What kind of boundaries do you see?
advertisement
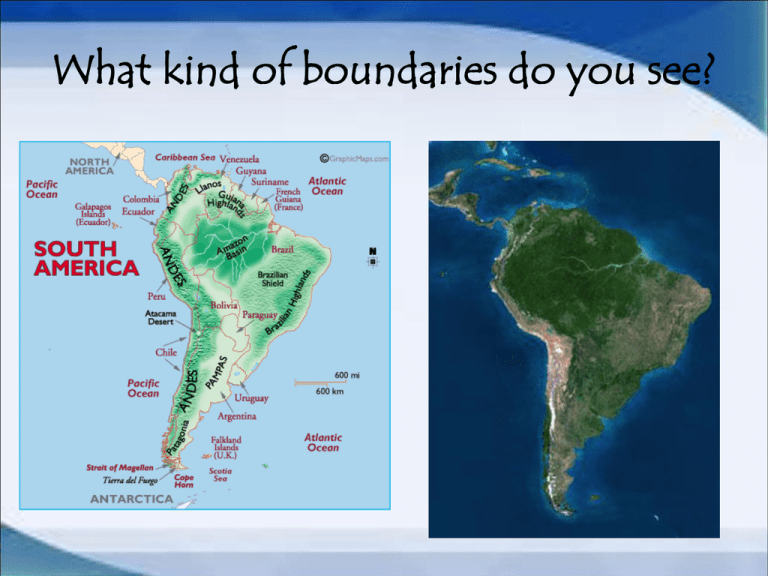
What kind of boundaries do you see? Function/Purpose • Keeping People IN • Keeping People OUT • Mark limits of jurisdiction – symbol of SOVEREIGNTY • Promotes nationalism Types of Boundaries Three types of boundaries Geometric Physical Cultural Best boundaries are those to which all affected states agree, regardless of the rationale used to draw the line Geometric Straight-line boundaries that do not related to the cultural or physical features of the territories involved Ex. North/South Korea 38th parallel Physical (or natural) Separate territories according to natural features in the landscape, such as mountains, deserts, or rivers Ex. France and Spain are divided by the Pyrenees What types of boundaries do you see? Types of Boundaries • Cultural Boundaries – Mark changes in the cultural landscape, such as boundaries that divide territories according to religion or language – Sometimes drawn according to geometric straight lines – Religious • Only a few cases where religion has been used to select the actual boundary line • Example: – South Asia, partition of India and Pakistan – Ireland and North Ireland – Language • Europe best example • Idea spread during 20th century – Versailles Conference Cyprus “Green Line” Boundary • Contains two nationalities – Turkish= north, eastern • 18% of population – Greek= south • 78% of population • Cyprus gained independence in 1960 – Constitution guaranteed Turkish minority rights – Cyprus never peacefully integrated the Greek and Turkish nationalities • Series of Coups led to Turkish section declaring itself independent in 1983 – no one except Turkey recognizes independence • Wall constructed between two areas – Buffer zone patrolled by UN – Accepted to EU in 2004 Boundary Evolution • Evolution – Another way to classify boundaries depends not on how they were created, but how they evolved over time • Antecedent boundaries – Existed before humans cultures developed into current forms • Subsequent boundaries – Grow to divide space as result of human interaction • Superimposed boundaries – Forcibly put on the landscape • Relict boundary – No longer functions has a boundary • Boundary Creation – Several steps on the growth of boundaries into final form • Definition – Phase in which the exact location of a boundary is legally described and negotiated » De Jure » De Facto • Delimitation – Is the step when the boundary’s definition is drawn onto a map • Demarcation – Is the visible marking of a boundary on the landscape with a fence, line, sign, wall, or other means • Administration – Is the enforcement by a government or people of the boundary that has been created Boundary disputes • Type of Disputes – Territorial Disputes • Conflicts over boundaries are divided into different categories – Can include mix of categories • Conflict because one state wants to annex a territory whose pop. is ethnically related to them – Definitional disputes • Fight over the language of border agreement in a treaty or contract – Japan and Russia – Locational /Positional disputes • Occur when conflicting parties agree on the definition but not on where the boundary exists on a map – Operational /Functional disputes • Conflicts over the way a boundary should operation or function – Allocational /Resource boundary disputes • Fights over resources that may by divided by the boundary Frontiers • Frontier: Region where no state exercises complete and political control or boundaries are weakly developed Antarctica Saudi Arabia and Yemen • A frontier area is uninhabited or sparsely settled by a few isolated pioneers • 19th Century (1800s) – Vast amounts of frontiers – Tangible geographic area whereas a boundary is a infinitely thin, invisible, imaginary line – Frontier provides an area of separation but a boundary brings two neighbors into direct contact • • • • Australia American West Canadian North Sub-Saharan Africa