Introduction to Genetics Probability
advertisement

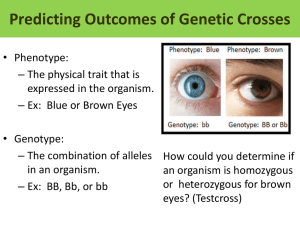
Introduction to Genetics Understanding Punnett Squares Notes (Chapter 11 and 14) Probability Probability: the ____________________ that a particular event will occur, it can be used to predict the outcomes of _______________________. Paperclip Demonstration 1) What is the probability of picking a red paperclip? 2) What is the probability of picking a red paperclip two times in a row? 3) What do you think would make your results close to the calculated probability? Punnett Squares Punnett Squares: a diagram that shows the ______________ of each possible outcome of a cross. Monohybrid Crosses 1. Brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes. If two heterozygous brown-eyed people marry, what are the chances that they will have a blue-eyed child? Key: Cross: Genotype: Phenotype: Dihybrid Crosses Dihybrid Cross: Used to determine the probability of specific genotypic and phenotypic ratios when looking at __________ traits at the same time. ** FOIL each parent’s genotype independently sorts to set up the cross *** 2. In guinea pigs, black coloring is dominant over brown coloring and rough fur is dominant over smooth. Cross two heterozygous black guinea pigs with rough fur. Key: Cross: Genotype: Phenotype: Incomplete Dominance Crosses Incomplete Dominance: A cross between organisms with two different phenotypes can produce heterozygous offspring with a _________ phenotype that is a _____________of the parental traits. IMPORTANT: Different letters are used to represent the different alleles and combinations are used for the heterozygous pair. Snapdragon Flowers 3. What results may be expected in a cross between two pink flowered snapdragons? Key: Red = ___________ White = ___________ Pink = _________ Cross: Genotype: Phenotype: Codominance Crosses Codominance: This happens with a cross between organisms with two different phenotypes produce offspring with a ________ phenotype in which both of the parental traits appear together. Tortoise Shell Cats 4. A cross between a black cat and an orange cat produces a striped condition know as tortoise shell. Cross a cat that has tortoise shell with an orange cat. Key: Black = ________ Orange = ________ Cross: Genotype: Phenotype: Tortoise -Shell = ________ Blood Groups (Codominance) Pages 344 to 345 There are three possible alleles for blood types ____________________ There are four different blood types ____________________________ A and B are codominant ____________ O is recessive ____________ 1. A man with blood type AB marries a woman with blood type O. Work out the possible blood types of their offspring. Key: Cross: Genotype: Phenotype: Table 1: Human Blood Groups Phenotype (Blood Types) Genotype Safe Transfusions To From Sex Linked Genes pg 350 to 353 One pair of chromosomes (X and Y) determines the sex of an individual; genes located on them are said to be _______________________ genes. Females: Females have _________ copies of the X - chromosome. Male: Males have just ________ X - chromosome. Thus, all X-linked alleles are _________________ in males, even if they are recessive. The Y - chromosome is much smaller and appears to contain only a few ___________. Eye color is a sex-linked trait in fruit flies carried on the X chromosome. Determine the sex and eye color for a father who has white eyes and mother who is homozygous dominant for red eyes. Key: Genotype: Cross: Phenotype: X- Chromosome Inactivation (page 352) If just one X chromosome is enough for cells in males, how does the cell “adjust” to the extra X chromosome? Chromosomal Disorders (page 353) Explain what happens during nondisjunction. Genetic Practice Problem Sets Assign each trait a LETTER—Make a Key Dominant trait = Capital letter (D) Recessive trait = small letter (d) Show the cross by determining the Genotypes of the Parents True Breeding — the same (DD) Homozygous Dominant (dd) Homozygous Recessive Hybrid — mixed (Dd) Heterozygous Set up and solve the Punnett Square. Then list the probable genotype and phenotype for the offspring. Answer the question(s). Monohybrid Crosses 1. Black is dominant to brown coat color in mice. Cross a heterozygous black mouse with a brown mouse. What are the chances of having a brown mouse? 2. Hitchhiker’s thumb is dominant to straight thumb in humans. Cross a heterozygous hitchhiker with an individual who is homozygous for the trait. Could they have a child with a straight thumb? Dihybrid Crosses 3. In horses, pacers are dominant over trotters, and chestnut is dominant over black coloring. What are the chances of getting a black pacer from a cross between two heterozygous chestnut pacers? Incomplete Dominance Cross 4. When red petunias are crossed with white ones, the resulting offspring are pink! Show a cross between one with pink flowers one with a red flowers. What are the chances of getting red flowers from such a cross? Codominance Crosses 5. Red coat color in cattle is codominant to white. The heterozygous is called “roan” (a red coat with white hairs). Cross cattle with a white coat with one that has a red coat. Blood Group Crosses 6. A woman sues a man for the support of her child. She has type A blood, her child has type O, and the man is type B. Show how this man could be the father of her child. 9 A woman sues a man for the support of her child. She has type B blood, her child has type A, and the man is type AB. Show how this man could be the father of her child. Sex Linked Crosses 10 In humans, colorblindness is a recessive trait that is carried on the X chromosome. A colorblind man marries a woman who is homozygous normal. 11 Pattern baldness is a sex-linked trait that is recessive. A man with a full head of hair marries a woman whose is heterozygous for baldness. Show this cross.