Biology Unit 2 Review: CLASSIFICATION
advertisement
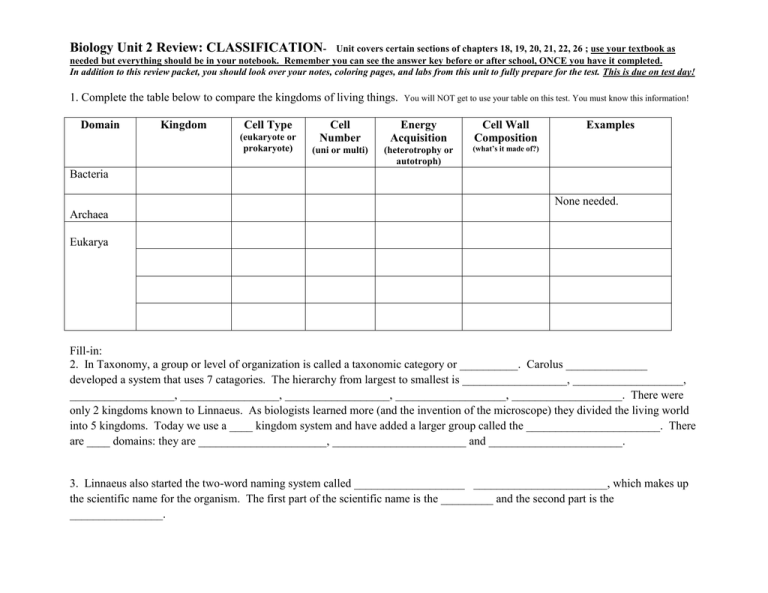
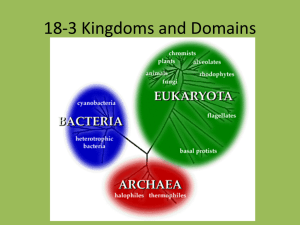
Biology Unit 2 Review: CLASSIFICATION- Unit covers certain sections of chapters 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26 ; use your textbook as needed but everything should be in your notebook. Remember you can see the answer key before or after school, ONCE you have it completed. In addition to this review packet, you should look over your notes, coloring pages, and labs from this unit to fully prepare for the test. This is due on test day! 1. Complete the table below to compare the kingdoms of living things. Domain Kingdom Cell Type (eukaryote or prokaryote) You will NOT get to use your table on this test. You must know this information! Cell Number Energy Acquisition Cell Wall Composition (uni or multi) (heterotrophy or autotroph) (what’s it made of?) Examples Bacteria None needed. Archaea Eukarya Fill-in: 2. In Taxonomy, a group or level of organization is called a taxonomic category or __________. Carolus ______________ developed a system that uses 7 catagories. The hierarchy from largest to smallest is __________________, ___________________, __________________, _________________, __________________, ___________________, ___________________. There were only 2 kingdoms known to Linnaeus. As biologists learned more (and the invention of the microscope) they divided the living world into 5 kingdoms. Today we use a ____ kingdom system and have added a larger group called the _______________________. There are ____ domains: they are ______________________, _______________________ and _______________________. 3. Linnaeus also started the two-word naming system called ___________________ _______________________, which makes up the scientific name for the organism. The first part of the scientific name is the _________ and the second part is the ________________. 4. A phylogenetic trees and cladograms shows the ______________________ relationships among various biological species that are thought to have a common ancestor. 5. According to the phylogenetic tree, which group is most closely related to humans? _________________ 6. Make a * at the spot that indicates the common ancestor to gorillas and humans. Place a + at the spot that indicates the organism that is the common ancestor for all. Often at the base of a tree, scientist will identify the common ancestor for the group. It is NOT identified in this particular diagram. 7. The diagram to the left is a cladogram. Cladistic analysis identifies and considers specific characteristics which are thought to be innovations (derived characteristic, something newly introduced/evolved) when showing relationships. What characteristic separates lizards, pigeons, mouse & chimp from salamanders? _______________________________. 8. Which are more closely related: Perch and hagfish OR Perch and lizard 9. Label the cladogram with the information below: Organism Earthworm Trout Lizard Human Hair absent absent absent present Legs absent absent present present Backbone absent present present present humans 10. Label the bacterial shapes with the scientific name/term. 11. On the typical bacterium- Identify: A- ______________ B- ______________ C- _______________ J- _______________ F- _______________ nitrogen fixation, binary fission, flagella, protozoa, algae, pseudopodia, cilia, conjugation, hyphae , mycelium, endospore, heterotroph, autotroph, Vocabulary terms to know: 12. __________________- tiny filaments that make up fungi 13. __________________- process of converting nitrogen gas to a form of nitrogen that plants can use. 14. __________________- long tail-like appendage for locomotion or feeding, typically 1 or 2 15. __________________- simple form of sexual reproduction where organisms exchange some genes. 16. __________________- tangle or mass of hyphae 17. __________________- organism able to make its own “food” through photosynthesis 18. __________________- dormant form of a bacterium, can become active once condition are right 19. __________________- animal-like protists 20. __________________- tiny hair-like filaments that usually cover the entire cell or organism, for cell movement and feeding. 21. __________________- plant-like protists 22. __________________- extensions of the cell’s cytoplasm that allow the cell to crawl. 23. _________________- ingests other organism as “food” 24. _________________- organism divides in half, asexual reproduction For 25-51 you may want to refer to the word box below for help. Try to do them without looking! These suggestions may help- some are not used at all: mycelium E. coli conifers mushrooms vertebrates unicellular chitin backbone dorsal nerve cord angiosperms bilaterally peptidoglycan gill slits multicellular antibiotics limbs bryophytes absorption bacteria nucleiod diatoms spores cellulose tail algae circular gymnosperms prokaryote(s) eukaryote(s) radially vascular disease hyphae base harsh protozoa invertebrates conjugation organic notochord mosses contractile vacuole macronucleus Eubacteria 25. The kingdom Eubacteria contains ______________________ that have ___________________ in their cell walls. 26. Some Eubacteria cause ________________________, some are decomposers and some “fix” nitrogen, some are used to make cheese and yogurt, while others form symbiotic relationships with other organisms. An example of a symbiotic relationship that is mutualistic (both organisms benefit) is the bacteria that lives in human intestines called _______________________. 27. The DNA in the prokaryotic cell is in ___________________ form and found in the area called the ______________________. 28. Bacteria can be killed using _________________________ which destroy the cell wall. Archaebacteria 29. Archaebacteria lack ___________________ in their cell walls. Their membranes and cell walls are quite different from other bacteria. 30. Archaebacteria are adapted to thrive in very ___________ environments (high temperature, no oxygen, high salinity…). Protista 31. Kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. The kingdom can be broken into 2 parts: the animal-like protists which are called ____________________________ and the plant-like protists which are called __________________. 32. Protozoa are __________________________ (one cell) and are motile. 33. Many protozoa reproduce asexually, but are able to alter their DNA(exchange some genes) through _________________________. 34. Algae called ______________________ are geometrically shaped and have a hard outer shell made of silicon dioxide (glass). 35. A common, filamentous green _____________ called Spirogyra has chloroplasts (green organelles) that form spiral shapes within their cells. 36. Protists are typically _____________________ although there are some multicellular algae. 37. Algae are protists that can be found at the ___________________ of many food chains. Ex: algae -> shrimp -> fish -> sea gull A 38. Identify: A- __________________ B B- __________________ C- __________________ C Fungi 39. The basic structure of the fungus is thin strands of cells called ____________________ that form tangled masses called ___________________________. 39. The cell wall of fungal cells have _________________. 40. Mycelium form different shapes which distinguishes different phyla within the kingdoms. Some make cup shaped structures, other form ____________________ some of which are edible and some are poisonous. Others form tiny stalks (bread mold). 41. Fungus are heterotrophs that get their nutrients by _____________________. 42. Fungi reproduce by making ____________________ either asexually or sexually. 43. Fungi are considered saprobes (or saprophytes) because they obtain food from dead_______________________matter. 54. Some fungi cause ____________, some are decomposers, some form symbiotic relationships with other species (example- lichens). Plantae 45. The plant kingdom is very diverse and includes 4 major groups; _______________________, ferns, ____________________ and angiosperms (flowering plants). All plant cell walls contain _______________________. 46. The plant kingdom can be broken into 2 groups based on whether the plants can move water and nutrients called ______________________________ and those that can’t called non-_________________________________. 47. Non-vascular plants are commonly known as ______________________ and can only be found in moist habitats. Mosses are small and short so that water can be absorb directly from the soil into cells. 48. Plants that make cones are in the group _______________________. Animalia 49. Animalia is a diverse kingdom that can be divided into two large groups the __________________________ (sponges, cnidarians, worms, insect, mollusks and sea stars) and the______________________________ (found in the phylum Chordata). 50. All Chordates have 4 characteristics in common: __________________________________(may form vertebral column/backbone), ______________ ________________, ______________________, a dorsal ______________ _________________. 51. Animals show different types of symmetry. Humans are _______________________ symmetric. Jelly-fish are _________________ symmetric and some animals (sponges) have no symmetry. 52. Identify the organisms above. a. _____________________ b. ______________________ c- ______________________ 53. Which move and what structures do they use? a. Move? _____ structure? ______________ b. Move? _____ structure? ____________ c. Move? _____