Unit 2 Voabulary
advertisement

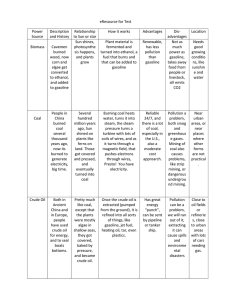
Unit 2 Voabulary 1.Natural Resources - natural things (land, water, air) that you would use. 2.) Lithosphere - the rigid outer layer of the Earth including the crust and upper mantle. 3.) Agriculture - impacts land, primary use is farming and herding of animals. 4.) Peat - the first stage that coal passes through, partially decayed plant material (sometimes like soil). 5.) Uranium - an important metal, a radioactive material that can be decayed and used as a power source. 6.) Alternative Energy Sources - different ways to get power/energy (clean energy - wind, solar geothermal, hydroelectric) 7.) Renewable Resources - a resource that is virtually inexhaustible or that can be replenished over relatively short time spans. 8.) Nonrenewable Resources - resources that take millions of years to form (can’t get back) 9.) Coal - important fossil fuel, formed when heat and pressure transform plant material over millions of years. 10.) Fossil Fuels - any hydrocarbon that may be used as a source of energy. 11.) Point Source Pollution - water pollution that comes from a known and specific location. 12.) Nonpoint Source Pollution - water pollution that does not have a specific point of origin. 13.) Runoff - water that flows over the land’s surface rather than seeping into the ground. 14.) Conservation - the careful use of resources. 15.) Sustainability - living on Earth in a way that allows humans to use its resources without depriving future generations of the resources. 16.) Urbanization - the transfer of land into an urban area. 17.) Deforestation - the cutting down of a forest to use the lumber for human use. 18.) Harvesting - when crops are gathered for human consumption - can lead to erosion. 19.) Mining - when people dig up large areas of land to gain resources (ex.gems, coal, etc.) 20.) Drilling - using heavy machinery to obtain resources from deep underground (ex. oil) 21.) Plutonium - another nuclear energy source, radioactive