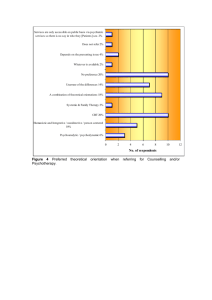
We’ve looked at how specific disorders • each of the major perspectives
advertisement

Therapy: Psychotherapy - background Treatment – general • We’ve looked at how specific disorders are explained and treated, based on each of the major perspectives • This part is looking at treatment in general; these are often treatments used to treatment a variety of mental illnesses. Therapy: Psychotherapy - background Psychotherapy - background Psychotherapy • Psychological therapy • Interaction between: • trained therapist • sufferer of psychological difficulties • Can be: • Alone • Group • Many varieties Therapy: Psychotherapy - background Psychotherapy - background Eclectic • Using a combination of different therapies, techniques • Most common • Rarely is one technique ever used • Any course of treatment usually involves therapy and another treatment Therapy: Psychotherapy - background Psychotherapy - background Eclectic • Using a combination of different therapies, techniques • Most common • Rarely is one technique ever used • Any course of treatment usually involves therapy and another treatment Example: Therapy & biochemical Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Classical Psychoanalysis •Sigmund Freud •Uses: •Projective tests •Free association •Dream interpretation •Rare Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Psychodynamic Therapy •Related to Psychoanalysis •Uses Freud’s ideas, but not as strict •Neo-Freudians •Unconscious & childhood important Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Transference •Feelings, conflicts, etc. transferred to the therapist •Hate of father, love of sister-in-law, etc. Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Transference •Feelings, conflicts, etc. transferred to the therapist •Hate of father, love of sister-in-law, etc. Resistance •Blocking from conscious painful memories, etc •“Being difficult” Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Humanistic Humanistic Psychotherapy • “Client-centered therapy” • Uses active listening • Unconditional positive regard • Find out what is troubling in the here and now • Responsibility on individual • Carl Rogers Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Psychoanalysis & Psychodynamic • If understand root of problem, then can determine best way to solve Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Behavioral therapy • Interested in treatment, not cause • Most psychological problems - learned behaviors • Learning new behaviors can eliminate unwanted ones Psychoanalysis & Psychodynamic vs. Humanistic & Behavioral Psychoanalysis & Psychodynamic vs. Humanistic & Behavioral Psychoanalysis & Psychodynamic • Need to find cause of problem before it can be treated. Psychoanalysis & Psychodynamic vs. Humanistic & Behavioral Psychoanalysis & Psychodynamic • Need to find cause of problem before it can be treated. Humanistic & Behavioral therapy • Interested in treatment, not cause Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Cognitive therapy • Psychological disorders come from maladaptive thinking • Teaches new, more adaptive ways of thinking and acting Issues with cognitive therapy: • Difficult for most people to change their way of thinking • People suffering from depression, anxiety, etc.? Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Cognitive therapy: Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) • When we have an emotional reaction (getting upset, becoming happy, etc.) because of an event: • it is not the event that upsets us, etc., • it is the beliefs that we hold that cause us to become depressed, anxious, enraged, etc. People associated: Albert Ellis Aaron Beck Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Cognitive therapy: Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) The ABC Model A. Something happens. B. You have a belief about the situation. C. You have an emotional reaction to the belief. For example: A. Your employer falsely accuses you of taking money from her purse & threatens to fire you. B. You believe, “She has no right to accuse me. She's a jerk!” C. You feel angry. Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Cognitive therapy: Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) The ABC Model A. Something happens. B. You have a belief about the situation. C. You have an emotional reaction to the belief. Instead… For example: A. Your employer falsely accuses you of taking money from her purse & threatens to fire you. B. You believe, “She is angry about the lost money; she’s not really mad at me.” C. You feel empathy. Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) Albert Ellis Aaron Beck Therapy: Psychotherapy – varieties Psychotherapy – varieties Other psychotherapy •Group therapy •Self-help organizations •Family therapy Therapy: Biological Therapy Biological Therapy – Electroconvulsive Therapy Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) • Often referred to as “electroshock therapy” • Passing electrical current through brain to treat illness • Now: treat major depression • Disrupts Long term potentiation effects short term memory Therapy: Biological Therapy Biological Therapy – Electroconvulsive Therapy Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Types: • Magnetic seizure therapy (MST) • Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) • Deep brain stimulation (DBS) Therapy: Biological Therapy Biological Therapy – Psychosurgery Psychosurgery • Destruction of brain tissue to treat disease • Now only used as last resort Types: • Prefrontal lobotomy • Severing corpus callosum (epilepsy) Therapy: Biological Therapy Biological Therapy – Psychosurgery Social control • Not treating person • Controlling them • Usually lobotomy & electroshock therapy • Now considered primitive Therapy: Biological Therapy Biological Therapy – Psychosurgery Deinstitutionalization • Under normal circumstances, would be treated in a mental hospital • Strong support system (family, etc.), instead treat them at home or halfway house • Familiar surroundings seen as beneficial Therapy: Biological Therapy Biological Therapy – Chemotherapy/Biomedical Chemotherapy/Biomedical •Medication •Most common Agonist •Increase amount of neurotransmitter absorbed by post-synaptic neuron Antagonist •Decrease amount of neurotransmitter absorbed by post-synaptic neuron