CHAPTERS 9 & 10 Cultural
advertisement

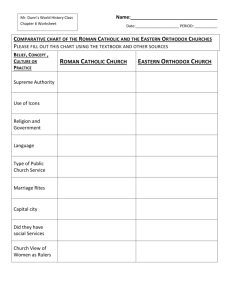
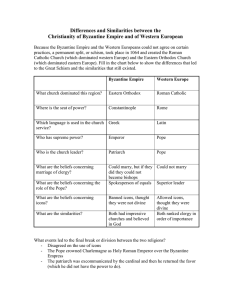
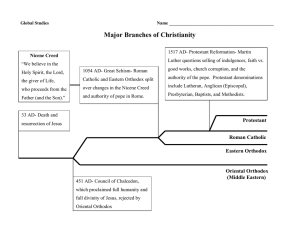
Cultural CHAPTERS 9 & 10 BYZANTIUM HAGIA SOPHIA First built by Constantine Rebuilt by Justinian The greatest surviving example of Byzantine Architecture It is an example of Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholic and Islam It was the seat of the Orthodox patriarch GREAT SCHISM SPLIT In 1054 a longstanding disagreement came to a head, and the Christian church split into two groups. The Western or Roman Catholic, and Eastern or Orthodox Catholic. The Byzantine Empire goes into slow decline DISAGREEMENTS Papal attempts to interfere over icons Charlemagne claims to be Roman Emperor Rituals in Latin not Greek Pope as first bishop Religious art Celibacy for priests EASTERN ORTHODOX Requires services to be in Greek Patriarch and bishops were head of the church The emperor was above the patriarch Believed in a different interpretation of the Bible Eastern Orthodox missionaries spread northward into Russia and the Balkans CYRILLIC Cyril and Methodius are the two most famous of the missionaries. Slavic language/alphabet derived from Greek letters Allowed for literature to be spread HOW? ICONS Images of religious figures venerated by byzantine Christians Iconoclasm The breaking of images Religious controversy of the 8th century Byzantine emperors attempted but failed to suppress icon veneration Believed it was the worship of idols AKA the Latin West WESTERN EUROPE THE CHURCH • Every aspect of life was dominated by the Church • • • • • • • Rulers were crowned by the “Grace of God” Political rule viewed as divinely sanctioned All Christians were expected to tithe to the church Education, art dictated by Church ideals Calendar organized by faith holidays Fair prices, economic practices dictated by church All answers to questions were dictated largely by faith • • Law was largely dictated by religion Serious matters submitted to Church for arbitration, resolution RELIGION IN WESTERN EUROPE Monastic rules St. Benedict (480-547 C.E.) provided a set of regulations Virtues of Benedictine monks: poverty, chastity, and obedience Western monastic rites differed from Eastern rites Western rites emphasized work, prayer, service to the poor Eastern rites were relatively isolated, dedicated to prayer but not outside contacts Catholic church provides only form of stability and order Hierarchy: Pope Bishops (regional) Priests (local) Constant give and take between Church and regional rulers RELIGIOUS REFORM AND EVOLUTION The roles of monasteries Became dominant feature in social and cultural life of western Europe Accumulated large landholdings but spread knowledge Wealthy patrons donated land to monks for monasteries Taught peasants, serfs techniques of farming Cleared forested lands, planted them Organized much of rural labor for agriculture Provided a variety of social services Inns and shelters for travelers and refugees Orphanages, medical centers Schools, libraries and scriptoria Monks served needs of rural population PAPAL POWER The Pope Spiritual head of all Christians including aristocrats, royalty Weapons included excommunication, interdict, canon law Economically received tithe, freedom from taxation, owned great economic wealth Popes became head of reform movements Abolished simony, insisted on celibacy of priests, reformed monasteries Established College of Cardinals to elect popes not kings, mobs Popes Gregory VIII and Innocent III defied, deposed kings Popes launched crusades against Muslims, heretic Christians, some Italians THE SPREAD OF THE CHURCH Popes took an active roll in sending out missionaries Pagan ways did not disappear immediately Scandinavia, Baltic lands were last to convert Pagan rituals often blended into Christianity Cities, towns largely Christian but countryside weakly so By 1000 C.E., western Europe was Roman Christianity Irish, Mozarabic rites of Christianity accepted by Pope Arian Christianity eliminated by Franks ART Art centered on religious ideas/themes ultimately allowed for development of scientific/philosophical ideas building blocks of later Western culture