Chapter 8: Photosynthesis Structured Notes
advertisement

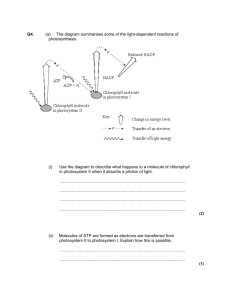
Chapter 8: Photosynthesis Structured Notes I. Photosynthesis – Process of converting ______________ energy from the __________ into energy that is stored in chemical bonds of glucose. A. General Equation: Note that this chemical equation is the reverse of cellular respiration B. General Photosynthesis Process: II. Where does Photosynthesis take place? A. Chloroplast – Membrane bound ____________________ that contains both _______________ and enzymes necessary for converting light energy into glucose. B. Types of Pigments (light absorbing compounds) 1. Chlorophyll a: Primary photosynesthetic pigment in all plants. It is located at the reaction center of photosystems. 2. Chlorophyll b, Carotenoids (Carotene and Xanthophyll): Secondary pigments that capture light energy and transfer it to chlorophyll a at the reaction center. C. The changing color of leaves: 3. Why do leaves change color in the fall? 4. List a few the conditions that have to be present for this change to occur. III. Photosynthesis consists of two steps: A. Light Reaction (Light Dependent Reaction): Name for the chemical process where _____________ and ______________ are formed in the ________________ membrane. B. Calvin Cycle (Light Independent Reaction, C3): Occurs in the __________________. _____________ and _________________ are not stable so plants use ________________ to create___________________, which can be stored. It takes _________ turns of the cycle to create ________ glucose. Step one: Light Reaction (Occurs in the ________________________) Type 1: Non Cycle Flow Reactants Used: Products Produced: Important Concepts to Know: 1. Photosystems: Chlorophyll reacting to the sunlight. When sunlight shines on the chlorophyll it excites electron (2e-) and they escape from the chlorophyll. These photosystems absorb colors in the red wavelengths of light (700 and 680). 2. Electron Acceptors: Their job is to capture the electrons lost by the photosystems so that these electrons (2e-) do not escape from the thylakoid membrane. We do not want to lose all that energy! 3. Electron Acceptor II: Needs to release the electrons (2e-) so that it can pick up more electrons. It does this by releasing the electrons (e-) to Photosystem I and creating ATP by utilizing the Electron Transport Chain. 4. Photosystem I: Picks up the electrons from the Electron Acceptor II (2e-) to replace its lost electrons. Now the electron acceptor I (2e-) needs to release its electrons so that it is capable of absorbing more electrons. It does this by releasing its electrons (2e-) to NADPH. 5. Water: Splits releasing oxygen, hydrogen and electrons (2e-). The hydrogen combines with NADP+ and the electrons released from Electron Acceptor I to form NADPH. The electrons from water are absorbed by Photosystem II to replace those that were lost. Oxygen is released. Step Two: Calvin Cycle (Occurs in the ________________________) RuBP GLUCOSE Forms a 6 Carbon Compound which is unstable Splits into 2 Which goes through a series of 3 Carbon Compounds reactions using energy from _________ and ___________ Factors Affecting Photosynthesis: Some plants have adapted to use different photosynthetic pathways besides the Calvin Cycle (C3). Plants have alternative pathways that allow for stomata to be closed during hot days which decrease the loss of water. A. C4 – Plants adapted to _________, dry climates are more efficient at using ______________ (4 times more efficient). This allows them to grow at _________ temperatures. It requires more _____________, but plants grow in abundant amounts of light where extra energy is available. Examples: Crab Grass, Corn, Sugar Cane B. CAM – Plants adapted to __________ habitats. _____________ fixation occurs at ______________. This means that their ____________ are not open during the day when they would be subject to much greater _____________ loss. Examples: Desert Plants such as cacti, pineapples and succulent water storing plants.