Addition Subtraction
advertisement

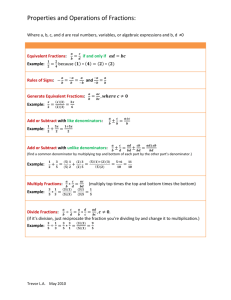
Addition Keywords: Add Altogether And Both How many How much In all Increased by Plus Sum Together Total Subtraction Keywords: Subtract Difference Fewer How many more How much more Left Less Minus Need to Remains Words ending in –er. (example: how much heavier.) Students should be able to read word problems and pull out the keywords and numbers being used to solve the problem. Example: Marcus went to the grocery store to buy some snacks. He bought a drink for $1.25, a candy bar for $2.45, and two different types of lunchables, each for $4.19. If he paid the clerk with a $20 bill, how much change will Marcus get back? To get the answer students would need to solve a multi-step problem. Add $1.25 + $2.45 + $4.19 + $4.19 altogether. Then you would have to subtract the answer which is: $12.08 from $20.00 to get the amount of change Marcus gets back, which is $7.92. Please note, that the $12.08 answer will more than likely be an option as well. **Students will also need to regroup for most all problems and subtract across zeros** Division Multiplication Students should know how to solve multiplication facts using adding, memorization, or other tricks we’ve discussed in class. Keywords: By (dimension) Double Each group Multiplied by Of Product of Times Triple Patterns In Out Know how to look at charts to find number or picture patterns and fill in the missing number that follows the same pattern. 2 3 4 5 6 4 6 ? (8) 10 12 Students should know how to solve division problems by using pictures, and multiplication. Keywords: As much Cut up Divided by Each group has Half (or other fractions) How many in each Parts Quotient of Separated Share something equally split Place Value Properties Commutative (Addition) o 3+2=2+3 o 7+3=?+7 Identity: o 8+0=0 Commutative (Multiplication) o 6x8=8x6 o 3x4=?x3 Identity: o 9 x 1=9 Students should be able to tell you the place value up to six digits and the value of each digit. 123,456 hundred thousands hundreds ones tens ten thousands thousands Rounding Round whole numbers that are 9,999 or less to the nearest ten, hundred, and thousand. If it’s 5 or more we round up. If it’s 4 or less it stays the same. Value of the 4 in this number is 400 Equalities Compare whole numbers that are between 0 and 9,999 with the correct symbols and words. Round to the nearest thousands: 238,783 Find the number that is in the thousands place. Draw a line under that number and an arrow to the number to its right. (One place value down). Decide if that number is 5 or more to round up, or 4 or less to stay the same. In this case the “7” is more than “5”, so we round the “8” to a “9”. We keep the numbers in front of the “8” and then change everything after the “8” to a zero. Answer: 239,000 > greater than < less than = equal to 234 > 212 132 < 432 876 = 876 Money Penny $ 0.01 Dime $ 0.10 Nickel $ 0.05 Quarter $ 0.25 Students should be able to add up the values of coins and dollars up to $5.00. Also, compare the value of coins and bills and make change (using subtraction). Fractions Time Students should be able to look at pictures and tell the fraction that goes along with the pictures as well as look at fractions and find the correlating picture. Also students should be able to compare fractions, and add and subtract fractions. Analog clock 4 6 Compare: < Congruent/NonCongruent Add/Subtract: 5 7 9 10 + - Tell time to the nearest minute. Determine elapsed time in onehour increments over a 12 hour period. Key terms: o Half past o Quarter past/after o Quarter till 7 days in a week 30 days in a month 365 days in a year Digital clock 4 weeks in a month 12 months in a year 60 seconds in a minute 60 minutes in an hour 24 hours in a day 1 = 6 7 7 7 10 For something to be congruent it has be the same shape and the same size. 2 = 10 Congruent Graphs Non-congruent Students should know the names of the following graphs and how to make them with given data. Also know where the title and key is on a graph. Turn Flip Slide Line plot Title Bar graph Picture graph /pictograph Measurement Lines & Angles Point Students should be able to use a ruler, etc, to measure objects. Also figure out the perimeter by using the given measurements or using a ruler to measure. Students should also be able to figure out the area of a figure. Perimeter- the outside of a figure, add up all the measurements to get the perimeter Area-the inside of a figure, usually shown in squares, so just count the squares. Volume-shown in stacked cubes, count the cubes, and remember the back ones have to have ones under them to stand. Perimeter = 19 (5+4+2+7+1=19) Area = 5 Ray—a ray only continues in one direction. Line—a line continues in both directions. Line Segment—a line segment is a piece of a line. It does not go in any direction. **Intersecting—all rays, lines, and line segments can intersect, when they intersect they only cross each other one time. EX: of intersecting lines: **Parallel—all rays, lines, and line segments can be parallel; when they are parallel they run side by side, but never cross each other. EX: of parallel lines: Right angle—makes a perfect square. Shapes Acute angle—is smaller than a right angle. Cube Sphere Obtuse angle—is bigger than a right angle. Rectangular prism Square pyramid Face Cylinder Cone Edge Edge—where two faces meet. Corner or Vertices—where two or more edges meet. Face—the plane figure on each solid figure. Corner Temperature Probability Students should be able to look at and read a thermometer to the nearest degree from both a Celsius and Fahrenheit thermometer. Students should be able to understand the concept of chance, and list the possible results of a given situation. Key words: Likely Unlikely Possible Impossible Example: It is likely I will pick a circle. It is unlikely I will pick a triangle. It is possible to pick a square. It is impossible to pick a rectangle. Fact Families 5, 9, 14 5 + 9=14 9 + 5=14 14 – 5=9 14 – 9=5 2, 20, 10 2 x 10=20 10 x 2=20 20÷10=2 20÷2=10