertisement

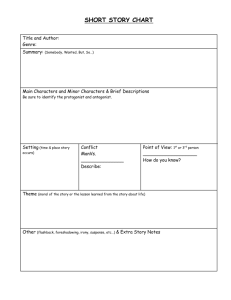
Terminology The conflict causes the action to rise Theme The general idea or insight that is revealed through the story. Examples: Friendship, betrayal, hate, greed, guilt, fate Prose Most writing that is not poetry, drama, or song. The ordinary form of written language. Dialogue A conversation between two characters. Plot A series of events that begins with a conflict and ends with a solution. Point of View 1st person-uses “I’’ 3rd person limited- is told by a narrator that can see the action, but can only tell the thoughts of one character. 3rd person omniscient- an “all-seeing” narrator Allusion A reference to an event, book, myth, place, or work of art The Bible Satire A type of writing that ridicules the shortcomings of people or institutions in an attempt to bring about a change. Narrative A story told in fiction, nonfiction, poetry, and drama. Parts of the plot The The The The The exposition rising action climax falling action resolution Foreshadowing Clues that suggest the events that are going to occur. In “The Monkey’s Paw” Herbert sees simian faces in the fire which suggest the doom to come. The CONFLICT... Can be Internal or external Characterization The method in which the author creates the characters. There are two main types: direct and indirect. Four kinds of conflict Man Man Man Man vs. vs. vs. vs. Man Nature Self Society Genre A category or type of literature. Indirect Characterization When the author shows the reader the character’s traits through their actions, or the actions and words of other characters. Example: Morgan laughs at yet another one of Marti’s funny jokes. Atmosphere/Mood The feeling created in the reader by the author through the literature. …”horror paralyzed him, as he stared between his legs at that terrible length of street far beneath him…” -Contents of the Dead Man’s Pockets Setting The time and place in which the story occurs. Imagery A word or phrase that appeals to one or more of the five senses. “The air was a mix of apples and cinnamon.” Vernacular The language spoken by the people who live in a particular locality. Aphorism A brief, cleverly worded statement that makes a wise observation about life. Ex. “Fish and visitors smell after three days.” Denotation A word’s dictionary definition. Anecdote A brief story, told to illustrate a point or serve as an example of something. Stream of Consciousness A style of writing that portrays the inner workings of a character’s mind. Ex. Catcher in the Rye Parallelism The repetition of words or phrases that have similar grammatical structures. Dramatic Irony Information that the audience is aware of, is withheld from the characters. Example: In “The Invalid’s Story” by Mark Twain, the protagonist thinks that he smells a dead body, but the readers know that it is just cheese. Analogy A comparison made between two things to show how they are alike. Flashback A scene that interrupts the normal chronological sequence of events in a story to depict something that happened at an earlier time. Connotation The associations and emotional overtones that have become attached to a word or phrase, in addition to its strict dictionary definition. Magic Realism A genre developed in Latin America that juxtaposes the everyday with the marvelous or magical. Idiom A phrase that is not logical in its literal meaning. Ex. It’s raining cats and dogs. Symbol An object or idea that stands for something other than itself. Example: The stars on the American flag stand for states. Fiction is prose writing that tells about imaginary characters and events. Suspense Is when the author creates tension in the story. Will he score the winning goal? Parody A work that makes fun of another work by imitating some aspect of the writer’s style. Ex. Weird Al Yankovich: “Eat It!” Michael Jackson’s “Beat It” Antagonist The character who opposes the protagonist. Ex. The Green Goblin Situational Irony A difference between what the characters or readers expect to happen and what really happens. “So they disarmed this bomb, huh?” Direct characterization When the author tells the reader about the character in a direct manner. Example: Shirley is a mean girl. Protagonist The main character in a work of fiction-the character readers would like to see succeed. Ex. Spiderman Catalog A group or listing of items or images; often used in poetry. There are two types of characters: Static -the character stays the same Dynamic-the character grows,changes, or learns. Tone It is like mood, but all encompassing. The overall attitude of the author, the connotation of the words chosen, the setting, the motifs, etc. Irony A contrast between what is and what seems to be. The are three kinds: Verbal Situational Dramatic Allegory A story or poem in which characters, setting, and events stand for other people or events or for abstract ideas or qualities. Motif A recurring structure, contrast, or literary devices that can help to develop and inform the piece’s major theme Archetype An original or fundamental imaginative pattern that is repeated through the ages. It can be a plot, an event, a character, a setting, or an object. The plot of selling one’s soul to the devil Verbal Irony Words are used to suggest the opposite of what is meant. In Shakespeare’s “Julius Caesar” Antony calls Brutus an “honorable man” when, in fact, he wants the audience to think the opposite.