Name: __________________________ Date: _________________
advertisement

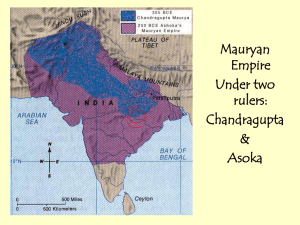
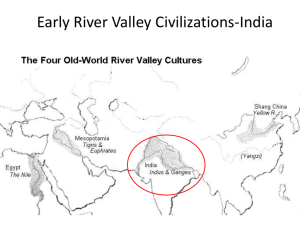
Name: __________________________ Date: _________________ Period: _____ Chapter 7.1 Reading Quiz 1. Who was Chandragupta Maurya? (Time Period, Location, Key Achievements) 321BCE: became king of Magadha, (northern India), began the Mauryan Empire Expanded territory, fought against Seleucus Raised huge army…heavily taxed peoples…set up bureaucracy…divided empire into 4 parts…advised by Kautilya 2. Who was Asoka? (Time Period, Location, Key Achievements) Grandson of Chandragupta Maurya…took over in 269BCE…ruled Mauryan Empire (India)…converted to Buddhism, helped spread Buddhism, Asoka’s Edicts 3. Who was Chandra Gupta I (Time Period, Location, Key Achievements) Married into a powerful family and came to power in AD 320 (India) Began the Gupta Empire “Great king of kings” Chapter 7.1 First Empires of India I. Chandragupta Maurya Builds an Empire Believed to have been born in the powerful kingdom of Magadha, (on lower Ganges River). 321BCE: Chandragupta Maurya had gathered an army, killed the Nanda king, and claimed the throne, beginning the Mauryan Empire A. Chandragupta Unifies North India Chandragupta then moved northwest, seizing all the land from Magadha to the Indus 305BCE: Chandragupta began battling Seleucus I (one of Alexander the Great’s generals who had inherited the eastern part of Alexander’s empire) o Seleucus I was trying to reassert Greek control over the Indus Valley o Chandragupta finally won…gained territory o By 303BCE- Mauryan Empire stretched more than 2,000 miles and united northern India politically for the first time. Chandragupta had raised a large army: 600,000 soldiers on foot, 30,000 soldiers on horseback, 9,000 elephants. Government levied high taxes to pay for this army o Farmers paying up to ½ value of crops to the king o Also heavily taxed income from trading, mining , and manufacturing B. Running the Empire Chandragupta relied on his advisor, Kautilya (a Brahmin). Kautilya wrote the book, Arthasastra, about how to hold a vast empire together o Arthasastra- proposed very tough-minded policies…army of spies, attack weak neighbors…influenced later thinkers like Machiavelli. o “The welfare of the king does not lie in the fulfillment of what is dear to him; whatever is dear to the subjects constitutes his welfare.” Chandragupta created a highly bureaucratic government, carefully chose officials and had them closely supervised o Chandragupta divided the empire into four provinces, each headed by a royal prince o Province then divided into local districts, whose officials assessed taxes and enforced the law C. City Life and Country Life Seleucus sent an ambassador, Megathenese, to Chandragupta’s capital…ambassador was very impressed o Megathenese “Farmers are exempted from military service and cultivate their lands undisturbed by fear” 301BCE: Chandragupta’s son assumed the throne and ruled for 32 years, then his grandson, Asoka took over and brought the Mauryan Empire to its greatest heights D.Asoka Promotes Buddhism Asoka became king of Mauryan Empire in 269BCE At first, he followed Kautilya’s advice, and waged war to expand his power into Kalinga…about 100,000 soldiers were slain and even more civilians Asoka felt sorrow over the slaughter at Kalinga…he then began studying Buddhism, and decided to rule by Buddha’s philosophy of nonviolence, “peace to all beings” Asoka erected stone pillars throughout the empire, inscribed with new policies inspired by Buddhism Asoka’s Edicts o Nonviolence, just rule, religious toleration Asoka also improved the infrastructure of India, with extensive road system…and made roads safer and travel easier, thus improving communication…trees for shade, wells every 9 miles, rest houses After Asoka died in 232BCE, the Mauryan Empire began to break up II. A Period of Turmoil After Asoka’s death, there was a power vacuum…regional kings challenged the imperial government…kingdoms in central India regained independence o Andhra Dynasty arose and dominated central India…profited from trade with Rome, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia Northern India suffered wave after wave of new people fleeing political instability: Greeks, Persians, Central Asians…cultural diffusion, and disruption Southern India- turmoil- 3 kingdoms that had never been conquered by the Mauryans…spoke Tamil language…fought against eachother and other states III. The Gupta Empire After 500 years of invasion and turmoil, strong leader emerged in northern state of Magadha…Chandra Gupta (no relation to earlier Chandragupta Maurya) Established the 2nd empire- Gupta Empire- great flowering of Indian civilization, especially Hindu culture A. Chandra Gupta Builds an Empire Came to power by marrying the daughter of an old, influential royal family…took the title of “Great King of Kings “ in AD 320 o Empire included Magadha, area to north, and central region of Ganges River Chandra Gupta I’s son, Samudra, became king in AD 335…loved poetry, music, and war o Samudra expanded the empire with 40 years of conquest B. Daily Life in India First period that we have a lot of info about daily life in India Small villages: craftspeople and merchants clustered in specific districts…shops on street level and residence above Majority of villagers were farmers…walked daily from towns to outlying fields Most Indian families were Patriarchal, headed by eldest male. Farmers had to irrigate crops, tax on water, had to donate day’s worth of labor each month to maintain wells, roads, etc (corvee) Southern India followed different cultural pattern…some Tamil groups were matriarchal, (mother was head of the family…property and throne was passed through family line) o Famous queen of the Pandyas C. Height of the Gupta Empire Chandra Gupta II(Royal court of the 3rd Gupta Emperor was a place of great excitement Chandra Gupta II: defeated the Shakas (enemy kingdom to the west coast)…then able to participate in valuable trade with the Mediterranean World Chandra Gupta II also strengthened his empire by negotiating diplomatic and marriage alliances o Ruled for 40 years o Faxian, Chinese Buddhist, recorded that his subjects seemed happy o After death of Chandra Gupta II, another wave of invaders threatened northern India (Hunas/ White Huns/ Huns) o Over next 100 years, Gupta Empire broke into small separate kingdoms, which were then overrun by the Huns and other Central Asian nomads.