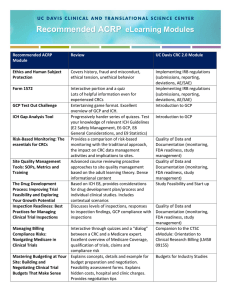
Complexity of the insulin signaling pathway
advertisement

Complexity of the insulin signaling pathway TNFα Plasma membrane TNFR PTEN p110α p110β p110γ aPKC IRS3 p85α p55α Akt2 Lipid Synthesis Akt3 GSK3 Glycogen Synthesis Jak Ras Erk1 Foxo1 Gluconeogenesis Erk2 Cell growth, differentiation p90rsk mTOR Protein Synthesis Stat IRS4 p50α p85β p55γ Akt1 SREBP PTP1B IRS2 Rac cdc42 ? IRS1 Jnk PDK 1,2 Glucose Uptake Rec Shc ? Cytokines IGF1R CAP cbl ? Insulin IGF1 SOCS1,3 RET SIGNALING PATHWAYS GFRα Lipid Raft membrane kinase domain GRB7/10 Y752 P PLC-γ Y928 P P Y1015 P Y1062 Short Isoform (RET9) Long Isoform (RET51) Intermediate isoform (RET43) Enigma IRS 1/2 P Y905 P Y1096 RAS SHC RAF SOS GRB2 MEK1 ERK1/2 GAB1 PI3K FRS2 JAK p85 RHO Focal Adhesion p110 CREB ELK-1 Lamellipodia RAC JNK STAT3 SHP2 Neoplastic Phenotype Differentiation MAPK ACT NF-B Cell Proliferation Cell Survival Mitogenesis Possible mechanisms of activation of wild-type RET and MEN2-associated RET mutations MEN 2A: MCT+FEO+PHPT (T2095C/C634R) I II 1 2 31 32 1 2 31 35 1 1 5 8 1 37 1 2 12 7 2 5 MEN 2b: neurinoma phenotype •Thick lips •marfanoid habitus •skeletal abnormalities Genetic Screening MTC and parafolicular C-cell hyperplasia in a 5 yr old girl Tatic S., Institute for Pathology, Medical School, Beograd Age- related penetrances and probabilities for gene carriers of MEN 2a 50 45 40 Gene carriar probability (%) 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0.5 0.3 0.1 0.08 0.05 0 <10 20-30 30-40 40-50 >50 Age (years) Clinical history Biochemical screening DNA markers +biochemical screening Thakker et al. 1993 Patients with familial pheochromocytoma in MEN 2 Analyzed patients for mutation in RET: 343 Total number of patients with pheochromocytoma due to mutation in RET protooncogene: 36 25 25 20 19 15 Unilateral Pheo 14 10 8 RET carriers without Pheo 6 5 2 2 3 1 1 c6 18 c6 20 c6 34 c6 49 c7 90 c7 91 c8 04 c8 26 c9 18 0 Bilateral Pheo 11 2 Oktobar 2007. – početak terapije ZD6474 April 2008. – progresija bolesti Nova lezija RECIST: Kompletan odgovor: povlačenje svih lezija Parcijalni odgovor: smanjenje LD za >30% Progresija: porast LD za >20% ili bar jedna nova lezija Pacijent 1 Pacijent 1 April 2008: prelazak na “open label” studiju Oktobar 2008: parcijalni odgovor Pacijent 1 placebo lek 3500 3000 2500 kalcitonin (pmol/l) CEA (g/L) 2000 1500 1000 500 . 08 O kt ju l.0 8 ja n. 08 A pr 08 . O kt 07 . 0 VHL tip 2c; V84M (GTGATG) 1 I 42 1 2 13 11 II 3 Hypoxic and non-hypoxic regulation of HIF1a Baldewijns MM, J Pathol, 2010 Protein expression of PHD1 in RCC What is ICH GCP? • A quality standard for the design, conduct, performance, monitoring, auditing, recording analyses and reporting of clinical trials that provides assurance that the data and reported results are credible and accurate, and that the rights, integrity and confidentiality of the subjects are protected. • The ICH (International Conference on Harmonization) develops standards on the elaboration and presentation of data so they are accepted worldwide (US, EU, JP). Slide No. 15 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe IRB/EC & Authority Subject Investigator Sponsor ICH GCP Principles 1. Clinical trials should be conducted in accordance with the ethical principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki, and that are consistent with GCP and the applicable regulatory requirement(s). 2. Before a trial is initiated, foreseeable risks and inconveniences should be weighed against the anticipated benefit for the individual trial subject and society. A trial should be initiated and continued only if the anticipated benefits justify the risks. 3. The rights, safety, and well-being of the trial subjects are the most important considerations and should prevail over interests of science and society. Slide No. 16 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe ICH GCP Principles (2) 4. The available nonclinical and clinical information on an investigational product should be adequate to support the proposed clinical trial. 5. Clinical trials should be scientifically sound, and describe in a clear, detailed protocol. 6. A trial should be conducted in compliance with the protocol that has received prior institutional review board (IRB)/independent ethics committee (IEC) approval/favourable opinion. Slide No. 17 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe ICH GCP Principles (3) 7. The medical care given to, and medical decisions made on behalf of, subjects should always be the responsibility of a qualified physician or, when appropriate, of a qualified dentist. 8. Each individual involved in conducting a trial should be qualified by education, training, and experience to perform his or her respective task(s). 9. Freely given informed consent should be obtained from every subject prior to clinical trial participation. 10. All clinical trial information should be recorded, handled, and stored in a way that allows its accurate reporting, interpretation and verification. Slide No. 18 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe ICH GCP Principles (4) 11. The confidentiality of records that could identify subjects should be protected,respecting the privacy and confidentiality rules in accordance with the applicable regulatory requirement(s). 12. Investigational products should be manufactured, handled, and stored in accordance with applicable good manufacturing practice (GMP). They should be used in accordance with the approved protocol. 13. Systems with procedures that assure the quality of every aspect of the trial should be implemented. Slide No. 19 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Good Clinical Practice – Why? • ICH GCP is a set of ethical and scientific quality requirements • to protect the rights, safety, & well- being of trial subjects • to guarantee reliability of data capture & credibility of study results • ICH GCP must be complied with in all clinical studies. Slide No. 20 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Who does GCP Affect? • Sponsors of studies • Companies, Academic Units, Contract research organizations • Investigators • all members of the study team • Ethics committees • new EU Directive imposes responsibilities Slide No. 21 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe What does GCP do? • Implementation of GCP can: • improve patient protection • facilitate good science • ensure meticulous documentation • improve quality of trials • improve decision making reliability Slide No. 22 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe The investigator • Has adequate qualification & appropriate experience (documented in the CV). • Has enough time to conduct the study (paperwork, study visits, meetings, audits and inspections). • Has suitable and sufficient trial subjects. • Has adequately trained research staff and adequate facilities. • Has to comply with the requirements of GCP. Slide No. 23 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Investigator’s Responsibilities • Store signed and dated CVs of all who recruit subjects, obtain informed consent, do assessments, complete CRFs or handle trial drugs. • Set-up and maintain a log of site staff who has significant trial related tasks. Keep it updated and signed. • Train/Inform research staff regularly about the study and any changes (document by minutes, notes etc.). Slide No. 24 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Study equipment and laboratory • Use suitable and correct equipment. • Calibrate & maintain instruments regularly (including ECG, centrifuges, thermometers). Documentation must be available. • Train research staff to ensure proper handling of study equipment. • Ensure correct collection and handling of samples, different tests as per protocol & laboratory guidelines. • Required documentation from the local lab are: reference ranges, details of analytical methods, quality assurance information, GLP-certificates/accreditation. Slide No. 25 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Lab The study Protocol Know it and follow it! • Read the study protocol and be familiar with it. • Accept and sign the protocol (final version). • Follow the protocol point by point. • Deviations from the protocol should not occur. However, if a deviation occur the sponsor must be informed. Any deviations must be documented stating the reason and date. • Provide the protocol to the whole research team. Slide No. 26 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Trial subject enrolment • Predict potential subject recruitment using both past data and current information. • Keep a log of all screened & recruited subjects. • Take enough time for recruitment of subjects. • Inform the subjects in word & writing about the trial and document it! • Answer all questions in detail. • Give ample time to the subject to make her/his decision and document it. Slide No. 27 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Source documents & SDV • Source Documents are all original documents, data, records (e.g. hospital records, laboratory notes, memoranda, diaries, X-rays ...). • Data to be recorded in source documents are defined in the study protocol. • Source Data Verification (SDV) is a mandatory review that checks consistence between source documents & CRF. • What must be recorded in the medical records: • All data asked in the CRF must be documented in the • medical records, unless otherwise described in the protocol. Furthermore, date of Informed Consent, trial no., screening no., randomization no., visit dates should be recorded. Slide No. 28 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Case Report Form (CRF) • Ensure that only authorized staff makes entries into the CRF. • Complete the case report form (CRF) entirely, legibly & accurately. • Use abbreviations as little as possible. • Date and initial all changes (crossing with a single line only!) and give reason for correction (transparency of correction process). Slide No. 29 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Case Report Form (CRF) • Do not use any correcting fluids on any trial related documents. • Missing data or data not assessed should be correspondingly marked, i.e. N/D, N/A • Give monitors, auditors, and regulatory authority inspectors access to all source documents and CRF. • Keep the CRFs, investigator file in a locked cupboard during the trial. Slide No. 30 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Trial product management • Explain drug administration to the subjects. • Keep detailed records of trial product handling, including storage and temperature log. • Ensure that the subject returns all used, empty and unused treatment packs. • Return all used & unused trial products to Novo Nordisk. • Ensure appropriate use of Investigational Product according to the Protocol (dosing,…) • Full responsibility for the appropriate management of the Investigational Product at the Site is with the Investigator Slide No. 31 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Adverse Events (AEs) Any untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical trial subject administered a medicinal product and which does not necessarily have a causal relationship with the treatment. This includes AEs from the first trial related activity after the subject has signed the informed consent. • Document all AEs in the CRF. Slide No. 32 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe SAFETY ! • Adverse Event (AE) = • Serious Adverse Event (SAE) An experience that at any dose results in any of the following • Death • A life-threatening experience • Patient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization • A persistent or significant disability/incapacity • A congenital anomaly/birth defect • Important medical events (jeopardizing the subject & possibly requiring medical/surgical intervention to prevent one of the outcomes listed above). • Immediately report all SAEs to the sponsor Slide No. 33 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe ! SAFETY ! Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) • All noxious and unintended responses to a medicinal product related to any dose should be considered Adverse Drug Reactions. • “responses to a medicinal product” = a causal relationship between a medicinal product and an adverse event is at least a reasonable possibility, i.e. the relationship cannot be ruled out. ! Slide No. 34 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe ! SAFETY ! Adverse Drug Reactions Files & Archives • Document every study-related action. Store all study files in a safe and secure place. • Archive the study-related documents for at least 15 years. Slide No. 35 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Benefits of GCP • • • • • • • • • • • More reliable data Greater protection of trial subjects Better performance and training Uniformity of methods among companies and Investigators Trust of regulatory authorities and inspectors Quality design of trials Ethics Committees’ approvals Appropriate statistics Authorities’ trust Validity of data Faster availability of new drugs on the markets Slide No. 36 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe Benefits of GCP: Investigator • Those who comply with GCP will be deemed acceptable – those who do not comply will not be invited to participate! Slide No. 37 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe “Disadvantages” of GCP • Greater demands of time and costs • Perception of irritating bureaucracy • Increasing of costs • Possibility of more frequent controls Slide No. 38 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe GCP stays in Clinical Trials! GCP requirements MUST be met! Only those who respect GCP will participate in Novo Nordisk Clinical Trials! Slide No. 39 • Basic GCP Facts • Sunday, 24 July 2016 • GVe