Evolution Vocabulary Worksheet: Definitions & Examples
advertisement
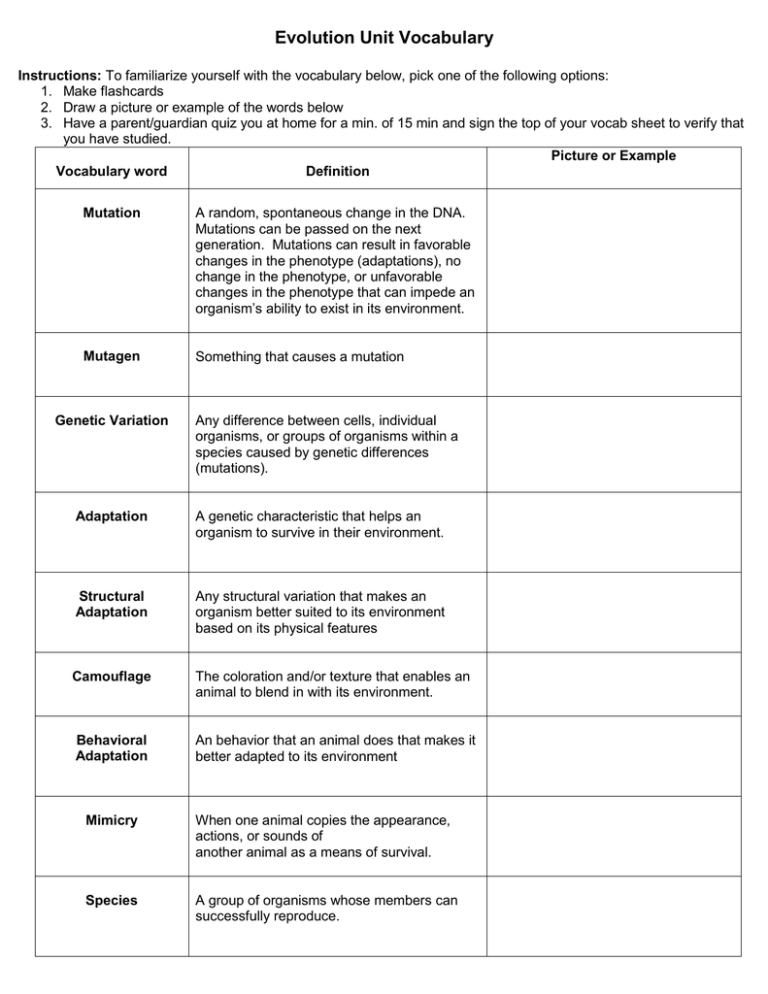
Evolution Unit Vocabulary Instructions: To familiarize yourself with the vocabulary below, pick one of the following options: 1. Make flashcards 2. Draw a picture or example of the words below 3. Have a parent/guardian quiz you at home for a min. of 15 min and sign the top of your vocab sheet to verify that you have studied. Picture or Example Vocabulary word Definition Mutation A random, spontaneous change in the DNA. Mutations can be passed on the next generation. Mutations can result in favorable changes in the phenotype (adaptations), no change in the phenotype, or unfavorable changes in the phenotype that can impede an organism’s ability to exist in its environment. Mutagen Something that causes a mutation Genetic Variation Any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms within a species caused by genetic differences (mutations). Adaptation A genetic characteristic that helps an organism to survive in their environment. Structural Adaptation Any structural variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment based on its physical features Camouflage The coloration and/or texture that enables an animal to blend in with its environment. Behavioral Adaptation An behavior that an animal does that makes it better adapted to its environment Mimicry When one animal copies the appearance, actions, or sounds of another animal as a means of survival. Species A group of organisms whose members can successfully reproduce. Population All the individuals of one species in a given area. Speciation The process by which two populations of the same species become so different that they can no longer interbreed. Natural Selection Limiting Factors Carrying Capacity The process by which organisms with favorable traits survive and reproduce at higher rates than organisms without the favorable trait Needed resources that are in limited supply. Organisms compete for limiting factors and those best able to obtain limiting factors are usually the organisms that are able to survive and reproduce. The largest population that a given environment can support over a long period of time. Extinction When a species of dies out completely. Evolution The process by which populations accumulate inherited changes over time. Vestigial Structure A body part that has become small and lost its use because of evolutionary change. Embryonic Structures The anatomical (body) parts that make up an organism in the early stages of development Fossil The solidified remains or imprints of a onceliving organism. Fossil Record Radiometric Dating (Carbon Dating) A historical sequence of life indicated by fossils found in layers of the Earth’s crust. The process of measuring the absolute age of geologic material by measuring the concentrations of radioactive isotopes and their decay products. Charles Darwin British naturalist who studied Galapagos finches and helped develop the theory of evolution microevolution Change within a population which can be observed generation to generation macroevolution Change in a population resulting in the formation of a new species. Macroevolution cannot be observed because it may takes too long to occur







