Final Exam 2009-2010 Study Guide
advertisement

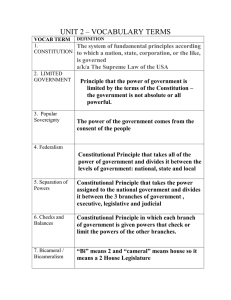
Final Exam 2009-2010 Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What is the indirect method we use to elect the President? The Electoral College How may Senators end a filibuster? 3/5 of the Senate What are the five consumer rights? Redress, choice, informed, safe product, heard What is a pocket veto? Ignore a bill for ten days and it is automatically vetoed Who are the people who start new businesses and introduce new products? entrepreneurs What is the Federal Reserve System? It’s the central bank of the U.S. What are the three qualifications to be a U.S. president? 35 yrs old, 14 yr. resident, native-born citizen What do police need to prove in order to obtain a search warrant? Probable cause What is fiscal policy? Fed governments use of spending & taxing policies to affect overall business activity 10. What is labor? Human effort directed toward producing goods and services 11. What is scarcity? Not having enough resources to produce all of the things we would like to have 12. What is consumer sovereignty? The role of the consumer as the ruler of the market, determining what products will produced 13. What is the major policy-making group of the Fed? FOMC 14. What is another name for the “necessary and proper” clause? Elastic clause 15. What are public goods? Economic goods that are consumed collectively, such as highways and national defense 16. What are the resources needed to produce goods and services called? Factors of production 17. What group of people approve presidential appointments? Senate 18. What is a subpoena? Court document requiring people to appear in court 19. What role is the president acting in when he greets kings, queens, and foreign leaders called? Head of State 20. What is the job of an appeals court? Review the lower court case to determine if there were errors 21. What are the rights of the accused? Due process, fair trial, lawyer, not to testify against oneself, no double jeopardy, hear & question all witnesses 22. What jurisdiction does district courts have? original 23. What Supreme Court case claimed the power of judicial review? Marbury v. Madison 24. What is the name of the role of the president when he is commanding the military? Commander in Chief 25. What is the study of how we make decisions in a world where resources are limited? economics 26. In Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, KS the Supreme Court ruled that segregation was a violation of the equal protection clause in which amendment? 14th Amendment 27. What is line-item veto? The ability of a governor to veto parts of a bill 28. What role is the most important of a U.S. president? Chief Executive 29. What do magistrates do? Handle most court documents and minor cases 30. What do financial institutions charge for loans? interest 31. Which federal courts are lawsuits and trials begun? District court 32. All together, what are the agencies and employees of the executive branch called? bureaucracy 33. Who manages the Fed? Board of Governors 34. Which amendment protects discrimination and you rights as a citizen? 14th 35. Who is the person who USUALLY is in charge of the U.S. Senate? President pro-tempore 36. What is crime? An act that breaks a law and causes harm to people or society in general 37. What is a free market economy? A system where the people own most, if not all of the means of production and decide how to use them, with little government interference 38. Buying U.S. bonds is a way the Fed stimulates the economy. 39. What are “wants”? things people would like to have 40. What is a command economy? Government run economy, with little consumer choice 41. What are civil disputes? Disputes between people or groups of people in which no criminal laws have been broken Final Exam 2009-2010 Study Guide 42. What type of financial institution offers full banking service? Commercial banks 43. What are standing committees? Permanent committees of Congress that continue their work from session to session 44. What are the three questions a society must ask when facing scarcity? What, for whom and how to produce 45. What are natural resources? Gifts of nature that make production possible 46. What are concurrent powers? Powers shared between the federal and state governments 47. What is a juvenile delinquent? A child or teenager who commits a serious crime or repeatedly breaks the law 48. What are anti-trust laws? Legislation to prevent new monopolies from forming and police those that already exist 49. Who are the owners of a corporation? stockholders 50. What is a circuit? The area of jurisdiction of a federal court of appeals 51. What is a sales tax? Tax levied on a product at the time of sale 52. What is a budget deficit? Where the government spends more than it collects 53. Who is the leader of the House of Representatives? Speaker of the House 54. What is monetary policy? Policy that involves changing the rate of growth of the money supply in circulation in order to affect the cost and availability of credit 55. What does the president do in the Economic Leader role? Watch over the U.S. economy and make decisions accordingly 56. Who makes the decisions in a command economy? The government 57. What happens at an arraignment? The person hears the charges against them and they make a plea of guilty or not guilty 58. What is the FDIC? Federal agency that insures individual accounts in financial institutions for up $100,000 59. What Article in the Constitution created the federal court system? Article III 60. In civil cases, what is the person called that is being sued? defendant 61. What is a county? Normally the largest territorial and political subdivision of a state 62. What is judicial review? The power of the S.C. to say whether any federal, state or local law or government action goes against the Constitution 63. What is capital? Previously manufactured goods used to make other goods and services 64. What personality trait do employers most look for? A good work ethic 65. What is remand? To send a case back to a lower court to be tried again 66. Who was John Marshall? The Chief Justice of the S.C. who established judicial review 67. Congress cannot vote to override a Supreme Court ruling. 68. What is the clearest statement of the administration’s plans and goals for the upcoming year? The federal budget 69. What powers are outlined in the 10th Amendment? Powers that belong to the states and the people 70. What does the 5th Amendment protect? (what rights) rights of the accused 71. What are incentives? Reward offered to try to persuade people to take certain economic actions 72. What jurisdiction does appeals courts have? appellate 73. What is bicameral? Two house legislature 74. What is foreign policy? A nation’s overall plan in dealing with other nations 75. What is the measure of the U.S. economy called? Gross Domestic Product 76. The General Assembly is to the state of Virginia, as ____ is to the U.S. government. Congress 77. What is the supremacy clause? The U.S. Constitution and laws Congress makes are the supreme law of the land 78. What is interest? Payment people receive when they lend money or allow someone else to use their money 79. What are stocks? Ownership share of a corporation Final Exam 2009-2010 Study Guide 80. What are the ways to self assess when selecting a career? Try new things, what are your talents, interests 81. What kind of court handles most misdemeanors and less serious crimes? General district court 82. What is person filing a lawsuit called? plaintiff 83. What is opportunity cost? The cost of the next best alternative use of time and money when choosing to do one thing rather than another 84. What are felonies? Serious crimes with serious consequences 85. What is a partnership? Two or more owners of a business 86. What is competition? The struggle that goes on between buyers and sellers to get the best products at the lowest prices 87. By _____the Supreme Court may decide if a law is constitutional. Judicial review 88. What is a budget? A plan for making and spending money 89. What are constituents? A person from a legislator’s district 90. What is a federal system? The sharing of power between the central and state governments 91. What is the basic goal of foreign policy? National defense 92. What are the four factors of production? Capital, human resources(labor), natural resources and entrepreneurship 93. How are each state’s electoral votes determined? The number of senators and representatives per state 94. How does the government work to maintain competition? Support business start ups, anti-trust laws 95. How long do Federal judges and Supreme Courts Justices serve? life Know these terms: Standing committee Concurrent powers Executive branch Federal system probable cause Felony General Assembly Consumer sovereignty Law of demand Profit Electoral college Veto conference committee reserved powers judicial branch county misdemeanor elector Board of Supervisors public goods fiscal policy proprietorship scarcity appeals expressed powers legislative branch due process of law apportion Governor Congress incentive law of supply monetary policy cabinet Miranda v. Arizona Short Answer: Academic – 1. What are the 5 characteristics of the U.S. economy? (list and explain/describe) Free Market, competition, Profit Motive, consumer sovereignty, Private property Honors1. How a bill becomes a law 2. Concurrent vs. Reserved Powers (be able to provide examples) 3. Executive roles of the president and governors (be able to provide examples) 4. The federal court system (be able to provide examples) Final Exam 2009-2010 Study Guide 5. What is scarcity and how does it relate to our wants, needs and the study of economics?