The Holocaust
advertisement

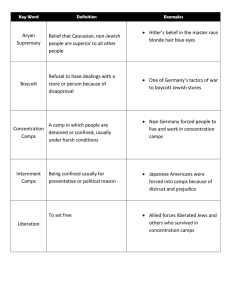
The Holocaust Agenda • • • • • • • Bell Ringer: Quick Quiz on World Wars Lecture: Beginning of the Holocaust (20) Cartoon Activity: German Propaganda (5) 8 steps to Genocide: Group Activity (12) Photo Analysis (10) Nazi Propaganda during the Holocaust (15) Video Clip: Nazi treatment in Concentration Camps (5) Hitler and the Jews • He had an animosity for the Jewish people since World War I. • Utilized Jews as scapegoats for everything, from the loss of war, to hyperinflation and depression. • As dictator, he would spread propaganda to brainwash the German people. Nuremburg Laws • 1935, all Jews barred from Civil Service, those positions going to Aryans. • Jews are no longer German citizens • They cannot associate with Aryans. • Later, required to wear the Star of David. • German diplomat murdered in 1938, led to the “night of broken glass” The move to the ghetto • By the late 1930s, after the “night of broken glass”, Jews were moved into ghettos. “Kristallnacht” • Equivalent to tenements, they were forced to leave their homes and possessions for confiscation by the Nazi’s • Now they crowded into rooms that held up to 16 people when it should only hold two or three. Warsaw • Most famous ghetto • Bricked off from the rest of the city, for Jews it was like a prison. • In reality it was a holding camp, for the extermination that was to follow in a few years. • Food riots were quickly quelled by Nazi secret police forces. Final Solution • The systematic killing of Jews. • Einsatzgruppen utilized as mass killing squads. • Others rounded up and taken to Concentration Camps. – Beaten and killed when they did not work hard enough at the camps. The Camps: Day 2 Agenda • Bell Ringer: What is Kristallnacht? How does it lead to the Holocaust? • Lecture Notes: Concentration Camps (20) • Life in a Concentration Camp Primary Analysis (15) • Photo Analysis: From the Camps (10) • Quick Video: The Camps (25) • Outline Information (15) The Use of the Camps • Initially used as work camps, companies such as IG Farben would use prisoners to work. • By 1942 gas chambers were created, and death camps were common. • Auschwitz is the most notorious. • 90% of Jewish population in Poland killed. Final Extermination • Two lines, one to take a “shower” and the other to be numbered and put into the camp • The Jewish prisoners would remove all clothing, heads were shaved, and any valuables were taken (including fillings from teeth). • Then they were sent to work until they died from starvation or abuse from the guards. After the War • London, many cities in Germany, and parts of the Soviet Union lay in ruins. • Conferences were held in Yalta and Potsdam to discuss how countries would recover after the war, and the division of lands held by Germany. • United Nations was formed, with permanent members controlling a peacekeeping force. Nuremberg and Occupation • Germans were held liable for the atrocities of the Holocaust. • 22 leaders charged with crimes against humanity. • Hermann Goring kills himself after being sentenced to execution, along with 11 others. • Similar trials occur in Japan as MacArthur restructures the government into Democracy. Japanese Internment Camps • After Pearl Harbor, there was animosity and distrust with Japanese-Americans. • 66% were American citizens, but they were forced into “internment camps” for the duration of the war. • 31,000 detained simply because of their race… sound familiar?