Markets, Equilibrium, & Price Right?
advertisement

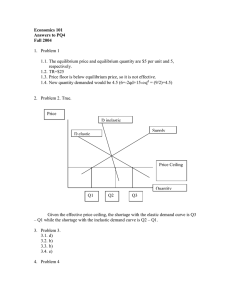
Markets, Equilibrium, & Price How Do You Know When the Price is Right? Preview 1. Think of a product you recently purchased. 2. On your handout, record the name of the product and the approximate price you paid. Then answer these questions: a. What are some reasons you were willing to buy the product at this price? b. What are some reasons the seller was willing to sell the product at this price? c. Do you think you paid the “right” price for this product? Why or why not? What Happens When Demand and Supply Meet? • In a free market, demand and supply work together to determine price. • The interaction of demand and supply drives prices to market equilibrium: Quantity consumers are willing to buy = Quantity producers are willing to sell Reaching Market Equilibrium On a graph, equilibrium is found at the point where the demand and supply curves interact Price Watermelons Demanded Watermelons Supplied $4.00 300 100 4.50 250 150 5.00 200 200 5.50 150 250 6.00 100 300 Graph the Supply & Demand for Watermelons Reaching Market Equilibrium 6.00 5.50 5.00 Price Watermelons Demanded Watermelons Supplied $4.00 300 100 4.50 250 150 5.00 200 200 5.50 150 250 6.00 100 300 4.50 4.00 100 150 200 250 300 350 Graph the Supply & Demand for Watermelons 6.00 . . . 5.50 Equilibrium Price . Equilibrium Quantity Price 5.00 4.50 4.00 0 SUPPLY 100 150 200 Quantity of Watermelons . . DEMAND 250 300 350 So, What is Market Price? • Market Price is the price a willing consumer pays to a willing producer for the sale of a good or service. • Supply and Demand are like a pair of scissors – it is impossible to determine which blade cuts that paper – the two blades operate in unison. What Happens When the Price Isn’t Right? • Equilibrium Price = “Right” price • What happens when producers set a market price that is above or below the equilibrium price? Disequilibrium Smoothie Demand & Supply Schedule Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied $1.50 5,000 1,000 $2.00 4,000 2,000 $2.50 3,000 3,000 $3.00 2,000 4,000 $3.50 1,000 5,000 Outcome Shortage from Excess demand Equilibrium Surplus from Excess supply Graph Your Demand and Supply Curves Smoothie Demand and Supply Surplus Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied $1.50 5,000 1,000 $2.00 4,000 2,000 $2.50 3,000 3,000 2.00 $3.00 2,000 4,000 1.50 $3.50 1,000 5,000 3.50 S1 3.00 2.50 D1 1000 2000 3000 4000 Shortage 5,000 6,000 How Do Shifts in Demand of Supply Affect Markets? • Does the event affect demand, supply, or both? A new study is published saying blueberries are good for you • Does the event shift the demand or supply curve right or left? The demand curve shifts to the right • What are the new equilibrium price and quantity and how have they changed as a result of the event? New equilibrium price is $3.00, new quantity is 4,000 Smoothie Demand and Supply S1 3.50 Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied $1.50 5,000 1,000 $2.00 4,000 2,000 $2.50 3,000 3,000 $3.00 2,000 4,000 $3.50 1,000 5,000 3.00 2.50 D2 2.00 D1 1.50 1000 2000 3000 4000 5,000 6,000 How Do Shifts in Demand of Supply Affect Markets? • Does the event affect demand, supply, or both? Blueberry crop damaged by drought • Does the event shift the demand or supply curve right or left? Supply curve moves to the left • What are the new equilibrium price and quantity and how have they changed as a result of the event? New equilibrium price is $3.00, new quantity is 2,000 Smoothie Demand and Supply S2 3.50 S1 Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied $1.50 5,000 1,000 $2.00 4,000 2,000 $2.50 3,000 3,000 $3.00 2,000 4,000 $3.50 1,000 5,000 3.00 2.50 2.00 D1 1.50 1000 2000 3000 4000 5,000 6,000 How Government Intervention Affects Markets • Price Ceilings: lead to excess demand – Maximum price consumers are required to pay for a good or service – Price above the ceiling is illegal Ex: Rent Control Blueberry Market Breaking News! The U.S. government has just announced a price ceiling on blueberries. • All blueberries must be bought and sold for $3 or less per box. • Graph it on your handout • Start with equilibrium P = $6, Q = 5 shortage • Price ceilings cause: ______________ How Government Intervention Affects Markets • Price Floors: lead to excess supply – Minimum price consumers are required to pay for a good or service – Pricing a good below the Price Floor is illegal Ex: Minimum Wage Blueberry Market Breaking News! The U.S. government has just announced a price floor on blueberries. • All blueberries must be bought and sold for $8 or more per box. • Graph it on your handout surplus • Price floors cause ________________ Excess Supply and Demand • Price Controls lead to surpluses and shortages • Shortages = Rationing – Controlled distribution of a limited supply of goods or services • Shortages = Black Market – Illegal market where goods and services are traded a quantities higher than those set by law Homework • Complete Worksheet • Quiz on Supply & Demand next class!