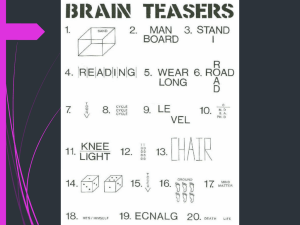
Warm Up Answers 3. YYURYYUBICURYY4ME Coffin
advertisement

Warm Up Answers 2.The maker doesn’t want it, the buyer doesn’t use it, and the user doesn’t see it. What is it. Coffin 3. YYURYYUBICURYY4ME Answer: Too wise you are, Too wise you be, I see you are, too wise for me. Warm Up •Find with a group of 2 or 3 to work 4. 1.How many passengers are left on the train? 15 2. How many passengers have gotten off the train since the first station? 50 3. How many passengers have gotten on the train since the first station? 65 4. How many stations were there? 6 5. How old was the train engineer Chapter 10 Thinking and Language: Cognition, Problem Solving, and Causes of Irrationality Chapter 10’s Focus: The Cognitive Perspective Cognition refers to mental activities associated with processing, interpreting, understanding, and communicating information. Cognitive Psychology studies: Concept Formation Problem Solving Decision Making Judgment Formation How We Think For Classification /Efficiency Purposes Humans Create: Concepts: mental grouping of similar objects , events, ideas, or people. Concepts are often organized into hierarchies. Types of Concepts How We Think Humans usually form concepts by creating a: Prototype: mental image or best example of a category. Allows us to incorporate items easily. To most people, a robin is “birdier” than a Penguin An Item’s Failure To Match Prototype Leads to Trouble Classifying It. Methods of Problem Solving 1. Trial and Error: guess and check Methods of Problem Solving 2. Algorithm: methodical, logical pattern or procedure that guarantees solving of a particular problem. Looks at all possible combinations or has specific formula to solve the problem. Methods of Problem Solving 3. Heuristics: “common sense” or rule of thumb strategies which allow us to solve problems efficiently and usually quickly. Short-cuts that involve our preconceptions. Who would you rather have baby sit your child? Answer is based on your heuristic for appearance. Algorithms vs. Heuristics Unscramble SPLOYOCHYG -Algorithms go through all 907,208 combinations -Heuristics would take out YY, etc. -Other heuristics? Methods of Problem Solving Insight: sudden realization of how to solve a problem without a real strategy involved. The Light-Bulb going off when you get an idea. Kohler’s Chimpanzee Study Illustrates Insight Obstacles to Problem Solving Confirmation Bias: human tendency to search for information that confirms your preconceptions Study: 2 What is the pattern? 4 6 Obstacles to Problem Solving Fixation: refers to the inability to see a problem from a new perspective. How would you arrange six matches to form 4 equal lateral triangles? Solution to Matchstick Problem Obstacles to Problem Solving Mental Set: tendency to approach a particular problem in a particular way. You usually use strategies that have been successful in the past at solving problems even though it may not be most efficient strategy for the new problem. The Three Jugs Problem Solution to the Jugs Problem B-A-2C=desired amount of water. Problem 6 & 7 had easier solutions though which were probably blocked by mental set. 6 & 7 Solution Candle Mounting Problem Using these materials, how would you mount the candle on a bulletin board? Candle Mounting Solution Inability to solve this problem may result from functional fixedness. Have to recognize that a box need not always serve as a container Obstacles to Problem Solving Functional Fixedness: tendency to think of objects only in terms of their usual functions. CAN EQUAL Possible Obstacles to Problem Solving Representative Heuristic: “common sense” way of judging likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to match our prototypes. May lead us to make incorrect assumptions. Example of Representative Heuristic Errors Below is Linda, she loves books and hates loud noises. Is she more likely to be a librarian or a beautician? Possible Obstacles to Problem Solving Availability Heuristic: judging the likelihood of an event based on how readily the event comes to mind. Availability Heuristic Can Lead Us to Irrationally Fear Things Which Are Unlikely. EX: People are tend to be more fearful of the dangers of airplane travel than of traveling in an automobile. EX: People are tend to be more fearful of being raped by a stranger even though it is more likely they will be raped by someone they know. Overconfidence Decision Making: Overconfidence When making decisions, humans tend to be overconfident in their decisions and abilities. On questions where 60% of respondents answer correctly, respondents usually feel 75% confident. Influences on Decision Making Framing: refers to the way an issue is posed; can drastically effect decision making. Best way to market ground beef: 25% fat OR 75% lean? Influences on Decision Making Belief Bias: the way pre-existing beliefs can distort logical reasoning; can make invalid conclusions seem valid, or valid conclusions seem invalid. Decisions influenced by subject matter. Is the following a valid Conclusion: 1. Democrats support free speech. 2. Dictators are not democrats. Conclusion: Dictators do Not support free speech. Influences on Decision Making Belief Perseverance: Once we have decided that we believe something, we will tend to keep on believing it, even in the face of disconfirming evidence. Riddles1. What is the next number in the series: 10,4,3,11,15….? A. 14 B. 1 C. 17 D.12 2. What is so unusual about the sentence below Jackdaws love my big sphinx of quartz 3. How can you physically stand behind your father while he is standing behind you? 4. What occurs once in every minute,twice in every moment,yet never in a thousand? 5. Can you translate the following into a sentence? 100204180