Early Modern Global Interactions 1450 CE- 1750 CE
advertisement

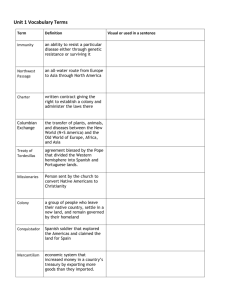
Early Modern Global Interactions 1450 CE- 1750 CE Summary • Starting with Prince Henry, Europeans are going to travel the world & be in everybody’s business. • This is going to make them incredibly wealthy & build them huge empires. • Along with this, comes disease, slavery, & horrible conditions for Native Americans. • There are also huge land empires from the Ottomans & Russians over to the Chinese. • The Columbian Exchange is arguably the most important thing ever. THE AP LOVE IT. They ask about it all the time. Count on a question about the COLUMBIAN EXCHANGE. Geography Key Concept 4.1: Globalizing Networks of Communication & Exchange Global exploration changes EVERYTHING. Trade, empire, migration, diets, disease… This is the first time we have dealt with a connected planet. Key Concept 4.1: Globalizing Networks of Communication & Exchange The Mariners Columbus Voyages across the Atlantic intiated the Spanish Colonization of the New World. Zhenghe Commaned expeditionary voyages to SE Asia, South Asia, Western Asia, & East Africa. Prince Henry (“The Navigator”) Regarded as the main initiator of the Age of Discoveries. Da Gama First European to reach India by sea, opening the way for an age of global imperialism. Key Concept 4.1: Globalizing Networks of Communication & Exchange Technology that Made it Possible • Astrolabe • Maps • Wind Patterns • Caravels – Small, highly maneuverable sailing ship (Portuguese) – Developed to explore along the West African Coast & into the Atlantic Ocean Key Concept 4.1: Globalizing Networks of Communication & Exchange Global Circulation of Goods • Facilitated by royal chartered European monopoly companies • Took silver from Spanish colonies in the Americas to purchase Asian goods for the Atlantic markets • Regional markets continued to flourish in AfroEurasia Key Concept 4.1: Globalizing Networks of Communication & Exchange New connections between the Eastern & Western hemispheres resulted in the COLUMBIAN EXCHANGE Key Concept 4.1: Globalizing Networks of Communication & Exchange • • • • • Global Circulation of Goods European merchants’ role was to transport goods from one Asian country to another. Joint stock companies competed against each other for global trade. Mercantilism- government control of foreign trade insures the military safety of the country, favorable balance of trade required Atlantic System= Africa -> Americas -> Europe -> Africa • Middle Passage (Africa -> Americas)= Slave Trade Columbian Exchange • From New World- Corn, potatoes, tomatoes, cacao • From Old World- Livestock, disease, sugar, grains Key Concept 4.1: Globalizing Networks of Communication & Exchange • • • • Impact of Interaction- On Religion Islam spread to Afro-Eurasia • By 1500 CE the rift in Islam is politically solidified by the conflict b/t Sunni Ottomans & Shia Safavids Christianity spread around the world • As it spread it diversified • Reformation = Protestant & Catholic Buddhism continued to spread to SE & E Asia Syncretic & new forms of religion • Vodun (Caribbean) • Cult of Saints (South America) • Sikhism (South Asia Key Concept 4.1: Globalizing Networks of Communication & Exchange Impact of PROFITS Innovations in Visual & Literacy expanded by Performing Arts popular authors • Renaissance (Europe) • Shakespeare (Europe) • Miniatures (Persia) • Wood Block Printing (Japan) • Codices (Latin America) • Cervantes (Europe) • Sundiata (Mali) • Journey to the West (Japan) • Kabuki (Japan) Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production The global demand for raw materials & finished goods expanded requiring corresponding increases in peasant labor & production. Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production Peasant Labor Increased Coerced Labor • Frontiermen (fur traders) • The biggest change in labor set out to settle Siberia, history (to this point) is the Russia transatlantic slave trade • British exports of cotton textiles to Europe increased • Chinese silk production increased • Cash crops grown on plantations led to huge increase in slavery & production of raw materials Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production Range of Coerced Labor used in the European Colonies • Spanish use of Inca Mita – Spanish system of subjugation of Inca – System of labor for the greater – In reality, the crown used labor to mine silver good Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production Range of Coerced Labor used in the European Colonies • Ecomienda/Hacienda System – In theory, Spanish colonial system where the Spaniard would receive labor from locals in return for teaching them Spanish & Catholicism Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production Range of Coerced Labor used in the European Colonies • Indentured Servitude – Temporary labor that is used to pay off a debt incurred by the servant until the debt is paid Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production Range of Coerced Labor used in the European Colonies • Chattel Slavery – People are personal property to be bought & sold – The original form of slavery Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production New Hierarchies- Elites New Existing Grew from widening global Had to deal with growing economic opportunities & power of absolute imperial conquests monarchies • Manchus in China • Mughal Zamindars • Spanish Creoles • Euro Nobility • Entrepreneur • Daimyo Japan Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production New Hierarchies- Gender & Family Roles Gender Family European men depended Smaller family size in on SE Asian Women Europe (The traditional merchants of the region) Key Concept 4.2: New Forms of Social Organization & Modes of Production New Hierarchies- Racial Mestizo = European + Native American Mulatto = European + African American Creole = Spaniard + Americans Key Concept 4.3: State Consolidation & Imperial Expansion This focuses on one thing… POWER Key Concept 4.3: State Consolidation & Imperial Expansion Maintaining Power The people in charge used many different ways to maintain that power: Arts • Architecture, Court literature Religion • Divine Right (Euro), Human Sacrifice Treatment of Subjects • Ottoman Dhimmi, Manchus in China Bureaucracy • Ottoman Devshirme • Chinese Civil Service Exam Key Concept 4.3: State Consolidation & Imperial Expansion Who Has the Power? Land Empires Maritime Empires Manchus Portuguese Mughals Spanish Ottomans French Russians British Key Concept 4.3: State Consolidation & Imperial Expansion Competing for POWER For Trade Routes • Ottomans v. Europeans • Piracy (Caribbean) State Rivalries • 30 Years War (Europe) • Ottomans v. Safavid (Middle East) Local Resistance • Peasant Uprisings (Europe) • Samurari Revolts (Japan)