Topic: Name: _____________________________________________________ Period: _______ Date: _______________________ Lab07: Polymorphism
advertisement
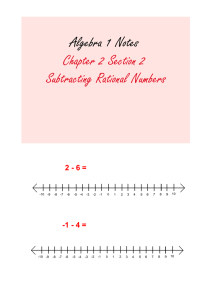
Topic:
Lab07: Polymorphism
Objectives
Definition of override
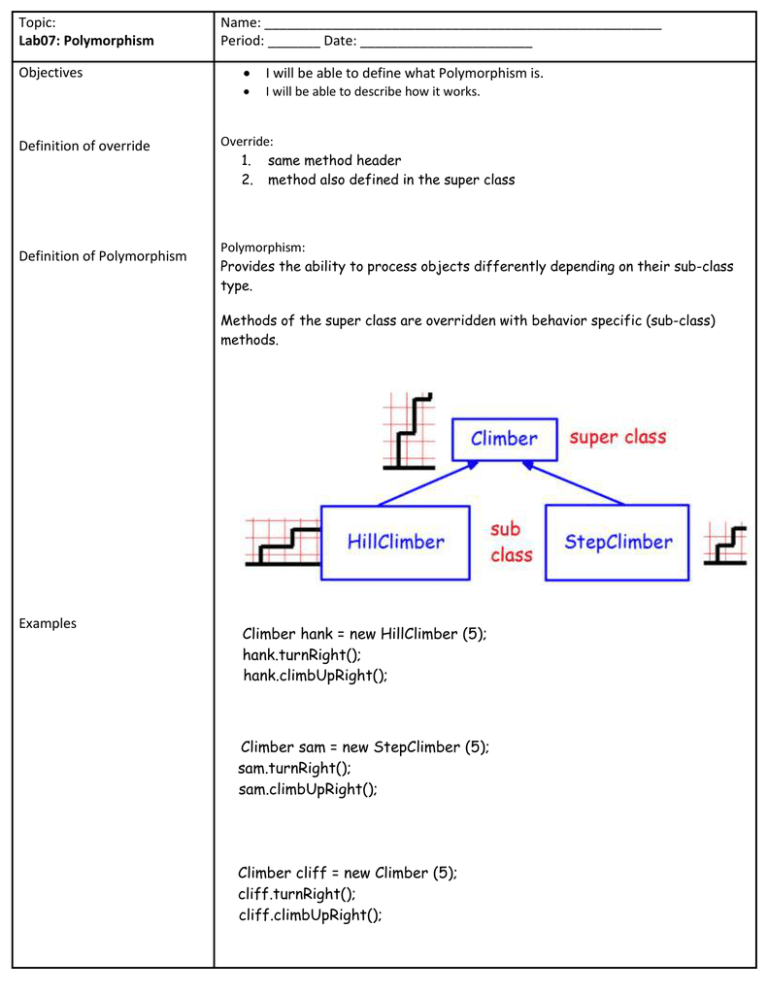
Definition of Polymorphism
Name: _____________________________________________________
Period: _______ Date: _______________________
I will be able to define what Polymorphism is.
I will be able to describe how it works.
Override:
1. same method header
2. method also defined in the super class
Polymorphism:
Provides the ability to process objects differently depending on their sub-class
type.
Methods of the super class are overridden with behavior specific (sub-class)
methods.
Examples
Climber hank = new HillClimber (5);
hank.turnRight();
hank.climbUpRight();
Climber sam = new StepClimber (5);
sam.turnRight();
sam.climbUpRight();
Climber cliff = new Climber (5);
cliff.turnRight();
cliff.climbUpRight();
How do you implement
Polymorphism
Polymorphism concepts:
1. super class reference
2. method is overridden
- defined in super class and the subclass
3. calls method in the subclass
4. decision is made at run-time
"dynamic binding"
Climber sam = new StepClimber (5);
sam.turnRight();
sam.climbUpRight();
What is checked at compile
time?
What happens at run time?
Lab 7: Explore
Compile time:
Is the method defined in the super class
Run time:
The JVM looks for the method from the bottom up of the hierarchy. It looks first in the
subclass and then the super class.
String type = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("What type of climber?");
if(type.equals("Climber"))
{
Climber sam = new Climber(x);
Mountain.explore( sam );
}
else if(type.equals("HillClimber"))
{
Climber hillary = new HillClimber(x);
Mountain.explore( hillary );
}
else if(type.equals("StepClimber"))
{
Climber steve = new StepClimber(x);
Mountain.explore( steve );
}
What type of method is explore() ? Class method
What are you passing to explore() ? super class reference.
Summary: