The Activity Series
advertisement

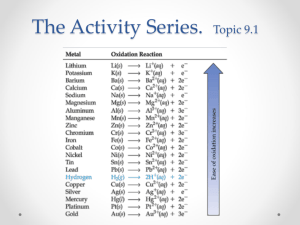
The Activity Series • ranks metals according to the ease they undergo oxidation o higher up metals are more reactive • displace those lower down from a solution o notice hydrogen in the series • metals above H will react in weak acids • metals below will not react with weak acids • the most reactive metal ends up as an ion and then reacts to form a new compound o Zn + CuSO4 • Zn is more reactive than Cu • Zn is oxidized (goes from 0 to +2) and then bonds with the -2 SO4 • Zn + CuSO4 Cu + ZnSO4 o Ni + 2AgNO3 2Ag + Ni(NO3)2 • Ni is more reactive than Ag • Ni is oxidized (goes from 0 to +2) and then bonds with the -1 NO3 o Ag + Zn(NO3)2 Ag + Zn (NO3)2 • Zn is more reactive than Ag • no reaction oZn will stay a 2+ ion and remain bonded to the 1- nitrate o Mg + H+ ? • Mg is more reactive than H obecomes an ion oMg + 2 H+ H2 + Mg2+ o Na+ + Al ? • Na is more reactive that Al • no reaction, Na+ will remain a ion Nonmetals • Which can occur? • Cl2 + 2I- I2 + 2 ClYes • I2 + 2 Cl- No • Consider the following reactions of three unknown metals X, Y and Z. 2XNO3(aq) + Y(s) → 2X(s) + Y(NO3)2(aq) Y(NO3)2(aq) + Z(s) → No reaction 2XNO3(aq) + Z(s) → 2X(s) + Z(NO3)2(aq) What is the order of increasing reactivity of the metals (least reactive first)? X < Z < Y Watch These Reactions! Combination (Synthesis) Reactions • a chemical change in which two or more substances react to form a single new substance • the general form is A + X AX o 2Cu(s) + S(s) Cu2S(s) o 2Fe(s) + 3S(s) Fe2S3(s) o 2K(s) + Cl2(g) 2KCl Decomposition Reactions • a chemical change in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simple products. • the general form is AX A + X o HgO(s) → • 2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l) + O2(g) o Zn(ClO3)2 ZnCl2 + 3O2 electricity o H2O(l) → ? • H2O(l) • 2H2O(l) → → H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2(g) + O2(g) Single Replacement Reactions • a chemical change in which one element replaces a second element in a compound o metal will replace a metal, or a nonmetal will replace a nonmetal o general form is A + BX AX + B o Zn (s) + HCl (aq) ? (Zn is +2) • Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) • Zn more reactive that H so is oxidized (0 to +2) and bonds with the negative Cl • Al + Fe2O3 ? o aluminum more reactive, will become and ion, and will replace iron(III) o 2Al + Fe2O3 2Fe + Al2O3 • Cl2 + NaI ? o Cl more reactive that I, will become an ion and replace I o Cl2 + 2NaI 2 NaCl + I2 Double Replacement Reactions • an exchange of positive ions between two chemicals • general form is AX + BY BX + AY • reaction occurred if a gas, a precipitate, or water is formed • CuSO4 + Na2CO3 Na2SO4 + CuCO3 • NaOH + CuSO4 ? o the Na+ and Cu2+ switch places. o Na+ combines with SO42- to form Na2SO4. o Cu2+ combines with OH- to form Cu(OH)2 o NaOH + CuSO4 Na2SO4 + Cu(OH)2 o 2NaOH + CuSO4 Na2SO4 + Cu(OH)2 • Na2CO3 + HCl ? o Na+1 combines with Cl-1 to form NaCl o H+ combines with CO32- to form H2CO3 o Na2CO3 + 2HCl 2NaCl + H2CO3 Combustion Reaction • a type of combination reaction where a substance reacts with oxygen • often the burning of a fuel that produces carbon dioxide, water, light, and heat • CH4 + O2 ? o CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O o CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O Practice • Classify each of the following as to type: • H2 + Cl2 2HCl o combination • Ca + 2H2O Ca(OH)2 + H2 o single replacement Practice • 2CO + O2 2CO2 o combination and combustion • 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 o decomposition Practice • FeS + 2HCl FeCl2 + H2S o double replacement • Zn + HCl ? o single replacement o Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2