Our Solar System
advertisement

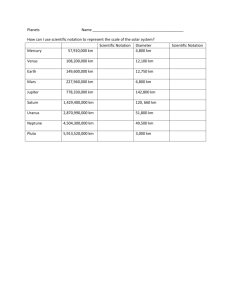
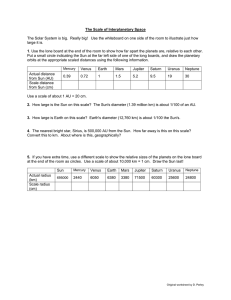
Honors Earth Science Ms. Touve 2015 Name: Block: Date: Our Solar System I. General Overview & Summary A. Characteristics of the Inner Planets (also called the planets) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. B. What separates the inner and outer planets? C. Characteristics of the Outer Planets (also called the giants) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. D. Why does Pluto not fit into either of the two groups of planets? planets or II. The Planets A. Mercury 1. What are the two main features of Mercury’s surface? 2. What causes Mercury’s surface temperature to change so drastically? 3. (True/False) Mercury is larger than Earth’s moon. 4. What is it called when planets, viewed from Earth, cross the face of the Sun? B. Venus 1. How is Venus’ direction of rotation unique? 2. (True/False) Venus’ day is longer than its year. 3. What are three key features of Venus’ surface? 4. Describe Venus’ atmospheric composition and temperature. C. Earth 1. (True/False) Earth is smaller than Venus, also called our “sister planet”. 2. Which season in the Northern hemisphere is the Earth the closest to the sun? What is this called? 3. What do satellite observations help scientists predict? 4. Name three benefits of our atmosphere. 5. Name the solstices and equinoxes and the dates that they occur. D. Mars 1. Why does Mars have seasons like the Earth? 2. Mars has ice caps made of . 3. Describe Mars’ atmospheric composition and temperature. 4. Differential heating of Mars’ atmosphere causes strong storms. 5. What are three key features of Mars’ surface? 6. What is the name of the largest volcano in the solar system? E. Jupiter 1. What is the Great Red Spot on Jupiter’s surface? 2. What are all of the dark and light belts on the ‘surface’ of Jupiter? 3. (True/False) Jupiter has rings. 4. What is the name of the largest moon in the solar system and the only one to have its own magnetic field? 5. Who discovered Jupiter’s four largest moons, Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto? F. Saturn 1. What are the colored belts on Saturn? 2. What is Saturn’s ring system made up of? 3. How does Saturn’s density compare to that of the other planets of the Solar System? How does the density compare to water? 4. Who discovered Saturn? G. Uranus 1. When was Uranus discovered? Why was it not discovered before then? 2. How is the axis of rotation of Uranus different than that of the other planets? What is the explanation scientists give for this? 3. (True/False) Uranus has rings. 4. Which planet is nearly a ‘twin’ to Uranus? 5. What gives Uranus its blue-green coloring? H. Neptune 1. Describe the composition and temperature of Neptune’s atmosphere. 2. Why will Neptune and Pluto never crash into each other? 3. Describe Neptune’s winds. 4. How was the Great Dark Spot that once circled Neptune like the spot on Jupiter? 5. (True/False) Neptune has rings. I. Pluto & other Dwarf Planets 1. How does the atmosphere of Pluto vary as it nears the Sun? 2. (True/False) Pluto is larger than our moon. 3. What is the composition of the ice that covers Pluto’s surface? 4. What is Pluto’s relationship with its largest moon, Charon? 5. List some characteristics of dwarf planets. III. Other Celestial Bodies in Our Solar System A. Earth’s Moon (Use chapter 25) 1. How many theories of the moon’s formation are there? What is the current theory? 2. The large, dark areas are called and were formed by what? 3. What are the lunar highlands called? 4. What is the major cause of erosion of the Moon’s surface today? 5. What is the moon’s orbital period and what period of time on the Earth’s calendar is it related to? 6. Compare and contrast a lunar and solar eclipse. 7. (True/False) We see the same side of the moon. 8. Describe apogee and perigee. B. The Sun (Use chapter 26.1) 1. Size, Energy, & Layers a. How many Earths would fit inside the sun? b. How long does it take light to travel to Earth? c. The sun contains % of the solar system’s mass. d. How far away from Earth is the sun? (on average) e. Fusion of f. into gives the sun its energy Fill out the following chart of the sun’s layers: 1 Layer Core Temperature (°C) 2 Radiative Zone 3 Convective Zone 4 Photosphere 5 Chromosphere 6 Corona Features (list) g. The surface of the sun is called the h. (True/False) The temperature of the sun’s atmosphere increases as you move out from the surface. i. The is the super hot, outer layer of the sun that can only be viewed during a solar eclipse. 2. Features a. are cooler, dark spots on the photosphere. b. What is the length of time in which the number of sunspots go from one solar maximum to the next? c. (True/False) During solar maximum, the activity on the Sun’s surface (solar flares and prominences) increases. d. What is the solar wind and how does it affect the Earth? e. What are granules? f. Describe solar prominences. C. Asteroids, Comets, Meteors 1. Fill out the following chart comparing the three: Object Asteroids Composition Location in Solar System Comets Meteors 2. (True/False) Some asteroids have moons. 3. What are the three parts of a comet? 4. A comet’s tail always faces , , from the sun. 5. What is the difference between a meteor and meteoroid? 6. Where do meteors come from? 7. How are meteors named? 8. When a meteoroid reaches the ground it’s called a 9. What is the Oort Cloud and where is it located? 10. What is the Kuiper Belt and where is it located? . Planetary Fact Sheet Mercury Mass (kg) Diameter (km) Density (g/cm3) Gravity (m/s2) Escape Velocity (m/s) Period of Revolution (compared to Earth) Length of Day (compared to Earth) Distance from the Sun (au) Number of moons Name and date of satellites that have explored the planet Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto