Chapter 5 Study Guide Living Systems
advertisement

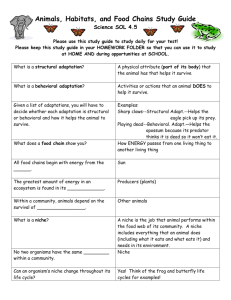
Chapter 5 Study Guide Living Systems Test Date: ________________________________________ Organism – Any living thing on the planet. Instinct- is a behavior that animals are born with. (spiders spinning a web) Survival Skill Learned behavior- are skills learned by watching others around us. Hibernate- is a deep winter sleep that allows an animal’s body to slow down so much it can survive without eating. Migrate- is a long-distance journey from one place to another to find food, due to temperature change, or to have babies. Camouflage- is a physical adaptation that lets a critter blend into the environment so the animal becomes hard to see. Hiding in plain view by blending in with the surroundings. Mimicry- is a physical adaptation that lets certain species look like other less tasty ones. Animals that look like other animals to avoid getting eaten. Dormancy- is a time when growth and physical activity temporarily stops for plants. (taking a rest or conserving energy in harsh environments) Behavioral Adaptation – an animal changes its behavior, or how it acts, to survive. Examples: Migration, Hibernation, and Dormancy Physical Adaptation – an animal changes how it looks, or physical appearance, to help it survive. Examples: Mimicry, camouflage, and Instinct Producer – Plants that make their own food, using sunlight, air, water, and nutrients in the soil. Consumer - An animal that eats living things-plants, other animals, or both. Decomposer - a living thing that feeds on dead things (mushroom) Herbivore – A consumer that eats only plants. Omnivore - A consumer that eats both plants and animals. Carnivore - A consumer that eats only other animals. Predator – An animal that hunts other animals to get its food. Prey – An animal that is hunted by other animals for food. Food Chain – The invisible chain that shows plants and animals in the order in which they eat each other. A community is all the populations that live in an ecosystem. A habitat provides a population with all its needs and includes living and nonliving things. A population is a group of the same kind of living thing that live in the same place at the same time. Ecosystem the living and non-living things that share a common environment. You need to know the following habitats (types of animals, plants, climate, where in the world, etc. all will be general information) TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEMS- land habitats such as deserts, grasslands, rainforests, and forests. Desert- includes hot, like the Sahara Desert, and cold, like the Antarctic Desert, Grassland- not enough rain for trees to grow but too much rain to form a desert Rain Forest- three parts, canopy, understory, forest floor Forest- made up mostly of trees AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS –water habitats such as ponds, marshes, swamps, rivers, and oceans Freshwater- includes ponds, marshes, swamps, streams, rivers Marsh- an area of soft, wet, low-lying land Swamp- flood lands during rainy season with woody plants like trees Saltwater- includes oceans and seas Also know……….. Be able to look at a picture and identify the habitat Know that oceans make up the earth’s largest ecosystem, and that 75% of the earth is covered in water. Know that living and nonliving things interact to help a living thing survive, be able to give examples of how living things use these resources to survive. You should know that environments change over time for a variety of reasons. Earthquakes, pollution, flooding, fires, deforestation, can all cause an environment to change. Not all of this is bad change. For example, sometimes a forest fire can kill small brush and weeds that are keeping the trees from growing. Seeds left buried underground will grow stronger after the fire has cleared away the extra brush. Know living things compete within an environment for resources; this is because all resources are limited. Be able to give an example.