Unit 7 Study Guide: I, ___________________, will study for my
advertisement

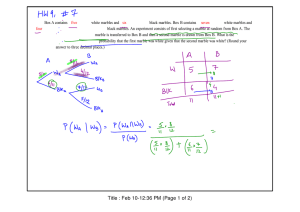
Unit 7 Study Guide: Probability and Statistics SOL 8.12,8.13 I, ___________________, will study for my Unit 7 Test given on _______________. PROBABILITY INDEPENDENT Events happen at the same time or one after the other, but they do not affect each other. Examples: rolling a dice, throwing a coin. Pulling an object out of group more than once will be independent ONLY if the first object will be returned to the group (WITH replacement). 1. Calculate the probability of the 1st event“how many out of total?” 2. Calculate the probability of the 2nd event 3. Multiply 1. DEPENDENT The chances of something happening can be affected by previous events. Examples: Take an object from a group, DO NOT RETURN, then take another one from the same group (WITHOUT replacement). 1. Calculate the probability of the 1st event 2. To calculate the probability of the 2nd event: a) Decrease the denominator of 1st probability by one b) IF getting the same object, then decrease the numerator one, IF different, then find it the regular way. 3. Multiply Independent or Dependent Events? a. b. c. d. e. Flipping two coins ________________________ Choosing two marbles from a bag, but not replacing the first one ________________________ Rolling a number cube and spinning a spinner ________________________ Picking two socks out of a drawer, but not replacing the first one ________________________ Choosing two marbles from a bag, with the first one replaced ________________________ 2. 2 blue and 3 red marbles are in a bag. What are the chances of getting a blue marble? The chance is _____ But after taking one out you change the chances! So the next time: if you got a red marble before, then the chance of a blue marble next is ______ if you got a blue marble before, then the chance of a blue marble next is _____ What are the chances of drawing 2 blue marbles? P(blue, red)= P(red, blue) = P(two red) = 3. A bag contains 3 red marbles and 4 green marbles. Two marbles are drawn at random without replacement. If the first marble drawn is red, what is the probability the second marble is a. green? b. red? 4. Two cards are chosen at random without replacement from a pack of 52 playing cards. Find each probability. b. P(Two red cards) c. P(Two Queens) d. P(Queen, King) e. Show how would calculation in 6c change if we would return the queen card back to the pack. STATISTICS 5. Use the stem and leaf plot to answer the following questions. Calculate: mean__________ Mode__________ median___________ range_____________ Which number is the lower extreme?_________________ Which number is the upper extreme? ______________ Which stem contains the greatest number of data elements?_____________ 6. Build a frequency table from the following data. Display the data in a stem-and-leaf (a), histogram (b), line plot(c), and box-and whiskers (d) plots. 5, 18, 45, 20, 10, 2, 37, 37, 28, 33, 21, 27, 11 a) Daily Low Temperatures in January Temperature Tally Frequency (°F) 0–9 10 – 19 20 – 29 30 – 39 40 – 49 b) c) 000 f) Why can’t we build a scatter plot for the data? 000 000 000 000 7. The bar graph shows the scores obtained from 20 throws of a die. What is the lower quartile? Use the histogram to answer the following questions. 9. How many people were surveyed about library visits? 10. How many of the people surveyed visited the library at least 20 times? Number of People Library Visits Per Year 8. How many people visited the library less than 40 times? 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0-9 10-19 20-29 30-39 40-49 Visits 11. Do the following scatter plots have positive, negative or no correlations? Strong or weak? 12. Identify the data sets as having a positive, a negative, or no correlation. a) The number of hours a person has driven and the number of miles driven b) The number of siblings a student has and the grade they have in math class c) The age of a car and the value of the car d) The number of weeks a CD has been out and the total sales e) The number of years a person went to school and their income f) The number of songs downloaded on your i-pod and the amount of memory available g) The amount of time spent on the computer instant messaging your friends and the number of computers in your house h) The age of a house and the number of people living in the house 13. Which graph shows the best 'Line of best fit' for the scatter plot? A. B. C. Write a sentence for other lines, why are they not good enough. Answer A _______________________________________________ Answer B _______________________________________________ Answer C _______________________________________________ Answer D _______________________________________________ _________ D.