WOODLAND HILLS SECONDARY LESSON PLANS

Name: Andrew Pollick
Date:2/2/15
WOODLAND HILLS SECONDARY
LESSON PLANS
Content Area: Algebraic Concepts
Length of Lesson: 5 days
Lesson Topic (Modules, if applicable):
Linear Functions
Student Objectives (Competencies/Outcomes):
Students will be able to:
1.
Find the slope of a line.
2.
Use the rate of change to solve problems.
3.
Solve problems involving direct variation, write and graph.
4.
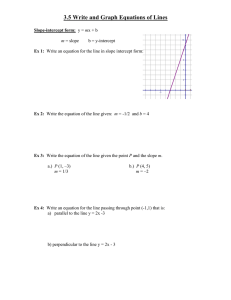
Write and graph linear equations in slopeintercept form.
5.
Write the equation of a line given the slope and one point.
6.
Write the equation of a line given two points.
7.
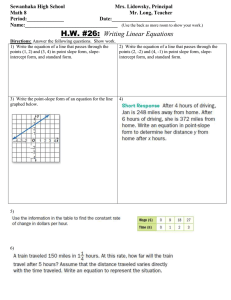
Write linear equations in multiple forms
(slope-intercept, standard, and point-slope).
8.
Write the equation of a line parallel/perpendicular to a given line, through a given point.
9.
Interpret points on a scatter plot and write an equation for a line of best fit.
(2 days review, 1 enrichment, 1 assessment)
Big Ideas:
STAGE I – DESIRED RESULTS
M11.D.2.1 Solve and/or graph linear equations and inequalities using various methods.
M11.D.3.1 Describe and/or determine change.
M11D.3.2 Compute and/or use the slope of a
Understanding Goals (Concepts):
Students will study the nature of linear functions in this unit. They will use their algebraic skills to identify and graph a linear knowing only two points, or a point and the slope. They will relate these skills to everyday realworld data. line.
M11.D.4.1 Interpret and/or use linear, quadratic and/or exponential functions and their equations, graphs or tables.
Essential Questions:
Why is it important to know the equation of a relationship?
Why would slope be important in careers such as architecture?
Where do we see evidence of slope on the interstates?
What does rise over run really mean? Relate it to real life.
Relate slope to plumbing and your shower… your height… the length of the shower.
How is slope correlated to direct variation?
How is slope and y-intercept related to a “start up” fee?
How can slope-intercept be used to form predictions?
How can you use slope-intercept form to write the equation of a line?
What about two slopes makes the lines parallel?
Perpendicular?
How can scatter plots help to predict trends?
Vocabulary:
Line of best fit, Positive correlation, negative correlation, Constant of variation ( proportionality), Rate of change, Direct variation, Slope, Interpolate, extrapolate,
Slope-intercept form, Point-slope form,
Parallel, perpendicular lines
STAGE II – ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
Performance Task:
Students will participate in class discussions, guided practice, computer work, and whiteboard activities
Formative Assessments:
Students will actively participate in class examples, discussion, class work, whiteboards, open ended assessments, graphic organizers, exit tickets, daily warm ups, homework, Study Island (or what is currently available) and unit tests, quizzes,
and other formative assessments.
Materials and Resources:
Chapter 3: Glencoe Text)
Unit 1 (Algebra Rescue Text)
Warm ups & Exit polls (daily)
Homework (daily)
Guided practice and Enrichment from Glencoe Grab & Go workbooks
Additional materials as needed
Positive/ negative counters
Number lines, etc.
Instructional Procedures*:
Monday
2/2 Day A
Review Friday’s Test
Do Now – into slope/rate/change
Lesson – Solving slope & rate of change
Tuesday
2/3 Day B
DO NOW- check homework assignments
Mini lesson – 10 minute review slope/ rate change.
Practice with partner –
Problem Set
STAGE III – LEARNING PLAN
Interventions:
Think Through Math, Study Island, A+ Math (if available), Math Lab, Online Self Check
Quizzes and Tests
Wednesday
2/4 Day A
DO NOW- check homework assignments
Mini lesson – 10 minute review slope Rate change.
Practice with partner –
Problem Set
Thursday
2/5 Day B
Review for Friday’s assessment
Friday
1/30 Day B
DO NOW – mini review
– Ch 5
Formative assessments –
25 question test
Intro to Multistep eqn problems – no more than 5
Problems not completed in class
Problems not completed in class
Review for Friday Test
Any assignments missed from the week
*Include Do Now, Mini Lesson, Guided Practice, Independent Practice, Summations/Formative Assessments, Reflections