CHAPTER 24: Industrialization and Imperialism: The Making of the... 1) What were the key causes of European expansion during the... 2) What were key aspects of imperialism?
advertisement

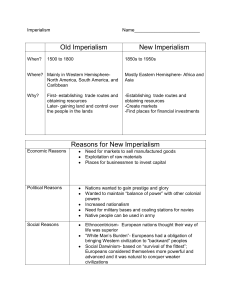
CHAPTER 24: Industrialization and Imperialism: The Making of the European Order 1) What were the key causes of European expansion during the pre-industrial era? 2) What were key aspects of imperialism? 3) When was the shift from pre-industrial to industrial imperialism? 4) What were the goals of Directors of the Dutch and British East India Companies? What were they not necessarily concerned with? 5) How were the 18th century land empires in Asia accumulated? How was public and private effort involved? 6) What is the earliest example of an overseas colony built largely through the initiative of company agents? 7) How did the Dutch East Indie Company relate to the Sultan of Mataram in the 1620s? 8) How did the Dutch get total control of Java? 9) Compare the British East Indie Company incursion into India with that of the Dutch East Indie Company in Java. How were they similar? How were they different? 10) What was significant about the Battle of Plassey? 11) Who was Robert Clive? 12) What did the British takeover from French influence after the Battle of Plassey? 13) How did the Fall of the Mughal Empire effect British colonization in India? 14) What were the administrative centers of the British East India Company? 15) In what ways were the Indian princes handicapped when defending their kingdoms against the British? 16) For what reasons was India known as the pivot of the great British Empire? 17) What was the impact of colonialism on the Indian and Javanese indigenous social systems prior to 1850? 18) Describe the social, sexual, and romantic relations between the Europeans and their colonial subjects in Java and India prior to 1850? 19) Who were nabobs? How did they achieve their wealth? 20) What did Lord Cornwallis do in India in the 1790s? 21) What English religious group was critical to the social reform movement in the British Empire in the early 19th century? Why? 22) What was Utilitarianism? Who were Jeremy Bentham and James Mills? 23) Which colonial power granted citizenship to their educated subjects? Why? 24) By which decade had most of Africa, Asia, and the Pacific been colonized or strongly influenced by the European powers? 25) Which European nation dominated sea trade during the first half of the 19th century? 26) What was Spain’s role in colonialism after 1870? The United States? Belgium? Germany? 27) How did competitive colonialism relate to militarism in Europe? 28) Specifically, what were the factors that motivated Europeans to expand in the late 19th century? 29) How did public opinion grow to become a major factor in foreign policy? 30) Describe general resistance to colonial rule in Asia and Africa. 31) By 1914 only one African nation had successfully resisted colonization. Which one? 32) What was Isandhlwana? 33) Define Tropical Dependencies 34) Define White Dominion 35) What type of colony was South Africa prior to 1902? 36) What strategies did the Europeans use to maintain control of tropical dependencies? 37) How did colonial educational systems in Africa, Java, and India compare? 38) What demographic factors caused tensions colonizers and African and Asian middle classes? 39) What was the goal of head and hut taxes that could be paid in commodities? 40) What products did not increase in production as a result of colonialism? 41) What happened to internal economies in the European colonies? 42) How were South Africa and Australia similar as colonies? 43) What were the results of the annexation of the Boer colony by the British in 1802? 44) What republic did the Boers found in the 1850s? 45) Specifically, how were the Maoris impacted by contact with the Europeans in the 1790s? 46) Who was James Cook? What was his role in colonialism?