STUDY GUIDE TEST DATE: _________________________________ MATCHING:
advertisement

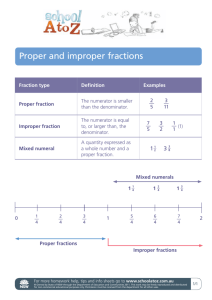
STUDY GUIDE Name ________________________________________________ Math 6 - Unit 2 Fractions Operations & Modeling TEST DATE: _________________________________ MATCHING: Match the term or phrase with the best definition. a. Proper fraction f. Improper fraction b. Mixed number g. Equivalent fractions c. Numerator h. Common denominator d. Simplest form i. Denominator e. Fraction ____ 1. Expresses a part of a whole; has a numerator and a denominator. ____2. A whole number and a fraction. ____3. When the numerator is larger than the denominator. ____4. A fraction is in __________________ when the numerator and the denominator have no common factor other than 1. ____5. When the numerator is smaller than the denominator. ____6. Fractions that name the same number or are of equal value. ____7. When the denominators in two or more fractions are the same. ____8. The top part of the fraction is called the ________________. Write each fraction in simplest form. To simplify a fraction, find the Greatest Common Factor of both the numerator and denominator, then divide both by that number. 12 9. 10. 60 14 32 Write each mixed number as an improper fraction. When converting a mixed number to an improper fraction, multiply the denominator and whole number, then add the numerator to the product to get the new numerator. The denominator stays the same. 11. 3 5 2 12. 2 8 7 Write each improper fraction as a mixed number. When converting an improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number, the remainder is the numerator and the denominator remains the same. Simplify the fraction if necessary. 13. 14 14. 3 21 4 Use <, >, or = to compare the fractions. Before comparing or ordering fractions, each fraction must have common denominators. In order to find common denominators, find the least common multiple of each denominator. Whatever the denominator must be multiplied by to become the least common denominator, must be multiplied to the numerator as well. Once the denominators are the same, compare or order the numerators. 15. 2 7 _____ 5 7 16. 6 8 _____ 3 17. 4 Order the fractions from least to greatest. 18. 7 1 3 , , 8 4 4 19. 1 9 1 , , 2 12 3 2 3 _____ 3 12 20. Order the fractions from greatest to least. 1 8 , , 7 5 10 20 Add or Subtract. Write your answers in simplest form. Each fraction must have common denominators before they can be added or subtracted. 21. 23. 3 5 1 4 + 1 22. 5 +2 2 3 2 2 9 3 25. 1 - 24. 26. 2 4 3 6 1 + 7 8 - 3 8 1 3 3 5 2 -1 Multiply. Write your answers in simplest form. To multiply fractions, find the product of the numerators and the product of the denominators. 27. 31. 𝟏 𝟐 x 𝟐 𝟐 𝟓 𝟓 𝟔 1 x 28. 𝟑 32. 𝟏𝟐 𝟏𝟑 × 𝟐𝟔 29. 𝟐𝟒 𝟕 𝟖 𝟗 𝟏𝟎 𝟕 × 𝟏𝟎 33. 𝟐 𝟑 𝟒 𝟖 2 x1 𝟒 𝟗 𝟖× 30. ×𝟑 𝟑 𝟏𝟐 𝟑 𝟒 𝟓 𝟗 34. 𝟑 × 𝟒 Divide. Write your answers in simplest form. We never “divide” fractions. Instead we MULTIPLY the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. REMEMBER: “Keep, Change, Flip.” Keep the first fraction the same, change the division sign to a multiplication sign, and flip the second fraction (the denominator becomes the numerator and the numerator becomes the denominator; this is called the reciprocal). 35. 38. 𝟑 𝟓 ÷ 𝟑÷ 𝟔 𝟖 𝟒 𝟗 36. 39. 𝟒 𝟗 ÷𝟑 𝟒 𝟐 𝟓 𝟏𝟎 2 ÷1 𝟑 𝟑 𝟒 𝟖 37. 1 ÷ 40. 2 ÷1 𝟏 𝟑 𝟒 𝟖 Modeling – Write AND Solve a division problem to describe the following models. 41. 43. 42. 44. Write AND Solve a multiplication problem to describe the following models. 45. 46. Draw a model and solve. 47. 49. 𝟐 ÷ 𝟑 𝟒 × 𝟏 𝟒 𝟐 𝟑 48. 50. 𝟑 𝟏 𝟑 𝟏 𝟒 ÷ × 𝟑 𝟒 𝟏 𝟑