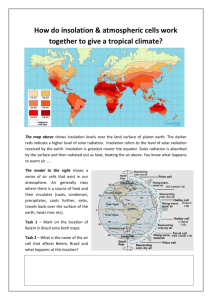
Topic/Objective:_______________ Full Name: _______________________________ _____________________________
advertisement

Tutor Use Only: Topic/Objective:_______________ Full Name: _______________________________ _____________________________ Class: ___________________ _____________________________ Date: _________________ Period: _____ Essential Question: Atmosphere (Chapter 17) Composition of the Atmosphere Major Constituents (99%): o Nitrogen: 78% o Oxygen: 21% Other : 1% Movement of Heat Energy Radiation: the transfer of energy through space in the form of electromagnetic waves Convection: the transfer of heat energy in a liquid or gas through the motion caused by difference in density. Conduction: the transfer of heat energy through collisions of the atoms or molecules of a substance. Heat and Temperature Temperature: is a measure of the average kinetic energy of atoms or molecules in the substance. Heat: the total kinetic energy of all of the particles of the substance. Layers of the Atmosphere: Troposphere: Lowest region of the atmosphere Where weather occurs Contains 99% of the water vapor and 75% of the atmospheric gases. Temperature decreases with altitude. Top of the troposphere is the tropopause. Stratosphere: 15 to 50 km altitude Heating occurs because of ozone (O3) absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. Summary: Essential Question: Temperature increases with altitude due to ozone absorbing ultraviolent radiation. Top of the stratosphere is known as the stratopause. Mesosphere: 50 to 90 km altitude Temperature decreases with altitude. Lowest temperature in the entire atmosphere are found at in this layer. Top of the mesosphere is known as the mesopause. Thermosphere: 90 to 500 km in altitude. Temperature increase with altitude above 90 km, and become constant about 200 km. Heating due to absorption of solar radiation. Highest temperatures in the atmosphere can be found in this layer. Ionosphere: Occurs within the mesosphere and thermosphere between 90 and 500 km. Layer of electrically charged particles. Effected by solar events Auroras, (Northern and Southern lights). Exosphere: The outer most layer of the atmosphere. Temperature in the exosphere increases with altitude Satellites orbit Earth in the exosphere. Insolation and the Atmosphere Insolation: incoming solar radiation. o Some solar radiation is absorbed by gasses in the atmosphere. o Some solar radiation reaches Earth’s surface. o Some solar radiation is researches in the atmosphere and is returned to space. Heat Budget of Earth and the Atmosphere 50% of solar radiation (insolation) reaches the Earth’s surface. o Small % of insolation is absorbed by the atmosphere. energy is transferred by o radiation o conduction o convection o evaporation o condensation of water Summary: Essential Question: energy transfer is the major cause of Earth’s weather. carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor o absorbs most of the infrared radiation o preventing from radiating back into space, creating the Greenhouse effect. Without the Greenhouse effect Earth o most of the heat energy would be lost to space. o Earth’s average temperature would be about 33o cooler o Increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes Earth’s heat budget to be out of balance and Global Warming. Temperature variations due to Insolation Intensity of insolation varies due to: o time of day o latitude o time of year color affects how much insolation is absorbed and how the absorbed energy affects the temperature. Intensity of Insolation Intensity of insolation is dependent on the angle at which the sun rays strike Earth’s surface. The sun at 90o, Earth receives the maximum amount of energy o Occurs at noon, Earth’s surface heats up quickly As the angle of insolation decreases the amount of energy received decreases. Intensity of insolation is affected by the amount. o Closer to the equator the sun rays are almost vertical (90o), climate is hotter o Moving either north or south of the equator the angle of insolation decreases, the energy spread out over a larger area, climate is colder At mid-latitudes (this is where the U.S. is located), o sun’s rays are nearly vertical (90o) in the summer; summers are hot. o winter the angle of insolation is at its lowest; winters are cold. Northern Hemisphere o Greatest angle of insolation occurs around June 21st, thus July is the warmest month o Lowest angle of insolation occurs around December 21st, thus January is the coldest month o The southern hemisphere is the reverse Summary: Essential Question: Human Impact on the Atmosphere: Acid Rain: Forms due to pollutants o sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide react with water vapor. Acidity is measured by pH. o The lower the pH the more acidic the rain. Smog Temperature inversion; when the temperature at the Earth’s surface is cooler than the air above it, convection does not occur. Ozone Depletion Hole in ozone due to pollution of chlorofluorocarbons’ (CFCs). Thin ozone/hole forms each spring over Antarctica Thinning Ozone/hole allows for exposure to ultraviolet radiation which is dangerous to living things. Summary: