Chapter 30: Vocabulary – Views of Earth’s Past
advertisement

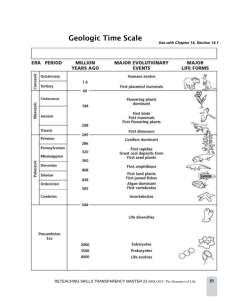
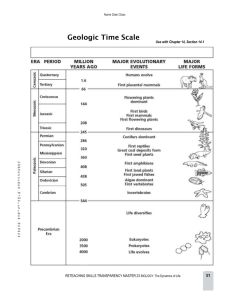
Chapter 30: Vocabulary – Views of Earth’s Past In your own words, rewrite the definition and draw a picture to illustrate the meaning. Ammonite: A fossil cephalopod that is an important index fossil of the Triassic Period. Bipedal: Walking upright on two legs. Crinoid: A sea lily, a relative of the sea star, common during the Mississippian Period. Dinosaur: One of many forms of now extinct animals that dominated the Mesozoic Era. Eon: The first division of the geologic time scale and therefore the longest. Epoch: A subdivision of a geological period on the geologic time scale. Era: A major division of geologic time. Eurypterid: A sea animal that was common during the Silurian Period; also called a sea scorpion. Evolution: The process of change that produces new life forms over time. Foraminifera: Single-celled organisms with calcite shells common during the Mississippian Period. Geologic time scale: A summary of major events in Earth’s history that are preserved in the rock record. Graptolite: Tiny sea animals that lived in colonies; used as index fossils of the Ordovician Period. Hominid: Modern human or humanlike ancestor. Natural selection: The theory that organisms that survive to produce offspring have inherited the most favorable traits for survival in a particular environment. Period: A subdivision of a geologic era. Precambrian: All the geologic time before the start of the Cambrian period in the Paleozoic Era. Shield: The exposed area of the oldest rocks, or craton, of a continent. Stomatolite: A layered dome or column formed of trapped sediments and mats of cyanobacteria. Trilobite: A crablike invertebrate that is the most common fossil of the Cambrian Period