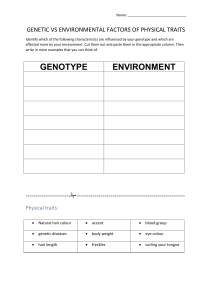
Unit 8: Application of Genetics
advertisement
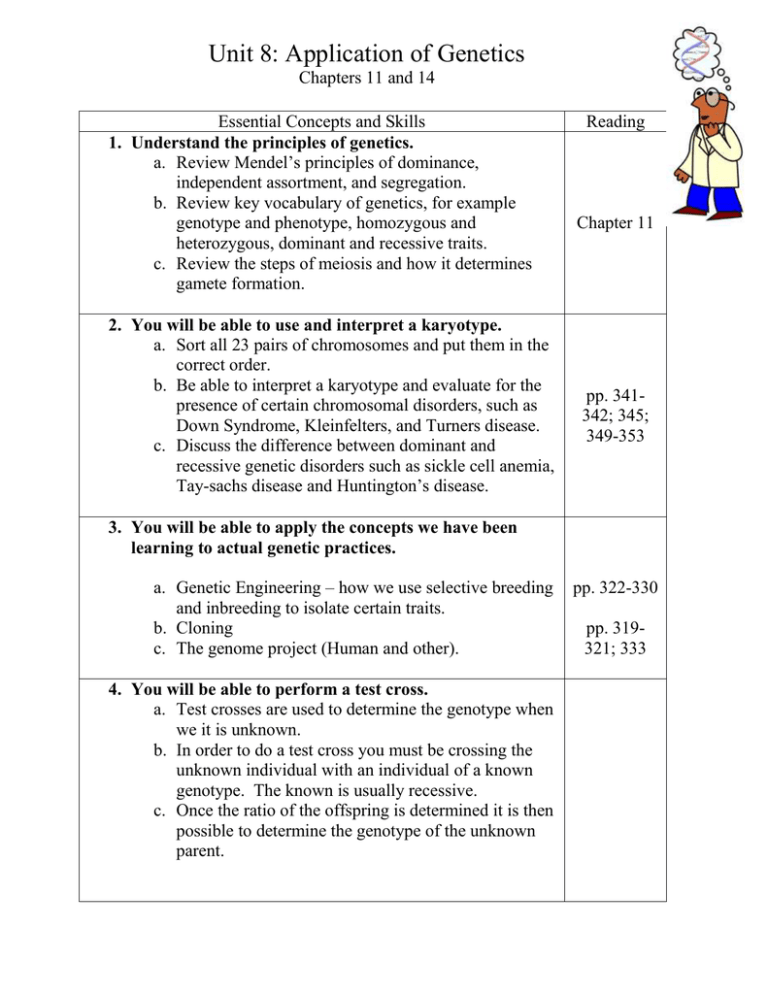
Unit 8: Application of Genetics Chapters 11 and 14 Essential Concepts and Skills 1. Understand the principles of genetics. a. Review Mendel’s principles of dominance, independent assortment, and segregation. b. Review key vocabulary of genetics, for example genotype and phenotype, homozygous and heterozygous, dominant and recessive traits. c. Review the steps of meiosis and how it determines gamete formation. 2. You will be able to use and interpret a karyotype. a. Sort all 23 pairs of chromosomes and put them in the correct order. b. Be able to interpret a karyotype and evaluate for the presence of certain chromosomal disorders, such as Down Syndrome, Kleinfelters, and Turners disease. c. Discuss the difference between dominant and recessive genetic disorders such as sickle cell anemia, Tay-sachs disease and Huntington’s disease. Reading Chapter 11 pp. 341342; 345; 349-353 3. You will be able to apply the concepts we have been learning to actual genetic practices. a. Genetic Engineering – how we use selective breeding and inbreeding to isolate certain traits. b. Cloning c. The genome project (Human and other). 4. You will be able to perform a test cross. a. Test crosses are used to determine the genotype when we it is unknown. b. In order to do a test cross you must be crossing the unknown individual with an individual of a known genotype. The known is usually recessive. c. Once the ratio of the offspring is determined it is then possible to determine the genotype of the unknown parent. pp. 322-330 pp. 319321; 333 5. You will be able to construct and interpret a pedigree. a. A pedigree chart is used to study the passing of traits through a number of generations. b. Pedigrees are most often used to show the inheritance of desired traits (such as eye color) or of certain diseases (such as sickle cell anemia). pp. 342-343 Assessments: Build a Baby Karyotype kit or paper model +/- Genetic Application Debate Create a Pedigree